Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five 333
Just when you thought your brain could unwind on a Friday, you realise that it would rather be challenged with some good old fashioned medical trivia FFFF, introducing the Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five 333
Question 1
What is IKEA bias?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
The IKEA effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers place a disproportionately high value on products they partially created
The same can occur with projects, when you invest your own time in a project you are far less likely to quit even if its falling (a sunk cost fallacy) and also reject projects or protocols if they were conceived by a different organisation (or hospital).
A study by Norton et al found that consumers would pay 63% more for IKEA objects they had made than for the original already assembled.
Pre- IKEA Betty Crocker in the 1950s faced the problem of consumers demanding speed and convenience but they also wanted to be involved in the process. Hence the role for baking kits, unfortunately they didn’t catch on until psychologist Ernest Dichter suggested they remove the processed powdered egg and requested consumers added their own to the mixture thus engaging them in the process, what followed was an instant rise in sales.
References
- Norton M, Mochon D and Ariely, D. “The IKEA effect: When labor leads to love”(PDF). Journal of Consumer Psychology. 22 (3): 453–460. doi:10.1016/j.jcps.2011.08.002
Question 2
A 38 year old male comes to thank you for saving his life post drug overdose. You remember he was in full arrest and you managed to get ROSC after 4 minutes. While he seems neurologically intact he’s in a wheel chair despite having 5/5 power. You ask why he needs the wheel chair and he says every time he does voluntary movements he gets spasms.
What is his diagnosis?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
Lance-Adams syndrome
Up to a third of post resuscitation patients will experience a seizure. Post-hypoxic myoclonus (PMH) is the most common type which can be repetitive, generalised, focal or multifocal. PMH can be classified many ways but simply there is an acute version and a chronic version (known as Lance-Adams syndrome).
The syndrome was first reported but neurologists Drs Lance and Adams in 1963 after they saw 4 patients at Massachusetts General who had experienced hypoxic events and were having muscle jerks. First the myoclonus was generalised but later became localised to the arms or legs and were made worse by voluntary action. The more precise the action required the more the patient experienced myoclonus. Only 150 cases are reported in the literature.
A 64 year old woman was having a hysterectomy… her heart stopped beating for at least three minutes. She then remained unconscious for four days. As soon as she became aware of her surroundings, she noticed frequent jumping movements which affected the arms more severely than the legs an these have now persisted for eight years..
Lance and Adams 1963
References
- Lance JW and Adams RD. The Syndrome of Intension or Action Myoclonus as a Sequel to Hypoxic Encephalopathy. Brain. 1963;86(1):111-36.
- Kim HS. A case of Lance-Adams Syndrome Post Life-threatening Bronchial Asthma. EMJ. 2019;4[4]:71-76
Question 3
How many Ramsay Hunt Syndromes do you know?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
There are three in total – not just herpes zoster on the tympanic membrane.
James Ramsay Hunt (1874 – 1937) was an American neurologist. In addition to describing the juvenile paralysis agitans of Ramsay Hunt in 1917, he described three other eponymous syndromes.
Ramsey Hunt syndrome 1 is also called Ramsay Hunt cerebellar syndrome, a rare condition secondary to cerebellar degeneration with causes myoclonic epilepsy, progressive ataxia and tremor.
This affection was characterised by generalised intention tremors, which began as a local manifestation and gradually extended to other parts of the voluntary muscular system. The extremities, and more especially the arms, showed the greatest involvement. The coarse ataxic-tremor … was only present when the muscles were in action, and ceased entirely during relaxation and rest. … associated with it a disorder of muscle tone and of the ability to measure direct and associated muscular movements, the clinical manifestations of which were dyssynergia, dysmetria, adiadokokinesis, hypotonia and asthenia. All of these symptoms … showed the existence of a fundamental disorder of cerebellar function.
James Ramsey Hunt
Ramsay Hunt syndrome type 2 is the herpes zoster infection of the geniculate ganglion. A triad of ipsilateral facial paralysis, ear pain and vesicles on the face or around the ear is classic. Patients can also complain of deafness and vertigo, and just like normal shingles the pain and paralysis can occur before the vesicles making the diagnosis difficult on first presentation.
Ramsay Hunt syndrome type 3 is an occupational induced neuropathy. It is caused by damage to the deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve (in Guyon’s canal) causing weakness and wasting of the small muscles in the hand. Motor function loss includes:
- Only the intrinsic muscles of the hand are affected.
- Abduction and adduction of the fingers cannot occur (due to paralysis of the interossei).
- Movement of the 4th and 5th digits is impaired (due to paralysis of the medial two lumbricals and hypothenar muscles).
- Adduction of the thumb is impaired, and the patient will have a positive Froment’s sign (due to paralysis of adductor pollicis).
Also called metal turner paralysis due to the tools grasped in the palm. For those in a wide life crisis, long days on a motorbike can also induce this syndrome.
References:
- Hunt JR. On herpetic inflammations of the geniculate ganglion. A new syndrome and its complications. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1907;34:73–96 [Ramsay Hunt syndrome I]
- Hunt JR. Occupational neurosis of the deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve.. A well-defined clinical type of professional palsy of the hand. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1908;35:673–89. [Ramsay Hunt syndrome III]
- Hunt JR. Dyssynergia cerebellaris progressiva: a chronic progressive form of cerebellar tremor. Brain 1914;37:247. [Ramsay Hunt syndrome II]
- Pearce JMS. Some syndromes of James Ramsay Hunt. Practical Neurology 2007; 7 139-139
Question 4
What is suitcase elbow?
Reveal the funtabulous answer
Medial Epicondylitis.
Just to add to the other names; golfer’s elbow, baseball elbow, throwing elbow and forehand tennis elbow. Yes, it’s not just tennis elbow anymore, it’s specific to the stroke – the backhand causes the lateral epicondylitis. Medial epicondylitis by repetitive, excessive force on the flexor muscles of the forearm, often it is not painful just at the elbow but along the medial aspect of the forearm and sometimes to the wrist.
If like me you have trouble remembering which clinical manoeuvre you do to test for these epicondylitides just think about which mechanism you want to stretch. Medial epicondylitis is from stressing the flexor muscles, by putting them at full stretch (extending the elbow in supination and extending the wrist will pull on the extensors). Equally the opposite is true for lateral epicondylitis, have a fully extended arm, pronate and flex at the wrist. And if that doesn’t help watch these videos below:
Question 5
What is the diagnosis here (and yes the image is the right way around)?
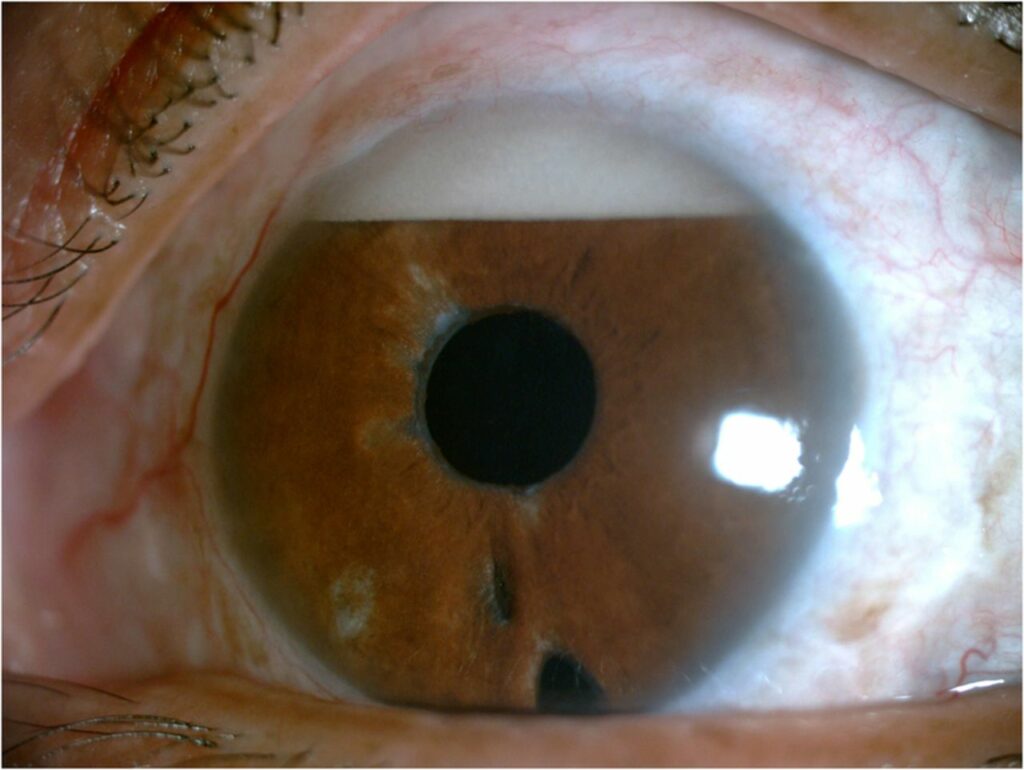
Reveal the funtabulous answer
Hyperoleon or inverted hypopyon
It is a layer of emulsified silicone oil in the superior anterior chamber. It is used in retinal surgery to act as an endotamponade such as retinal detachment. Rarely the silicone oil can prolapse through anatomically compromised areas. The density of silicone oil is lower than that of aqueous humor, and therefore, it settles at the top of the anterior chamber.
Reference:
- Tripathy K, Sharma YR. Inverted hypopyon in the eye. BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Feb 17;2016:bcr2016214638
…and Finally – what to do beyond Tier 4?

FFFF
Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five
Dr Neil Long BMBS FACEM FRCEM FRCPC. Emergency Physician at Kelowna hospital, British Columbia. Loves the misery of alpine climbing and working in austere environments (namely tertiary trauma centres). Supporter of FOAMed, lifelong education and trying to find that elusive peak performance.


Molto interessante