Rigler sign
Description
Rigler sign: Radiographic sign of pneumoperitoneum. Air in the peritoneum and air within the intraluminal spaces outline the luminal and serosal surfaces of the bowel wall.
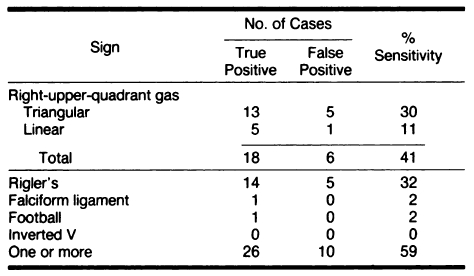
Rigler sign may be seen in up to 32% of patients with pneumoperitoneum demonstrated by supine abdominal radiographs
History
1924
1941 – Leo George Rigler (1896-1979) described the pneumoperitoneum sign and emphasized that it would only be observed when large quantities of free gas were present.
A roentgenologic sign of pneumoperitoneum hitherto not reported or clearly defined is described. I t consists of the demonstration of the outer as well as the inner bowel wall due to the accumulation of gas between the loops of bowel. It is of value because it can be observed in roentgenograms of the abdomen made in the supine position.
This sign may be the first evidence of the presence of pneumoperitoneum in cases in which such a condition is entirely unsuspected. Routine roentgenograms of the abdomen should be made at frequent intervals in all cases of obstruction of the gastro-intestinal tract which are being treated conservatively. Such films should always be examined for evidences of pneumoperitoneum because of the possibility of supervention of perforation without obvious clinical signs.
Rigler, Radiology 1941
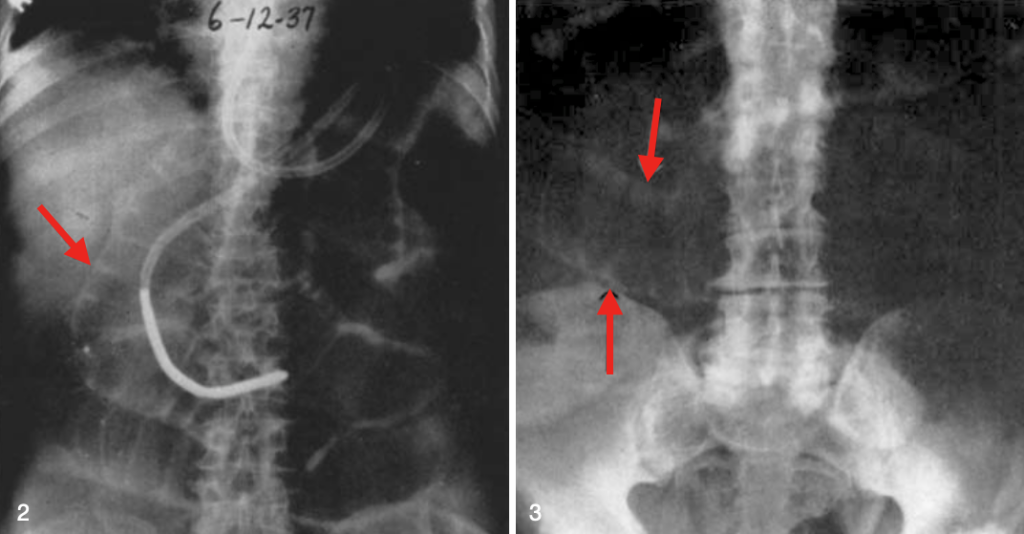
Fig. 3. Case of perforation of the colon with pneumoperitoneum; roentgenogram of abdomen, supine position. Note the distended loops of small bowel, both their inner and outer contours (arrows) being readily visible. Rigler 1941
1991
Pseudo-Rigler sign
Form of pseudopneumoperitoneum, and mimic of the classic Rigler sign, which can be encountered on normal abdominal X-rays.
Caused by omental / mesenteric fat; oral contrast media outlining the bowel loops; or overlapping gas-filled bowel loops making the wall contours appear more prominent.
In such cases further examination with erect or lateral decubitus views, or CT are required to rule in or out the presence of free gas.
Associated Persons
- Leo George Rigler (1896-1979)
Alternative names
- Rigler’s sign
- Double-Wall Sign, double-lumen sign
- bas-relief sign
References
Original references
- Vaughn RT, Brams WA. The early recognition of acute perforation of gastric and duodenal ulcer by x-ray examination of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1924; 39: 610-617
- Rigler LG. Spontaneous pneumoperitoneum: a roentgenologic sign found in the supine position. Radiology 1941; 37: 604–607
Review articles
- Miller RE, Nelson SW. The roentgenologic demonstration of tiny amounts of free intraperitoneal gas: experimental and clinical studies. AJR 1971; 112: 574-585
- Williams N, Everson NW. Radiological confirmation of intraperitoneal free gas. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1997 Jan;79(1):8-12
- Levine MS, Scheiner JD, Rubesin SE, Laufer I, Herlinger H. Diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum on supine abdominal radiographs. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1991; 156(4): 731–735
- Ly JQ. The Rigler sign. Radiology. 2003 Sep;228(3):706-7.
- Lewicki AM. The Rigler sign and Leo G. Rigler. Radiology. 2004 Oct;233(1): 7-12
- Daya S, Mahomed N, Andronikou S. Rigler’s sign and the football sign. South African Journal of Radiology. 2012; 16(4): a263
- Indiran V, Sivakumar V. Rigler sign. Abdominal Radiology, 2017; 42(10): 2588–2588
- Al Kabbani A. Rigler sign (bowel). Radiopaedia
[ciet]
Third year M.D. student at the University of Notre Dame Fremantle. Passionate about emergency and retrieval medicine, rural practice and clinical research


