Paul White

Paul Dudley White (1886-1973) was an American cardiologist
A global pioneer in cardiology during the early 1900s, White was an advocate for healthy living in preventing cardiac disease, promoting physical exercise, sleep and a nutritious diet.
In 1930, White along with Louis Wolff and John Parkinson, described bundle-branch block associated with a short P-R period in healthy young people prone to paroxysmal tachycardia (the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome); and with Sylvester McGinn described McGinn-White sign
Honoured on September 15, 1986 on the 3¢ stamp of the Great Americans postage stamp series
Death from a heart attack before the age of 80 is not God’s will, it is man’s will.
Paul Dudley White
Biography
- Born on June 6, 1886 in Massachusetts
- 1911 – MD, Harvard Medical School
- 1911-1913 Fellowship in cardiovascular physiology, University College Hospital, London.
- 1914 – Early proponent of the electrocardiogram. Installed a machine in the basement of the Massachusetts General Hospital
- 1914-1918 WW1 initially serving for the British Force in France and then the American Expeditionary force and Red Cross in Greece
- 1919-1949 Cardiologist and Professor of Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital
- 1922 – Founded the American Heart Association
- 1931 – Published his hugely popular monograph ‘Heart Disease’ based on 21,160 ECGs collected and reviewed since 1914. The thousand page tome became the standard text on cardiology for decades
- 1942 – President of American Heart Association
- 1948 – President of International Society of Cardiology
- 1955 – Cardiologist to President Dwight D. Eisenhower following his heart attack. White examined the ailing president and reported his findings to the worried nation. He took the opportunity to lecture the country about heart disease, using simple language to describe the illness, its causes and its treatment that it could be understood by the layperson.
- 1964 – President Johnson presents White with the Presidential Medal of Freedom
- Died on October 31, 1973 at 87 years
Medical Eponyms
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (1930)
WPW syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.
On April 2, 1928 a young man was referred to Paul Dudley White because his physician was perplexed by the occurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in a healthy individual. White was preparing for visits to overseas medical centers and took the ECGs with him.
- Vienna: the tracing was deemed to represent nothing more unusual than bundle-branch block and atrioventricular (AV) nodal rhythm
- London: Parkinson was interested and found a further seven cases to add to the four from Boston.
1930 – Wolff L, Parkinson J, and White PD publish the eleven cases as definitive description of the syndrome – ‘Bundle Branch Block with Short P-R Interval in Healthy Young People Prone to Paroxysmal Tachycardia.’ A review of the literature confirmed and acknowledged the previously described cases as above. Wolff, Parkinson, and White erroneously thought that the wide QRS complex was caused by a type of bundle-branch block.
WPW is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia. When recognised in 1930 during a case study of 11 patients, it was first described as:
Functional bundle-branch block and abnormally short P-R interval, occurring mostly in otherwise healthy young people with paroxysms of tachycardia or of auricular fibrillation.
Wolff L, Parkinson J, White PD
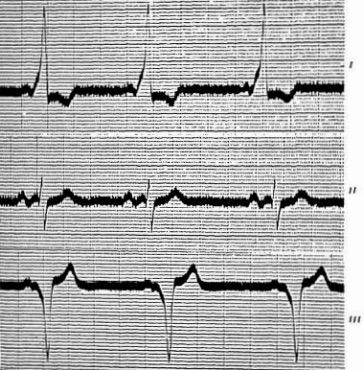
McGinn-White pattern (1935)
SI QIII TIII pattern on ECG representing right heart strain in an acute pulmonary embolism. McGinn and White first described the so-called S1Q3T3 pattern in five patients with acute cor pulmonale secondary to pulmonary embolism.
(1)The prominent S wave and low origin of the T wave in lead 1, the ST segment starting slightly below the baseline, (2) the gradual staircase ascent of the ST interval from the S wave to the T wave in lead 2, and especially (3) the Q wave and definite late inversion of the T wave in lead 3.
McGinn S and White PD
Major Publications
- Lee RI, White PD. A clinical study of the coagulation time of blood. Am J Med Sci 1913; 145:495-503.
- Wolff L, White PD. Acute coronary occlusion: Report of 23 autopsied cases. Boston Med Surg J 1926; 195: 13-25.
- Wolff L, Parkinson J, White PD. Bundle-branch block with short P-R interval in healthy young people prone to paroxysmal tachycardia. American Heart Journal. 1930; 5: 685-704 [Reprint: Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2006 Oct;11(4):340-53] [WPW syndrome]
- White PD. Heart Disease. Macmillan. 1931 [3e 1947]
- McGinn S and White PD. Acute Cor Pulmonale Resulting From Pulmonary Embolism. JAMA 1935; 104(17): 1473-1480 [McGinn-White sign; S1Q3T3 pattern]
- White PD. The Second World Congress of Cardiology. Circulation Research. 1954; 2: 189-190
- White PD. Clues in the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease. American lectures in circulation 1956; 295
- White PD, Mitchell C. Fitness for the whole family. 1964
- White PD. My life and medicine – An autobiographical memoir. Gambit. 1971
References
Biography
- Obituary: Dr. Paul Dudley White Is Dead at 87. NY Times Nov 1, 1973
- Spodick DH. P.D.W.-the gentle titan Paul Dudley White, June 6, 1886 – Oct 31, 1973. JAMA. 1973; 226(12): 1459.
- Smith KS. Paul Dudley White. Br Heart J. 1974; 36(6): 608.
- Davis GP. Paul Dudley White, Crusading cardiologist. In: The heart, the living pump. 1981: 87
- Hurst JW. Paul Dudley White: The Father of American Cardiology. Clinical Cardiology. 1991; 14(7): 622-626.
- Davies MK, Hollman A. Paul Dudley White (1886-1973). Heart. 1996; 76(2): 182.
- Tan SY, Kwock E. Paul Dudley White (1886–1973): Pioneer in modern cardiology. Singapore Med J. 2016; 57(4): 215–216.
- Portrait: Paul Dudley White. Alchetron 17.11.2017
- Bibliography. White, Paul Dudley. WorldCat Identities
Eponymous terms
- Cadogan M. History of the Electrocardiogram. LITFL