McGinn-White pattern
The McGinn-White Pattern, also known as the S₁Q₃T₃ pattern, or McGinn-White sign, is a classic but infrequently seen electrocardiographic marker suggestive of acute pulmonary embolism (PE), particularly in the setting of acute cor pulmonale. Defined as a prominent S wave in lead I, a Q wave in lead III, and an inverted T wave in lead III, it reflects right ventricular strain and axis deviation due to acute pulmonary hypertension.
First described in 1935 by Sylvester McGinn and Paul Dudley White, the pattern was identified in patients with confirmed pulmonary embolism and acute right heart strain. Although not pathognomonic and lacking in sensitivity, its presence is associated with severe PE, hemodynamic instability, and right ventricular dysfunction. In modern medicine, while it appears in fewer than 25% of PE cases, it retains clinical significance, especially when paired with other ECG features of RV strain such as RBBB, tachycardia, and T wave inversions in the anterior leads.
The S₁Q₃T₃ sign is often cited in ECG education as a “must know” finding for junior doctors, despite its relatively low sensitivity, due to its historical value and specificity for large pulmonary emboli.
History of the McGinn-White pattern
1935 – Sylvester McGinn (1904–1984) and Paul Dudley White (1886–1973) publish “Acute Cor Pulmonale Resulting from Pulmonary Embolism: Its Clinical Recognition” in JAMA. They describe “S wave in lead I, Q wave and inverted T wave in lead III” in cases of PE-induced right heart strain.
(1)The prominent S wave and low origin of the T wave in lead 1, the ST segment starting slightly below the baseline, (2) the gradual staircase ascent of the ST interval from the S wave to the T wave in lead 2, and especially (3) the Q wave and definite late inversion of the T wave in lead 3.
McGinn, White. 1935
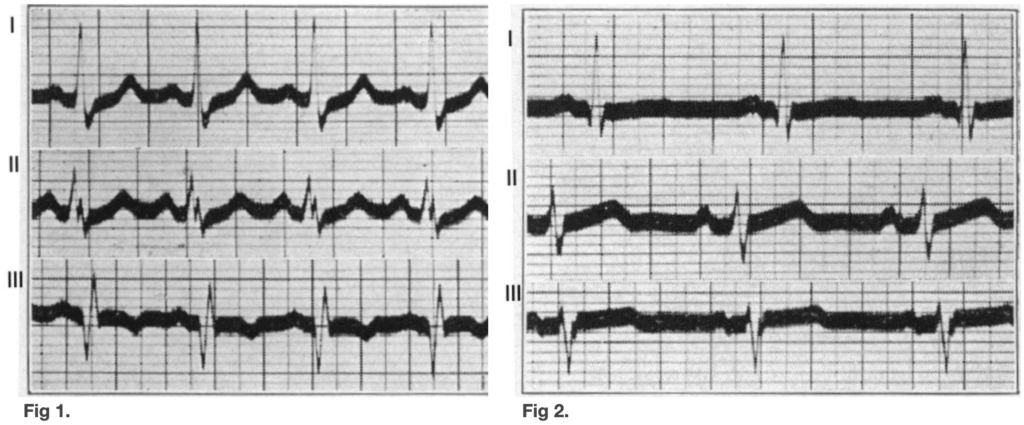
Fig. 2. Leads I, II, III four weeks after pulmonary embolism.
Case 1: McGinn, White. 1935
1971 – Scott SJM links the S₁Q₃ pattern to possible transient left posterior hemiblock, proposing electrophysiological explanations for the sign’s components, reinforcing its association with massive PE.
2001 – Daniel et al. develop an ECG severity score (Daniel Score), incorporating S₁Q₃T₃ as a key component for predicting PE severity. A a 21-point scoring system used to assess the severity of pulmonary embolism (PE) based on electrocardiogram (ECG) findings
2015 – Shopp et al. publish a systematic review/meta-analysis confirming S₁Q₃T₃ as one of six ECG signs predictive of circulatory shock and 30-day mortality in acute PE. Systematic review and meta-analysis of 3,007 patients with acute PE
- Prevalence of S₁Q₃T₃ pattern: 16%
- Associated with increased odds of hemodynamic collapse and 30-day mortality
- Included in the Daniel Score as a key feature predictive of RV strain and shock
2019 – Thomson et al. find S₁Q₃T₃ present in only 3.7% of CT-confirmed PE cases, but strongly associated with right ventricular strain and large clot burden. Retrospective case-control of 189 PE-positive vs. 189 PE-negative patients:
- Prevalence of S₁Q₃T₃: 3.7%
- Specificity: 98.4%, but sensitivity: 3.7%
- Strong association with large clot burden and right ventricular strain
- Conclusion: highly specific but rare — “of limited diagnostic value alone”
2020 – Carrascosa et al. publish a case report illustrating McGinn-White pattern in bilateral PE, highlighting its role in diagnosis and prognosis.
- Describes a typical case of bilateral PE with McGinn-White pattern
- Notes reported incidence of ~24% in PE and association with circulatory shock and in-hospital mortality
2020 – Elsayed reviews the historical and clinical context of the McGinn-White sign, noting its value in risk stratification and association with RV dysfunction and hemodynamic collapse.
- Summarises reported incidence range of 10–50%, based on review of 13 studies
- S₁Q₃T₃ strongly linked to right ventricular dysfunction and used as a risk stratification marker
- Lists 13 clinical uses including prognostication, earlier diagnosis, and prompting imaging
2018 – Fei Teng, Guo Xuefeng et al. evaluate electrocardiographic findings in combination with clinical scores to improve risk stratification in acute PE. In a retrospective study of 1318 patients, the McGinn–White sign was independently associated with high-risk classification (OR 2.82, 95% CI 2.03–3.93) and contributed to a composite qSOFA–ECG model with 81.5% sensitivity and 72.3% specificity for predicting early death and hemodynamic collapse.
2024 – Mitesh Karn et al. present a case of massive pulmonary embolism in QJM, illustrating a textbook McGinn–White (S1Q3T3) pattern on ECG. The report reaffirms the sign’s specificity for acute cor pulmonale and its clinical utility as a prompt for urgent PE-directed therapy, including thrombolysis.
Associated Persons
- Sylvester McGinn (1904–1984)
- Paul Dudley White (1886–1973)
References
Historical references
- McGinn S, White PD. Acute cor pulmonale resulting from pulmonary embolism. JAMA. 1935; 104(17): 1473-1480 [McGinn-White pattern; and defined acute cor pulmonale]
Eponymous term review
- Scott RC. The S1Q3 (McGinn-White) pattern in acute cor pulmonale: a form of transient left posterior hemiblock? Am Heart J. 1971 Jul;82(1):135-7.
- Daniel KR, Courtney DM, Kline JA. Assessment of cardiac stress from massive pulmonary embolism with 12-lead ECG. Chest. 2001 Aug;120(2):474-81. [Daniel score]
- Shopp JD, Stewart LK, Emmett TW, Kline JA. Findings From 12-lead Electrocardiography That Predict Circulatory Shock From Pulmonary Embolism: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Oct;22(10):1127-37.
- Thomson D, Kourounis G, Trenear R, Messow CM, Hrobar P, Mackay A, Isles C. ECG in suspected pulmonary embolism. Postgrad Med J. 2019 Jan;95(1119):12-17.
- Carrascosa MF, Izquierdo RG, Hoz MC. McGinn-White pattern. Eur J Intern Med. 2020 Sep;79:112-113.
- Elsayed YMH. McGinn-White Sign or S1Q3T3-Pattern in Pulmonary Embolism; Significance and Differential Diagnosis; Narrative Updating Review. International Journal of Research Studies in Medical and Health Sciences. 2020; 5(11): 15-24
- Karn M, Yonghang S, Barma A, Sharma A. The classic S1Q3T3/McGinn-White sign in acute pulmonary embolism. QJM. 2024 Sep 1;117(9):665-666
- Teng F, Chen YX, He XH, Guo SB. Contribution of Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score Combined with Electrocardiography in Risk Stratification of Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Oct 20;131(20):2395-2401.
- Golzarian H, Chakraborty S, Shaikh MU, Hinegardner-Hendricks J, Toro DF. Severe Acute Cor Pulmonale With Impending Shock: An Insidious Incidental. JACC Case Rep. 2024 Feb 9;29(6):102241
eponymictionary
the names behind the name
FACEM, MBBS (Hon), B. Pharm. Emergency Medicine Education Fellow at Liverpool Hospital, Australia. Special interests in clinical education, ECG interpretation and diagnostic ultrasound. Proud father and husband, sadly a golf tragic
BA MA (Oxon) MBChB (Edin) FACEM FFSEM. Emergency physician, Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital. Passion for rugby; medical history; medical education; and asynchronous learning #FOAMed evangelist. Co-founder and CTO of Life in the Fast lane | On Call: Principles and Protocol 4e| Eponyms | Books |

