Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five 347
Just when you thought your brain could unwind on a Friday, you realise that it would rather be challenged with some good old fashioned medical trivia FFFF, introducing the Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five 347
Question 1
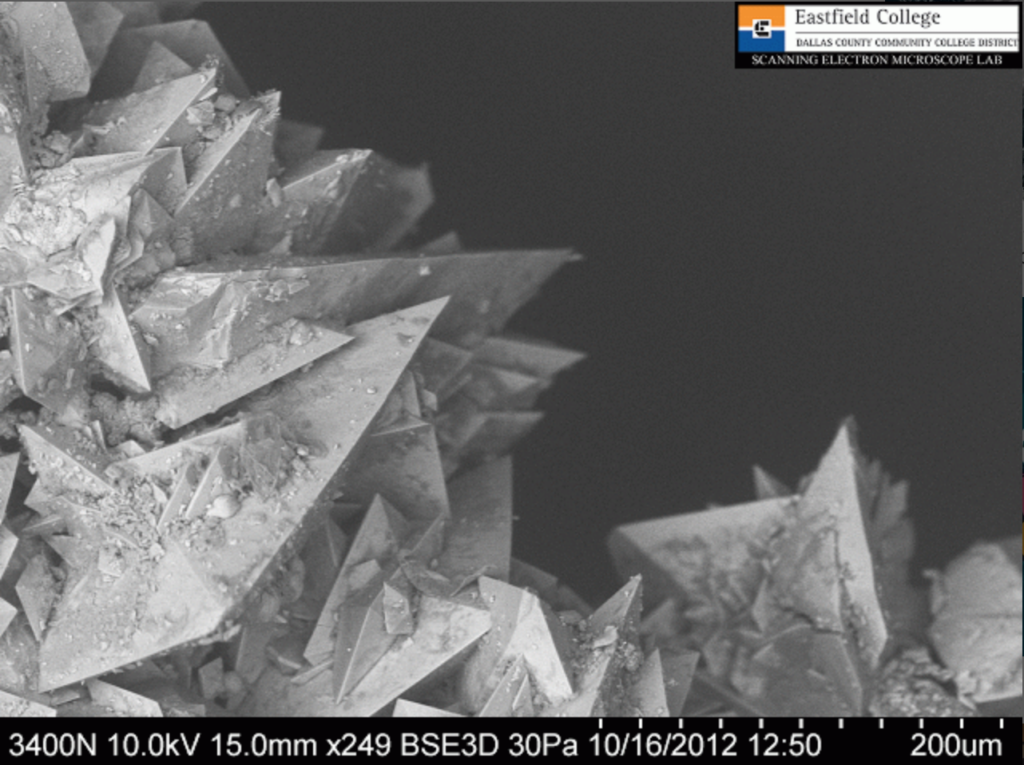
What is shown in the image below?

Reveal the funtabulous answer
A kidney stone under electron microscopy.
No wonder they hurt!
A colleague of Murry Gans, brought in their recently passed kidney stone for him to put on the electron microscope – as you do. The above image shows calcium and uric acid crystals forming jagged needles.
Reference:
- Kidney stones under the microscope look like jagged spikes of pain – Vox.com – Accessed 26th Sept 2022
Question 2
What international prize did a Swedish moose just win?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
The 2022 Ig Nobel prize.
I love a good Ig Nobel. IT engineer Magnus Gens wanted to improve Swedish road safety by using a moose crash-test dummy to see how cars would crumple when they collided with big wildlife. The moose was constructed with thick rubber plates to make for a life-like impact.

Reference:
- BBC News – Swedish moose crash-test dummy wins spoof Ig Nobel prize – accessed 17th Sept 2022
- Ig Nobel website
Question 3
What is ‘Wasping‘, ‘wasp dope‘ or ‘hot shots‘?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
Pyrethroid misuse
Effectively getting euphoria from the insecticide.
Users will either electrify the insecticide bottle or spray the contents onto a heated metal sheet until crystals form. The crystals can be inhaled, smoked or even injected to create a ‘high’.
PyrethRINs are naturally occurring insecticides from Chrysanthemum cinerariefolium. PyrethrRINS are generally fairly unstable, so toxicity in humans is minimal. PyrethROIDs are the synthetic derivatives and are more heat stable, less volatile and have a longer duration. We use Pyrethroids pharmaceutically for topical application for lice and scabies.
Their primary action is to open voltage-dependent sodium channels, resulting in hyperexcitability. At higher concentrations, they can antagonise GABA-gated chloride channels.
Tremors, hyperexcitability and seizures can be seen in patients. Inhaling large amounts can result in wheezing, hypersensitivity pneumonitis and pulmonary oedema. Treatment is supportive, with benzodiazepines at the forefront. Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and NIV can be used for respiratory complications.
Reference:
- oxTidbits: Euphoria from pyrethROIDs? Maryland Poison Centre
Question 4
What is ‘sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia‘ more commonly know as?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
‘Brain freeze’ or ‘ice cream headache.’
My personal trick is to put my tongue on the roof of my mouth but for those who want to eat uninterrupted ice cream perhaps a sphenopalatine block might work? Research project anyone – it could be the next Ig Nobel?
Question 5
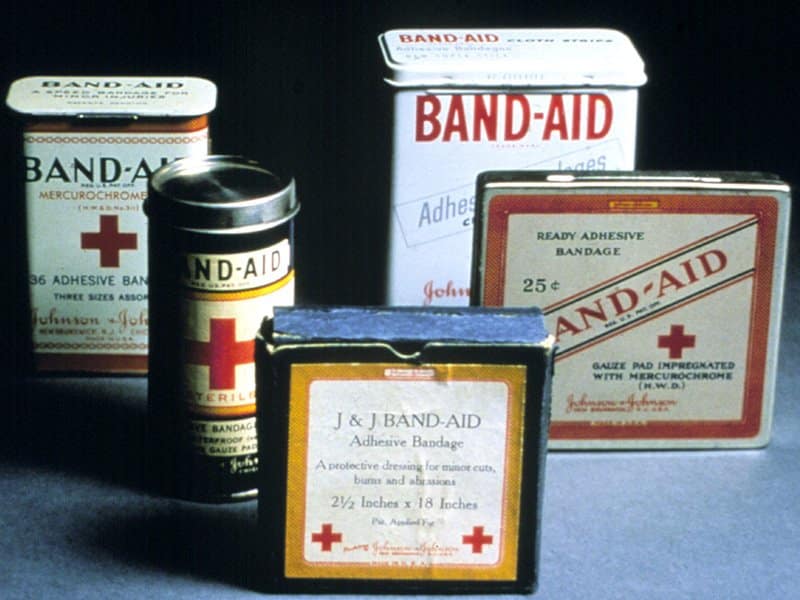
How did the invention of the Band-Aid come about?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
Earle Dickson worked at Johnson & Johnson. His wife (Josephine Knight) kept cutting herself in the kitchen and he found the large gauzes he was used to working with were too large to be practical. He then made small gauze strips attached on tape in intervals for his wife to use. James Wood Johnson, his boss liked the idea so much they went into production. Following their success Dickson was promoted to vice president.
In the year 2000, Johnson & Johnson celebrated their 1 billionth Band-Aid.
For a history, and more random Band-Aid facts see the company site – BAND-AID

FFFF
Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five
Dr Neil Long BMBS FACEM FRCEM FRCPC. Emergency Physician at Kelowna hospital, British Columbia. Loves the misery of alpine climbing and working in austere environments (namely tertiary trauma centres). Supporter of FOAMed, lifelong education and trying to find that elusive peak performance.

Does “Wasping” result in consistent ECG changes?
Nothing pathognomonic, non-specific ST and T wave changes, ventricular ectopics and occasional bradycardia, but this is all based on limited case reports.