Pulmonary panic
aka Pulmonary Puzzler 005
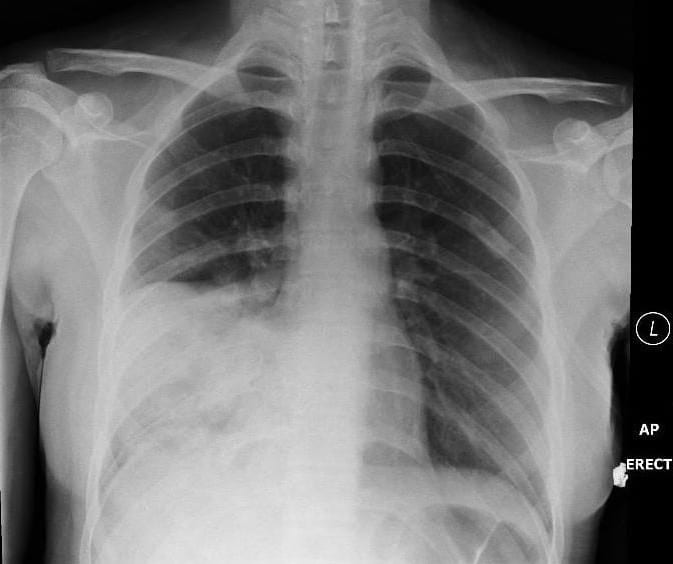
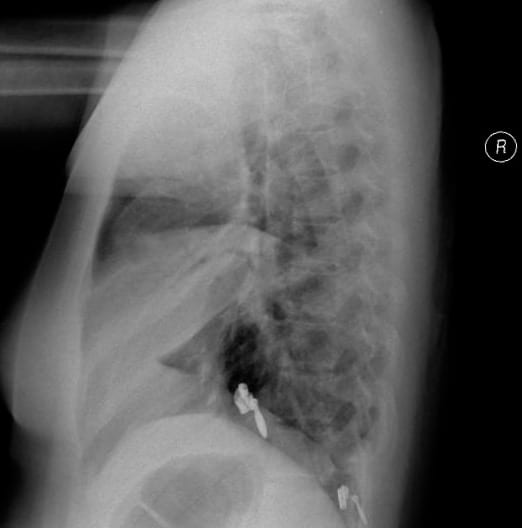
A 17 year old female with a background history of HIV presents with a 3 day history of fevers, chills and rigors. Her admission chest X-rays are shown below:
Questions
Q1. Describe the chest X-ray.
Answer and interpretation
The chest X-ray shows dense consolidation of the right middle lobe.
The radiographic features of lobar consolidation are:
- homogeneous opacification.
- minimal volume loss.
- air bronchograms and air alveolograms (lucent areas due to air-filled acini).
- sharp border where the infiltrate abuts an interlobar fissure.
- silhouette sign – loss of the right heart border on the AP film indicates that the right middle lobe is involved; this occurs because of obliteration of the normal interface between lung air and mediastinal tissue/fluid.
- obliteration of normal vascular markings.
Q2. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer and interpretation
The commonest cause of pneumonia in patients with HIV is pneumococcal pneumonia.
The clinical history and radiological features are consistent with this diagnosis.
Q3. A decision is made to perform a diagnostic bronchoscopy. Where will you aim the bronchoscope?
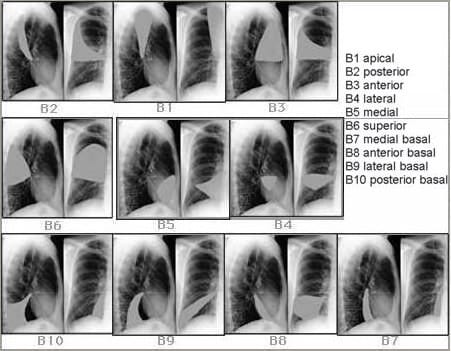
Q4. How do you navigate your way to the right middle lobe?
Answer and interpretation
Q5. How should wounds such as this be appropriately explored?
Answer and interpretation
You practice!
Bronchoscopy International is a fantastic learning resource for learning endobronchial anatomy.
NB: The Step-by-Step presentation is optimised for use on Microsoft internet Explorer and works well in Safari, but looks like a pig’s breakfast in Firefox!
The following video, which is one of many at the site, demonstrates how to get from the right main bronchus to the bronchus intermedius:
From the distal bronchus intermedius the bronchoscope can then access the segments of the right middle lobe (RB4 and RB5) as well as the superior segment of the right lower lobe (RB6).
References
- For more Pulmonary cases check out the LITFL Top 150 Chest X-Rays
CLINICAL CASES
Pulmonary Puzzler
Intensivist in Wellington, New Zealand. Started out in ED, but now feels physically ill whenever he steps foot on the front line. Clinical researcher, kite-surfer | @DogICUma |