Jersey Finger
Definition
Avulsion of the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon from the base of the distal phalanx.
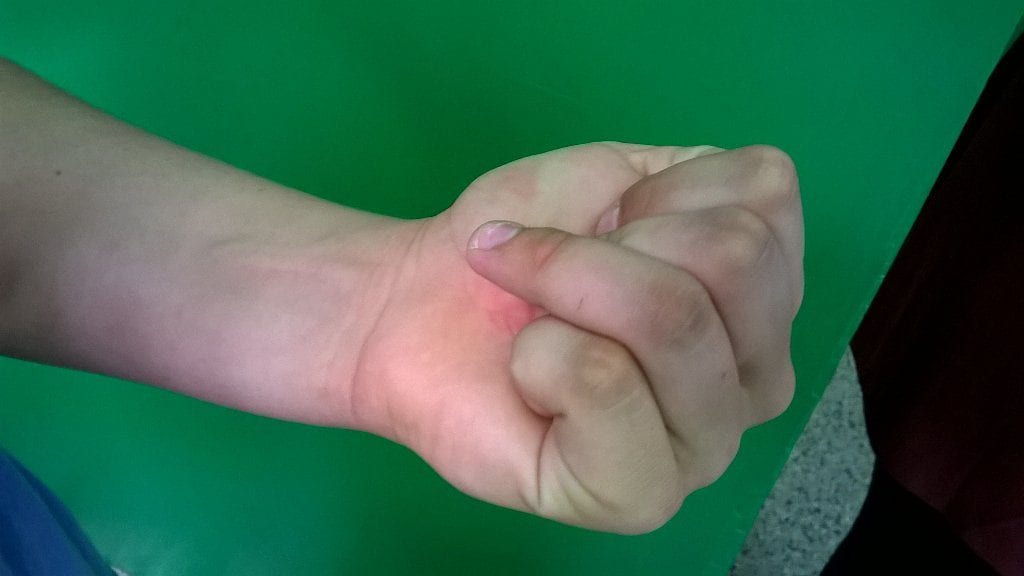
Mechanism
- Sudden forcible extension of an actively flexed finger.
- Classically occurs in sports such as soccer or rugby, where a player grabs another player’s jersey as they pull away.
Anatomy
- Most commonly occurs in the ring finger (?why).
- The tendon avulses from its attachment to the distal phalanx and may retract proximally towards the PIP joint or even further into the palm.
Clinical Assessment
LOOK
- Swollen finger distally.
- Bruising over distal phalanx and DIP joint.
FEEL
- Maximally tender at base of distal phalanx and DIP joint on volar surface.
- May be tender all along the volar surface of the finger.
MOVE
- Unable to actively flex DIP joint.
- Flexion at PIP and MCP joints preserved.
Imaging
- Finger x-ray to assess for avulsion fracture.
- USS/MRI to assess the degree of tendon retraction.
Radiological Assessment
- The x-ray may be normal or may show evidence of an avulsion fracture.
- Look for an avulsion fracture arising from the FDP insertion site on the volar aspect of the base of the distal phalanx.
- A fleck of bone often retracts proximally with the tendon and may be visualised volar to the PIP joint.
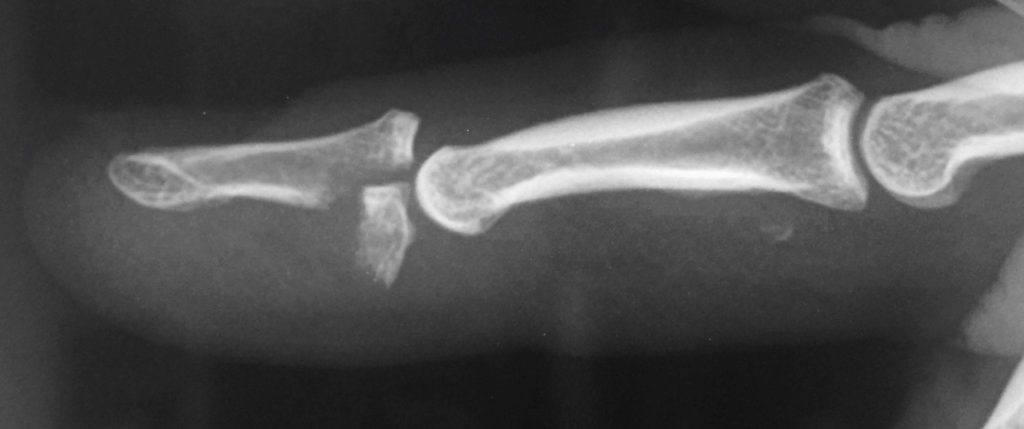
Clinical Cases
Case 1
This 30-year old male presented with pain, swelling and bruising in his distal ring finger after a game of rugby. He gave a history of a sudden “pop” and immediate pain in the finger after grabbing another player’s jersey. On examination he was unable to actively flex his distal phalanx.

Case 1 Interpretation
- His X-ray shows a large avulsion fracture at the FDP insertion site on the volar aspect of the base of the distal phalanx.
- There also appears to be a smaller fleck of bone at the level of the PIP joint, suggesting that the FDP tendon has retracted proximally to this level.
- USS confirmed tendon retraction and he was immobilised in a POSI splint and referred urgently to a hand surgeon, with open tendon repair performed a few days later.
Emergency Management
- Analgesia
- Splintage: Apply a POSI splint (position of safe immobilisation) and elevate the limb in a High Arm Sling.
VIDEO TUTORIAL | POSI splint; High Arm Sling
- POSI splint (position of safe immobilisation) [Vimeo Video]
- Triangular Bandage High and Broad Arm [Vimeo Video]
Lilian Wong and Matt Lutze demonstrate how to apply a POSI splint and High Arm Sling in these short videos from the Emergency Care Institute (with commentary by John Mackenzie).
Disposition
- Refer urgently to a hand surgeon.
- The patient will require an open tendon repair within 7-10 days.
- These injuries carry a worse prognosis if not repaired within 7-10 days as the tendon contracts and becomes less viable.
Discharge Advice
- Provide the patient with plaster care advice.
- Ensure they are aware of the need for early surgical repair and hence the need to follow up promptly with the hand surgeon.
Pearls & Pitfalls
- Examining specifically for loss of DIPJ flexion is critical to making this diagnosis.
- Ensure you always isolate FDP and FDS when assessing the patient with a hand injury. Read how to do this here.
- Partial FDP avulsion may present with pain on resisted DIPJ flexion but otherwise preserved FDP function. If uncertain whether a patient has an FDP injury, it is safer to immobilise them in POSI and refer to a hand surgeon.
References
- Dobson P, Taylor R, Dunkin C. Safe splinting in hand surgery. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011 Jan;93(1):94.
- Eddy M. Hands, fingers, thumbs – assessment and management of common hand injuries in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 2012 Apr;41(4):202-9.
- Bauones S. Clinical Case: Jersey Finger. Radiopedia. 2013
- Bachoura A, Ferikes AJ, Lubahn JD. A review of mallet finger and jersey finger injuries in the athlete. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017 Mar;10(1):1-9.
- Emergency Care Institute. MSK Videos: Splinting and Plaster Immobilisation Techniques.
Authors
- Lilian Wong (ED Physiotherapy Practitioner, Sydney)
- Ed Burns (Emergency Physician, Sydney)
- Matt Lutze (ED Nurse Practitioner, Sydney)
[cite]
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
