James Ramsay Hunt

James Ramsay Hunt (1874-1937) was an American neurologist.
Renowned for his contributions to the field of neurology conducting significant research on the anatomy and disorders of the corpus striatum and the extrapyramidal system, describing several movement disorders.
Several disorders bear his name, such as Ramsay Hunt syndrome, a condition characterised by facial paralysis and a rash around the ear due to reactivation of the varicella zoster virus
Biography
- Born on February 1, 1874 in Philadelphia
- Quaker School at the Friends’ Central School of Philadelphia
- 1893 – MD, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine
- 1893-1895 Resident physician Pennsylvania University Hospital
- 1896 Personal physician for a wealthy patient of Silas Weir Mitchell, whilst he travelled to Japan, China and India.
- 1897-1900 Studied medicine and pathology in Europe, working with Heinrich Obersteiner (Vienna), Hermann Oppenheim (Berlin), as well as Pierre Marie, Joseph Babinski and Jules-Joseph Déjerine (Paris).
- 1900 – Clinical Assistant and then Instructor at Cornell University, New York
- Died on July 22, 1937
Medical Eponyms
Ramsay Hunt syndrome type I
Herpes zoster infection of the geniculate ganglion. A triad of ipsilateral facial paralysis, ear pain and vesicles on the face or around the ear is classic. Patients can also complain of deafness and vertigo, and just like normal shingles the pain and paralysis can occur before the vesicles making the diagnosis difficult on first presentation.
Ramsay Hunt presented presented his findings at the meeting of the American Neurological Association, June 4 and 5, 1906, and later published in The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease in 1907
Herpes Auricularis with Facial Palsy. — In this manifestation of the affection, there is superadded to the herpes auricularis, as just described a peripheral facial palsy, which appears on the same side as the zoster. The time of the appearance of this palsy varies, coming on in some cases simultaneously with the eruption, in others it may be delayed a week or even longer. In the majority of instances it appears on the second or third day
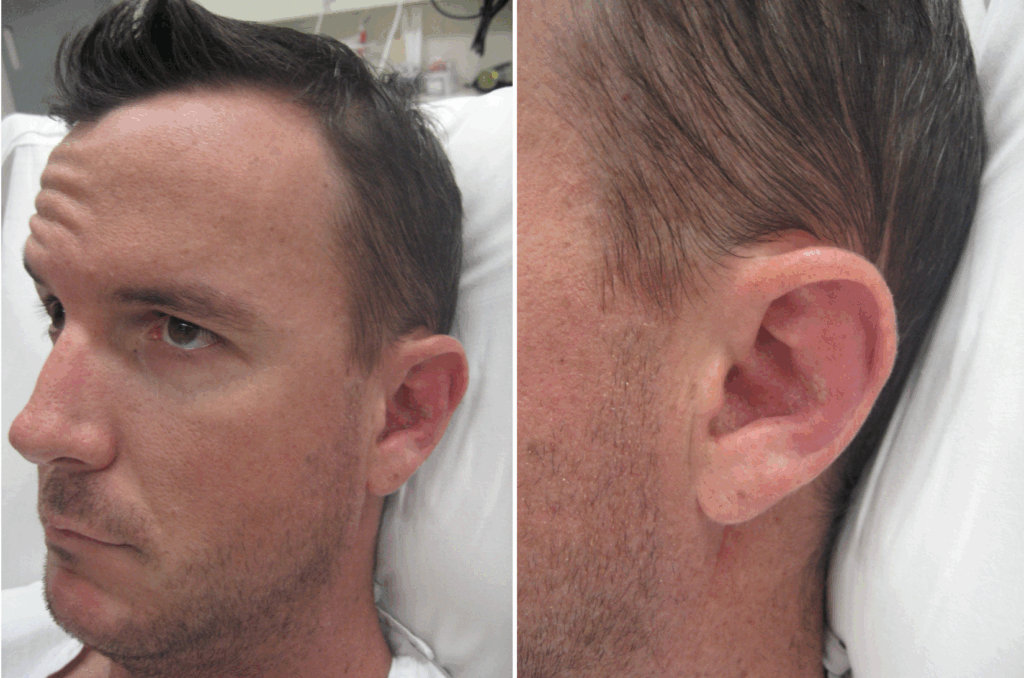
Ramsay Hunt syndrome II (1907)
Ramsay Hunt cerebellar syndrome; Herpes zoster oticus; Herpetic inflammation of the Gasserian ganglion, a rare condition secondary to cerebellar degeneration with causes myoclonic epilepsy, progressive ataxia and tremor.
This affection was characterised by generalised intention tremors, which began as a local manifestation and gradually extended to other parts of the voluntary muscular system. The extremities, and more especially the arms, showed the greatest involvement. The coarse ataxic-tremor … was only present when the muscles were in action, and ceased entirely during relaxation and rest. … associated with it a disorder of muscle tone and of the ability to measure direct and associated muscular movements, the clinical manifestations of which were dyssynergia, dysmetria, adiadokokinesis, hypotonia and asthenia. All of these symptoms … showed the existence of a fundamental disorder of cerebellar function.
Ramsay Hunt syndrome type III
Occupational induced neuropathy. It is caused by damage to the deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve (in Guyon’s canal) causing weakness and wasting of the small muscles in the hand. Motor function loss includes:
- Only the intrinsic muscles of the hand are affected.
- Abduction and adduction of the fingers cannot occur (due to paralysis of the interossei).
- Movement of the 4th and 5th digits is impaired (due to paralysis of the medial two lumbricals and hypothenar muscles).
- Adduction of the thumb is impaired, and the patient will have a positive Froment’s sign (due to paralysis of adductor pollicis).
Also called metal turner paralysis due to the tools grasped in the palm. For those in a wide life crisis, long days on a motorbike can also induce this syndrome.
Ramsay Hunt paralysis (1917)
Juvenile paralysis agitans of Ramsay Hunt
Major Publications
- Hunt JR. On herpetic inflammations of the geniculate ganglion. A new syndrome and its complications. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1907;34:73–96 [Ramsay Hunt syndrome I]
- Hunt JR. Occupational neurosis of the deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve.. A well-defined clinical type of professional palsy of the hand. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1908;35:673–89. [Ramsay Hunt syndrome III]
- Hunt JR. Dyssynergia cerebellaris progressiva: a chronic progressive form of cerebellar tremor. Brain 1914;37:247. [Ramsay Hunt syndrome II]
- Hunt JR. Hunt JR. The role of the carotid arteries in the causation of vascular lesions of the brain, with remarks on certain special features of the symptomatology. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1914;147:704–13 [Ramsay Hunt syndrome II]
- Hunt JR. Progressive atrophy of the globus pallidus (primary atrophy of the pallidal system). A system disease of the paralysis agitans type, characterized by atrophy of the motor cells of the corpus striatum. A contribution to the functions of the corpus striatum. Brain 1917;40:58–148 [Ramsay Hunt paralysis]
- Hunt JR. Dyssynergia cerebellaris myoclonica- primary atrophy of the dentate system. A contribution to the pathology and symptomatology of the cerebellum. Brain 1922; 44(4): 490–538 [presented in abstract at the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association, June 13, 1921] [Ramsay Hunt syndrome II]
References
Biography
- Louis ED, Williams M. A biography of James Ramsay Hunt (1874-1937). J Hist Neurosci. 2003 Sep;12(3):266-75
- Louis ED. James Ramsay Hunt (1874-1937). J Neurol. 2004 Feb;251(2):240-1.
Eponymous terms
- Pearce JMS. Some syndromes of James Ramsay Hunt. Practical Neurology 2007; 7 139-139
- Compston A. Progressive atrophy of the globus pallidus (primary atrophy of the pallidal system). A system disease of the paralysis agitans type, characterized by atrophy of the motor cells of the corpus striatum. A contribution to the function of the corpus striatum. By J. Ramsay Hunt MD, New York. Brain 1917; 40: 58-148. Brain. 2017 Jun 1;140(6):1808-1813.
Eponym
the person behind the name
