Echo basics: Apical and Subcostal Views
Echocardiography Views
Patient position coupled with probe placement and orientation for optimal apical and subcostal views. See previous post for parasternal long-axis (PLAX) and parasternal short-axis (PSAX) views
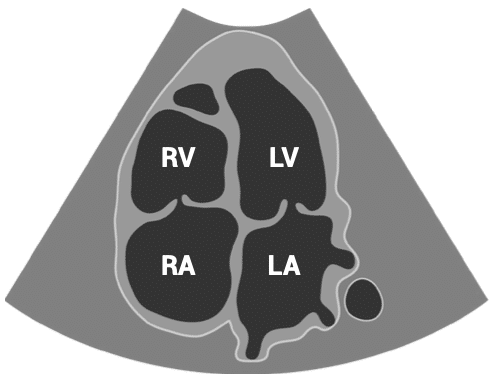
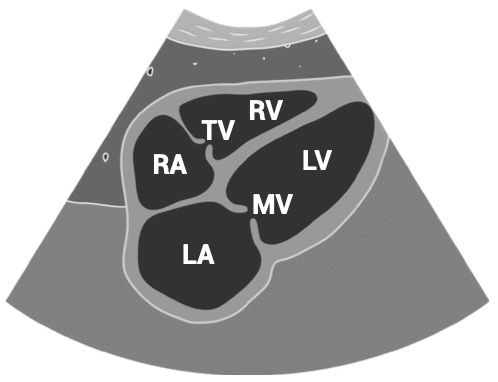
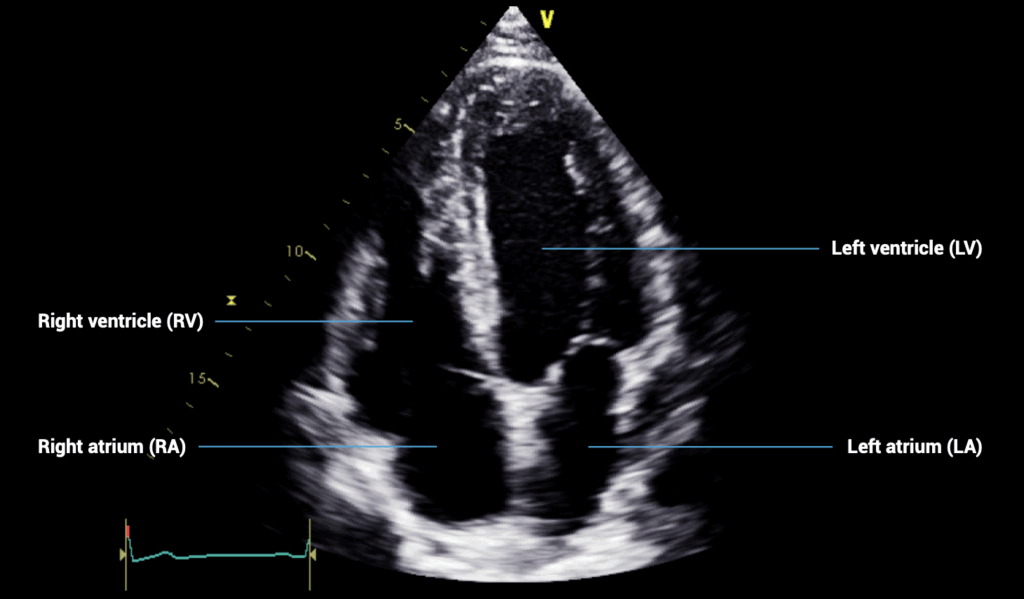
APICAL VIEWS – apical four-chamber view
- Patient position: lying on left side, left arm raised, raise the back of the bed or use pillows under the left shoulder
- Probe position: over the apex beat, or V5 of the ECG
- Probe orientation: notch towards patient’s left shoulder
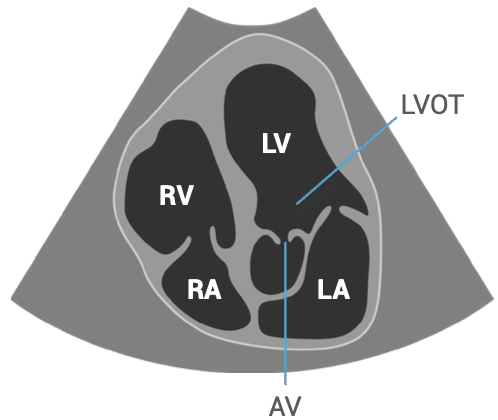
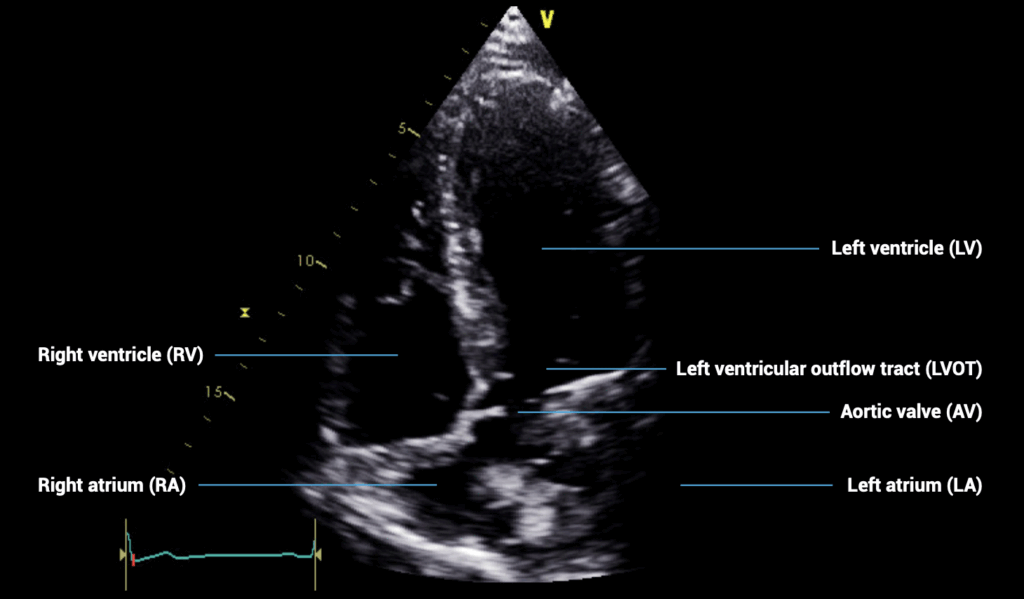
APICAL VIEWS – apical five-chamber view
- Patient position: lying on left side, left arm raised, raise the back of the bed or use pillows under the left shoulder
- Probe position: over the apex beat, or V5 of the ECG
- Probe orientation: notch towards patient’s left shoulder, tilt upwards from four-chamber view
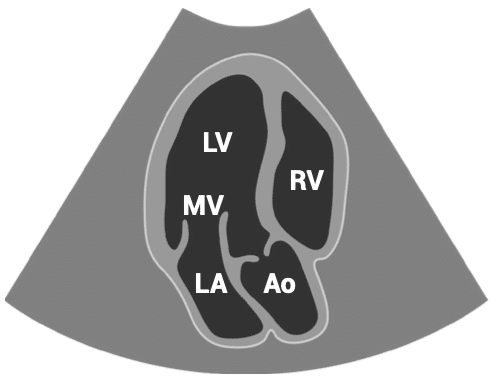
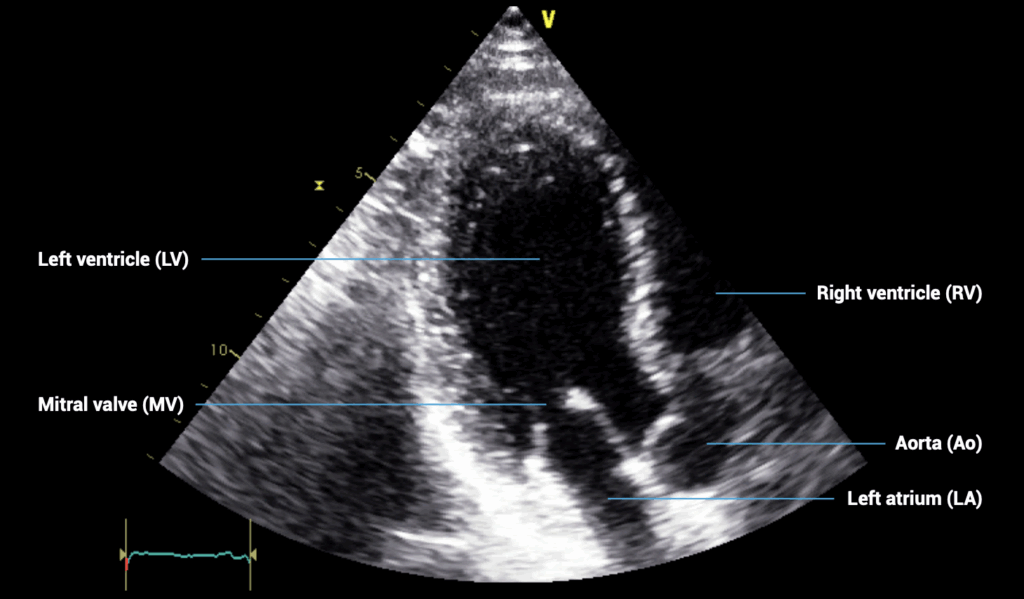
APICAL VIEWS – apical three-chamber view
- Patient position: lying on left side, left arm raised, raise the back of the bed or use pillows under the left shoulder
- Probe position: over the apex beat, or V5 of the ECG
- Probe orientation: notch towards patient’s right shoulder, tilt upwards from four-chamber view
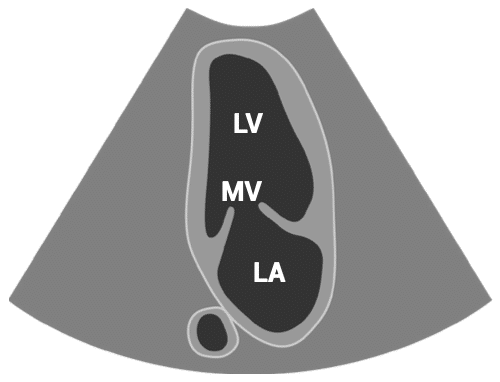
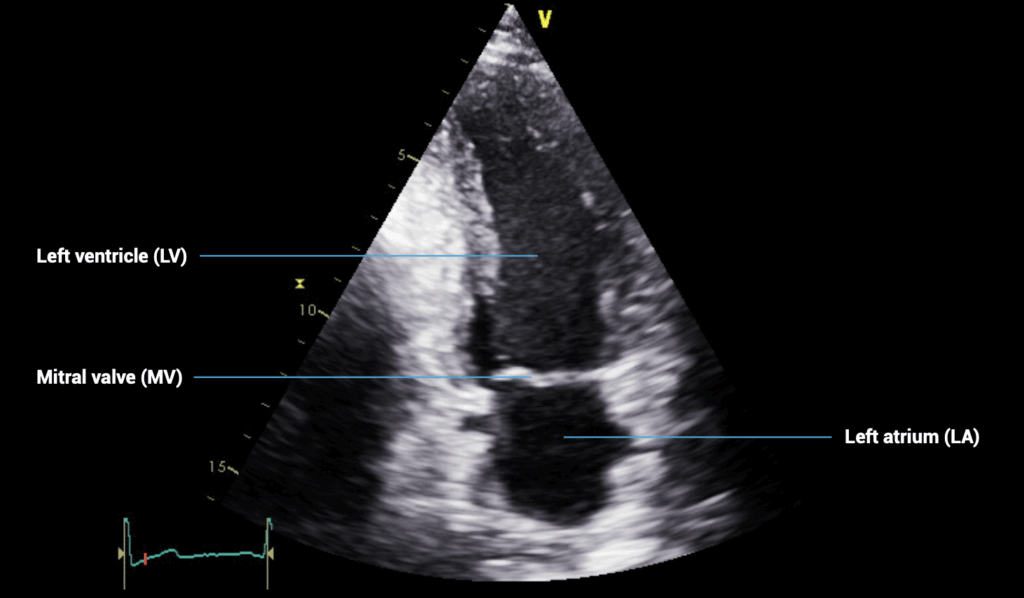
APICAL VIEWS – apical two-chamber view
- Patient position: lying on left side, left arm raised, raise the back of the bed or use pillows under the left shoulder
- Probe position: over the apex beat, or V5 of the ECG
- Probe orientation: rotated about 60 degrees counterclockwise from the four-chamber view
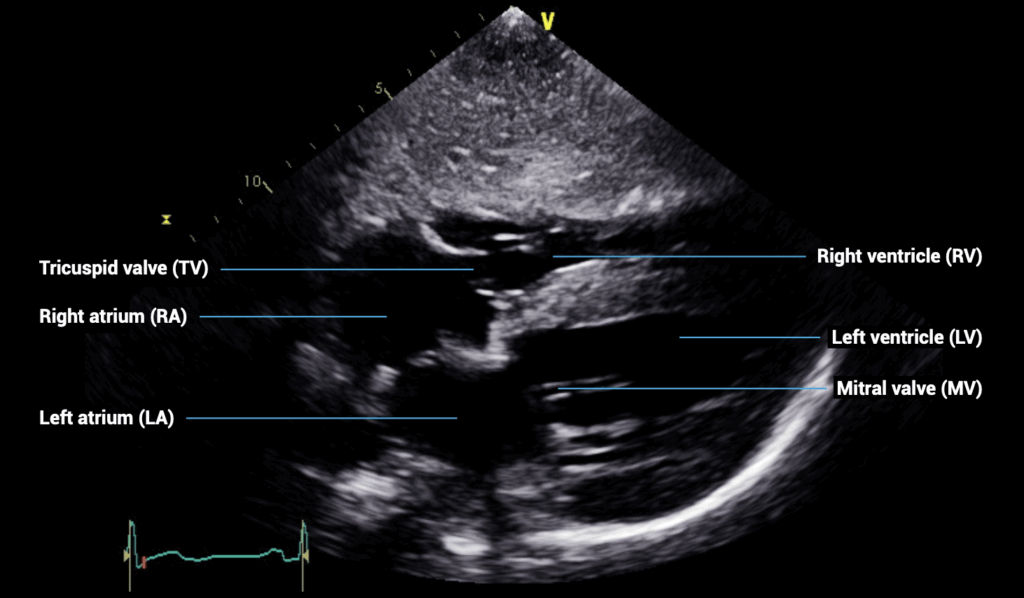
SUBCOSTAL VIEWS – subcostal four-chamber view
- Patient position: lying supine
- Probe position: below sternum, almost flat to skin
- Probe orientation: notch towards patient’s left shoulder
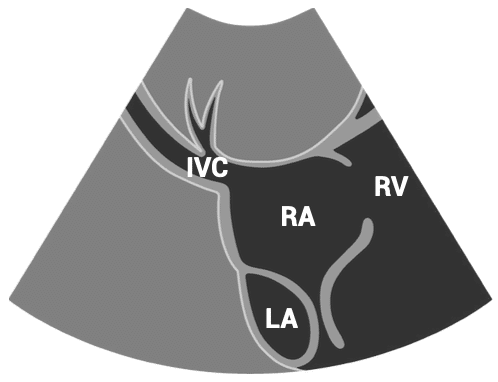
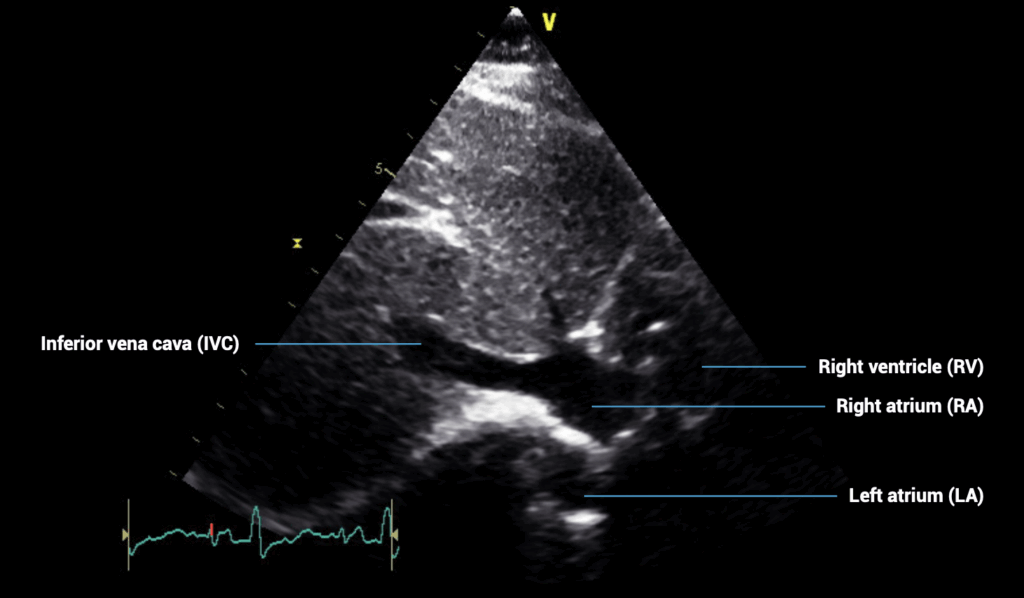
SUBCOSTAL VIEWS – subcostal IVC view
- Patient position: lying supine
- Probe position: below sternum, almost flat to skin
- Probe orientation: rotated slightly counterclockwise from the subcostal four-chamber view
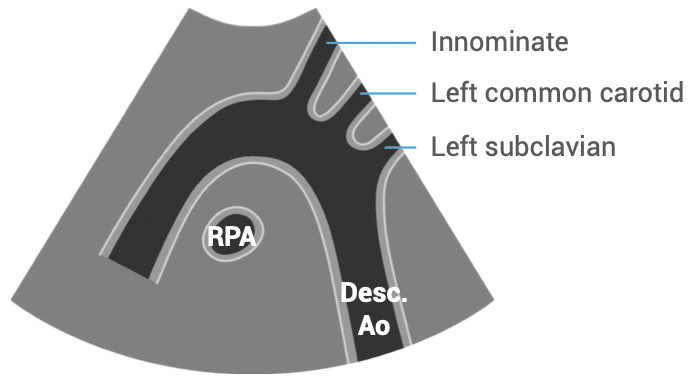
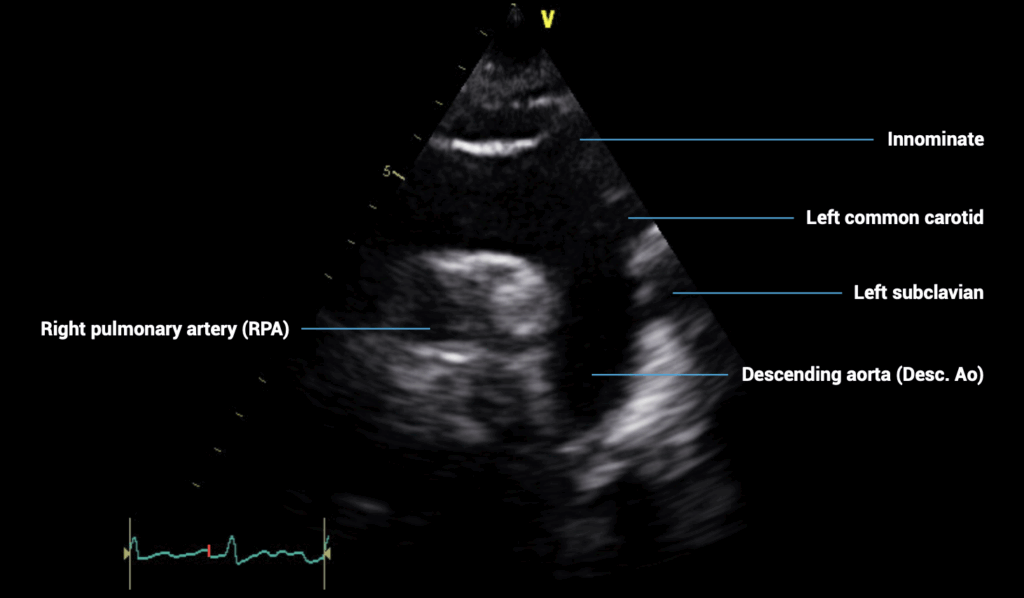
SUBCOSTAL VIEWS – suprasternal view of the aorta
- Patient position: lying supine with neck extended
- Probe position: in suprasternal notch
- Probe orientation: notch towards patient’s left shoulder
This is an edited excerpt from the Medmastery course Echocardiography Essentials by Helen Rimington, PhD. Acknowledgement and attribution to Medmastery for providing course transcripts.
Additional echocardiography resources:
- Na, M. Echo Masterclass: Left Ventricular Strain. Medmastery
- Monteiro, C. Echo Masterclass: The Right Heart. Medmastery
- Eggett, C. Echo Masterclass: The Valves. Medmastery
- West, C. Echo Masterclass: Adult Congenital Heart Disease. Medmastery
- Naderi, H. Echo Masterclass: The Power of 3D Imaging. Medmastery
Radiology Library: Echocardiography basics
- Rimington H. Echo basics: Machines and probes. LITFL
- Rimington H. Echo basics: Tips and Tricks. LITFL
- Rimington H. Echo basics: Key concepts and Doppler modalities. LITFL
- Rimington H. Echo basics: Parasternal Views. LITFL
- Rimington H. Echo basics: Apical and Subcostal Views. LITFL
Further reading
- European Society of Cardiology. 2017. The EACVI Textbook of Echocardiography 2017 (2e). Lancellotti P, Zamorano JL, Habib G, and Badano L (Eds). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Anderson, B. Echocardiography: The Normal Examination and Echocardiographic Measurements 2006 (2e). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Wharton G, Steeds R et al. A minimum dataset for a standard adult transthoracic echocardiogram: a guideline protocol from the British Society of Echocardiography. Echo Res Pract. 2015 Mar 1;2(1):G9-G24.
Echocardiography Essentials
Helen is a Consultant Cardiac Physiologist at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Trust, in London (UK). She's also a co-author of Echocardiography: A Practical Guide for Reporting. | Medmastery