Tetanus Immunoglobulin
Indications and Role:
The tetanus immunoglobulin is used for those wounds that are tetanus prone and high risk as vaccination alone may not provide enough protection if the incubation period is faster than the host’s own immune response.
Administration and dosing:
- 250 IU by intramuscular injection, or 500IU if more than 24 hours have elapsed since the injury or there is heavy contamination or following burns. The usual preparation is 1ml ampoules containing 25oIU.
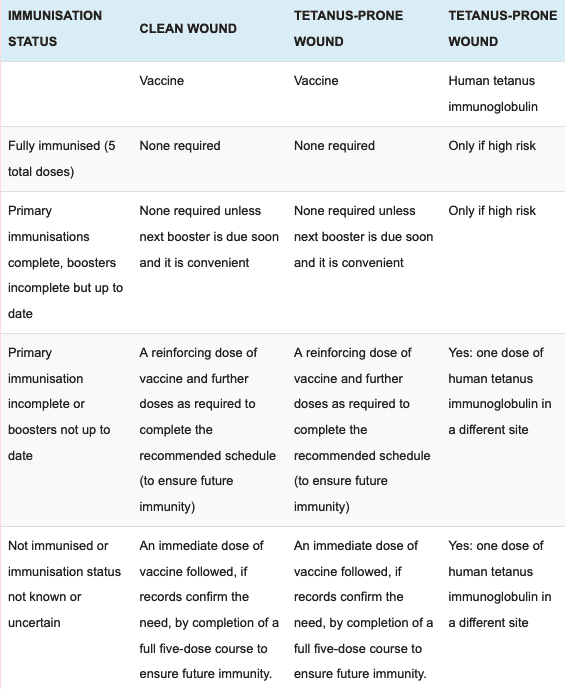
Immunisation recommendations for clean and tetanus prone wounds (UK):
Tetanus prone wounds:
- Wounds or burns that require surgical intervention that is delayed for more than 6 hours.
- Wounds or burns that show a significant degree of devitalised tissue or a puncture-type injury, particularly where there has been contact with soil or manure.
- Wounds containing foreign bodies.
- Compound fractures.
- Wounds or burns in patients who have systemic sepsis.
High risk is regarded as any wound mentioned above that is heavily contained with material likely to contain tetanus spores and/or extensive devitalised tissue.
Contraindications or complications and special populations:
- Intravenous drug users are at particular risk and when they develop symptoms of tetanus they should be given 5000-10,000 IU by intravenous infusion. If IV administration is not possible then 15o IU/kg intramuscularly but this will need to be split and given at different sites.
References
Dr Neil Long BMBS FACEM FRCEM FRCPC. Emergency Physician at Kelowna hospital, British Columbia. Loves the misery of alpine climbing and working in austere environments (namely tertiary trauma centres). Supporter of FOAMed, lifelong education and trying to find that elusive peak performance.