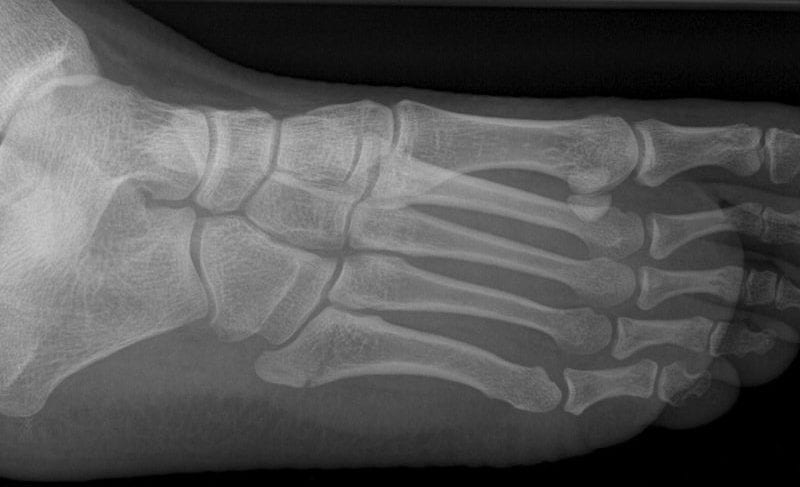
Jones Fracture
Description
Jones Fracture: Fracture of the proximal diaphysis of the 5th metatarsal, distal to the tuberosity, without joint involvement. Caused by foot inversion / twisting and repetitive stress
The term ‘Jones fracture’ is used inconsistently; some referring to fracture at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction and others define it as a fracture at the proximal diaphysis.
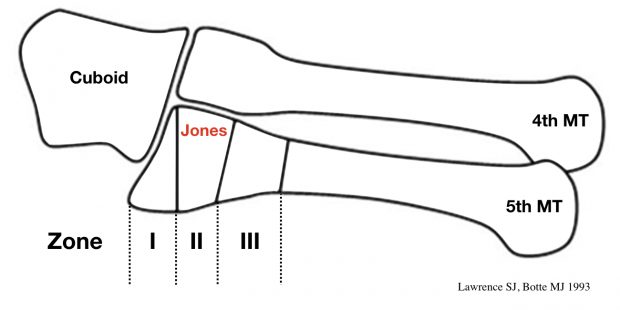
The ‘Zone I, II, III‘ method of description is more accurate, replicable and assists in determining immediate treatment and ongoing management.
History of the Jones fracture
1902 – Sir Robert Jones, general surgeon with a passion for orthopaedics and radiology, sustained this injury whilst dancing. In 1902 he wrote up a case report of five similar injuries specifically noting that the fracture is caused by ‘indirect violence’
Whilst dancing, I trod on the outer side of my foot, my heel at the moment being off the ground. Something gave way midway down my foot, and I at once suspected a rupture of the peroneus longus tendon…The following morning I carefully examined my foot and discovered that my tendon was intact. There was a slight swelling over the base of the fifth metatarsal bone… A finger on the spot gave exquisite pain…Extension of the ankle and flexion of the toes were immediately felt at the base of the fifth metatarsal. I hobbled down-stairs to my colleague…to X-ray my foot. This was done, and the fifth metatarsal was found fractured about three-fourths of an inch from its base.
Jones R, Ann Surg. 1902: 697
1960 – Stewart differentiated an avulsion fracture of the tuberosity / styloid from fractures of the proximal diaphysis. He named the latter: ‘Jones fracture’.
1984 – Torg et al reported fractures of proximal diaphysis are likely located at a site of pre-existing stress pressure.
1993 – Lawrence and Botte release a classification system distinguishing 3 zones
- Zone 1: Tuberosity avulsion fracture, with or without involvement of the tarsometatarsal articulation. Caused by forces by the peroneus brevis tendon or the lateral band of the plantar fascia during foot inversion.
- Zone 2: Jones fracture; metaphysis-diaphysis junction fracture, which extend into the fourth-fifth intermetatarsal facet. Caused by forced forefoot adduction with the hindfoot in plantar flexion.
- Zone 3: Diaphyseal stress fracture; proximal diaphyseal fractures, distal to the fourth and fifth metatarsal base articulation. Caused by acute excessive bearing of the region or chronic overloading as in stress fractures
Associated Persons
- Sir Robert Jones (1857-1933)
Alternative names
- Jones’ fracture; Jones’s fracture
- Zone II 5th Metatarsal fracture
References
Original articles
- Jones R. Fracture of the Base of the Fifth Metatarsal Bone by Indirect Violence. Ann Surg. 1902; 35(6): 697–700
- Stewart IM. Jones’s fracture: fracture of base of fifth metatarsal. Clin Orthop. 1960;16:190-8.
- Torg JS, Balduini FC, Zelko RR, Pavlov H, Peff TC, Das M. Fractures of the base of the fifth metatarsal distal to the tuberosity. Classification and guidelines for non-surgical and surgical management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984 Feb;66(2):209-14.
- Torg JS. Fractures of the base of the fifth metatarsal distal to the tuberosity. Orthopedics. 1990;13(7):731–7.
- Lawrence SJ, Botte MJ. Jones’ fractures and related fractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal. Foot Ankle. 1993 Jul-Aug;14(6):358-65.
Review articles
- Petrisor BA, Ekrol I, Court-Brown C. The epidemiology of metatarsal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2006 Mar;27(3):172-4.
- Zwitser EW, Breederveld RS. Fractures of the fifth metatarsal; diagnosis and treatment. Injury. 2010 Jun;41(6):555-62.
- Polzer H, Polzer S, Mutschler W, Prall WC. Acute fractures to the proximal fifth metatarsal bone: development of classification and treatment recommendations based on the current evidence. Injury. 2012 Oct;43(10):1626-32
- Cheung CN, Lui TH. Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fractures: Anatomy, Classification, Treatment and Complications. Arch Trauma Res. 2016 Dec; 5(4): e33298.
- Gomez A, Cadogan M. Eponymythology of foot injuries. LITFL
- Cadogan M. Jones fracture. Eponym A Day. Instagram
[cite]
eponymictionary
the names behind the name