POCUS Made Easy: Basic Echo
Focussed ECHO in Life support (FELS) is used to define cardiac pathologies such as cardiogenic shock, pericardial tamponade, signs of submassive/massive PE or hypovolaemia
Global assessment of RV and LV function, assessment of IVC and assessment for pathological findings.
Tip: cardiac setting by convention flips the image like a mirror, so in contrast to eFAST / AAA scans screen marker is on the right-hand side.
Pre-reading
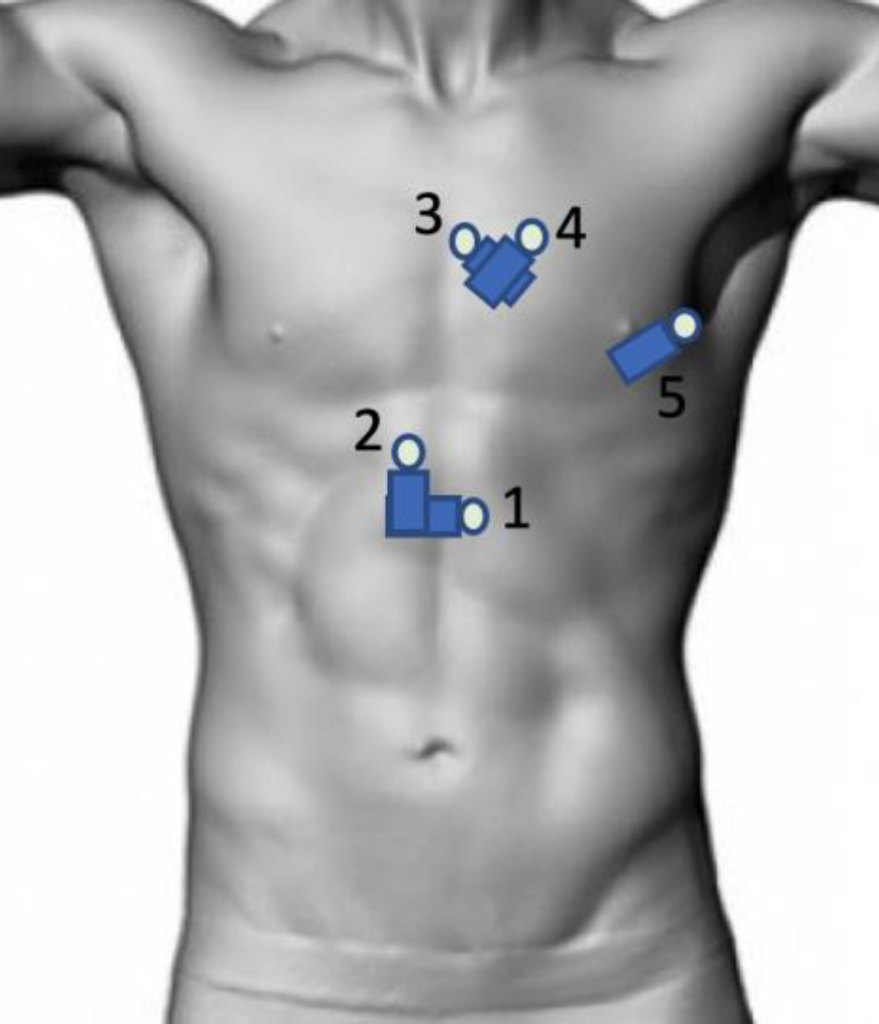
1. Subxiphoid Long Axis View (4 Chamber view)
- Labelled SUBX
- Patient position Supine
- Start under xiphoid process
- Probe marker faces Patient’s LEFT
2. Subxiphoid IVC view
- Labelled SUBX
- Holding SUBX 4 chamber view, rotate 90 degrees anticlockwise
- Probe marker now facing caudally
- Identify IVC, measure size + sniff test
3. Parasternal Long Axis view
- Labelled PLAX
- Patient position supine / left lateral
- Start at 3rd ICS left of sternum and move up/down
- Probe marker towards Right Shoulder
4. Parasternal Short Axis view
- Labelled PSAX
- Patient position supine / left lateral
- Holding PLAX view, rotate probe 90 degrees clockwise
- Probe marker now faces towards Left Shoulder
5. Apical 4 Chamber View
- Labelled APICAL
- Ideally Left lateral position
- Transducer at cardiac apex pointing towards right shoulder
- Probe marker pointing towards Left axilla
Image Sets
- Minimum 5 Video loops + 1 image (IVC) 5-8 Video Loops
- Optional extra views including:
- Apical 5 Chamber
- Apical 2 Chamber
- Subx Short Axis 2 Chamber
- Suprasternal
Machine Settings
- PHASED ARRAY Probe
- Cardiac setting for all images
Documentation – POCUS FELS
- Views: Adequate/ Inadequate
- Findings: NAD / Abnormal
- Pericardial Effusion: Yes/ No. And if so, is it tamponading Global RV + LV function: hypodynamic/ normal/ hyperdynamic
- LV and RV size: normal/ abnormal. Is RV > 2/3 LV. Gross abnormalities in chamber sizes
- IVC size and collapsibility: >2cm / <2cm. Collapsing: yes/no or images
Positive Findings (always consider clinical context)
Cardiac Tamponade: Clinical Diagnosis. TTE features- pericardial effusion (usually >1-2cm) + Dilated IVC non-collapsing. R Atrial Collapse in Systole. Right Ventricular Diastolic Collapse. Swinging Heart.
Acute Submassive/ Massive PE: dilated RV (>2/3 L). Septal Bowing. Dilated IVC. Dilated RA. RV wall hypokinesis. McConnell’s Sign. Intramural Thrombus.
Cardiogenic Shock: hypodynamic heart. Dilated chambers. Often dilated and non-collapsing IVC.
Hypovolaemia: hyperdynamic heart. Small chambers. Small and collapsing IVC. (Consider looking for cause)
References and Further reading
- Bendigo ED Resource PDF – Basic Echo
Clinical Cases
[cite]

POCUS
made easy
MBChB FACEM CCPU. Emergency Physician at Bendigo Hospital and Royal Melbourne Hospital, Victoria. Australia.
I studied in Scotland before completing my Emergency Medicine training in Melbourne. I have a big interest in point-of-care ultrasound use and training in Emergency Medicine. I'm also interested in Choosing Wisely and sustainability initiatives in healthcare.
In my free time you'll find me playing tennis and soccer, or heading outdoors on camping trips.