
CT Case 103
A 35 year old male presents with recurrent episodes of spontaneous bleeding from his right ear. What does the CT angiogram show?

A 35 year old male presents with recurrent episodes of spontaneous bleeding from his right ear. What does the CT angiogram show?

A 52 year old man is brought to hospital by ambulance complaining of 2 weeks of abdominal pain and constipation. What does the abdominal CT show?

Charles T Dotter (1920–1985): father of interventional radiology; coronary imaging pioneer, 1964 angioplasty, catheter thrombolysis, and stents.

Brain Herniation Syndromes. Clinical and radiological assessment of 13 cases. Neuroimaging case study series with Teresa Crow, Troy Carnwath, Scott DiMeo, L. Erin Miller and Natalie Rall

Xray and ultrasound (POCUS) evaluation of integrity of quadriceps tendon, patella tendon, and patella evaluating for tendon rupture and patella fracture.

Echocardiography basics and the differences between 2D imaging, M-mode, pulsed wave Doppler, continuous wave Doppler, and tissue Doppler imaging.

Neurocysticercosis. Third edition in our Neuroimaging case study series with guest editors Drs. Michael Leonard and David Weinrib

Leo George Rigler (1896-1979) was an American radiologist. Eponymously affiliated with Rigler sign; Rigler triad; Rigler notch sign; Hoffman-Rigler sign
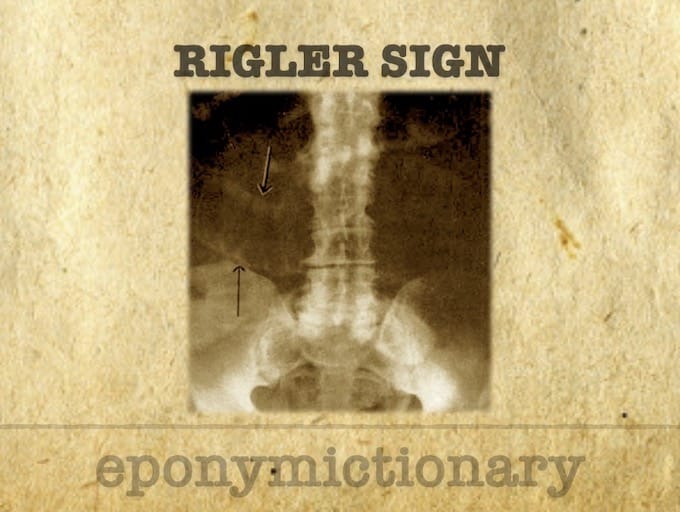
Radiological signs of pneumoperitoneum: history, diagnosis, and key eponyms including Rigler’s sign, Popper’s sign, football sign, and inverted V sign

Understand and identify prosthetic valves. Learn what can go wrong with prosthetic valves; how to assess their function and examine transcatheter valves

Understand and identify the pulmonary valve. Learn how to identify and grade pulmonary regurgitation and quantify pulmonary stenosis. Basic management of pulmonary valve dysfunction.

Understand and identify the tricuspid valves. Learn how to identify and grade tricuspid regurgitation and quantify tricuspid stenosis. Basic management of tricuspid valve dysfunction.