Robert Todd
Robert Bentley Todd (1809-1860) was an Irish physician. Provided early depictions of migraine, peripheral neuritis, and postepileptic paralysis (Todd's palsy). He also gave an important discourse on locomotor ataxy (tabes dorsalis).

Robert Bentley Todd (1809-1860) was an Irish physician. Provided early depictions of migraine, peripheral neuritis, and postepileptic paralysis (Todd's palsy). He also gave an important discourse on locomotor ataxy (tabes dorsalis).
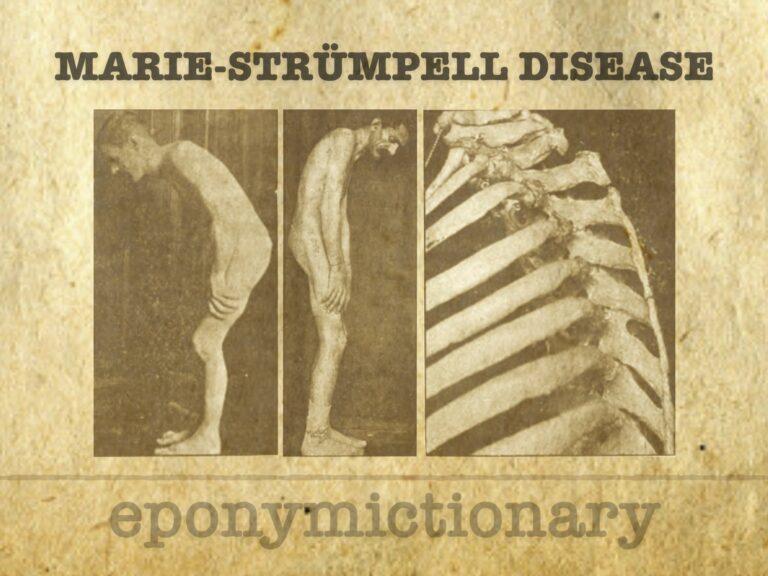
Marie-Strümpell disease (ankylosing spondylitis): a chronic inflammatory spinal arthritis with progressive axial fusion, first described by Pierre Marie and Adolf Strümpell in the late 19th century.

Sylvester McGinn (1904–1984); American cardiologist; McGinn-White sign (S1Q3T3) in pulmonary embolism; pioneer in Boston cardiac care and research.

Moritz Heinrich Romberg (1795–1873) a founder of clinical neurology, Romberg’s sign, Parry–Romberg syndrome and Howship–Romberg sign

August Gottlieb Richter (1742–1812), German surgeon; Richter’s hernia, advanced cataract extraction, and elevated surgery into academia

Understand and identify prosthetic valves. Learn what can go wrong with prosthetic valves; how to assess their function and examine transcatheter valves

Manfred J. Sakel (1900–1957), Austrian neuropsychiatrist, pioneered insulin coma therapy—an early somatic treatment for schizophrenia, now obsolete

Ladislas J. Meduna (1896–1964), pioneer of convulsive therapy, explored epilepsy-schizophrenia antagonism, CO₂ therapy, and oneirophrenia in psychiatry.

Mary Broadfoot Walker (1888 - 1974) was a Scottish physician. Mary Walker effect (1934); neostigmine and myasthenia gravis

Henry Koplik (1858–1927), American pediatrician, discovered Koplik’s spots—an early diagnostic sign of measles—and pioneered infant health reform
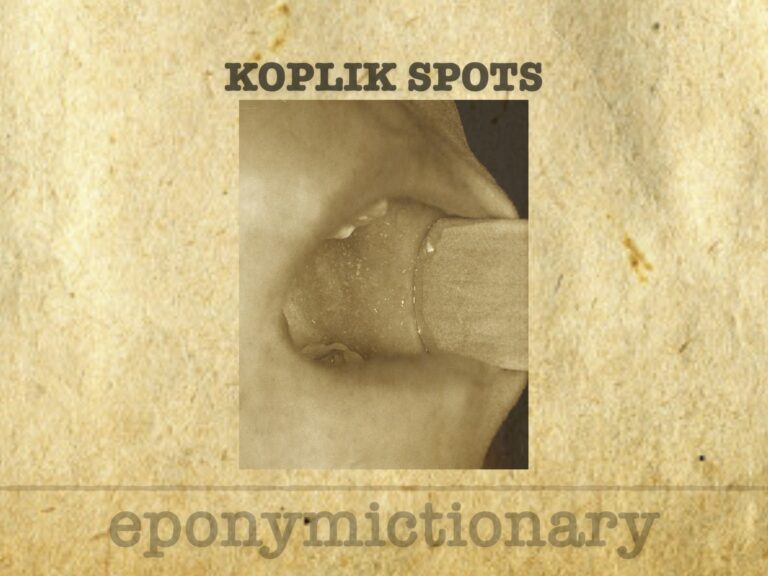
Koplik spots are pathognomonic buccal lesions in early measles, first described by Henry Koplik in 1896, aiding pre-rash diagnosis and outbreak control.

Sir William Stokes (1839–1900), Irish surgeon and son of William Stokes, pioneered surgical techniques and served as RCSI professor and Queen Victoria’s surgeon