Eleventh Cranial Nerve Lesions
The accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI) is a motor nerve.
Lesions are rare but may occur with penetrating injuries to the posterior triangle of the neck.
Anatomy
Course and Components
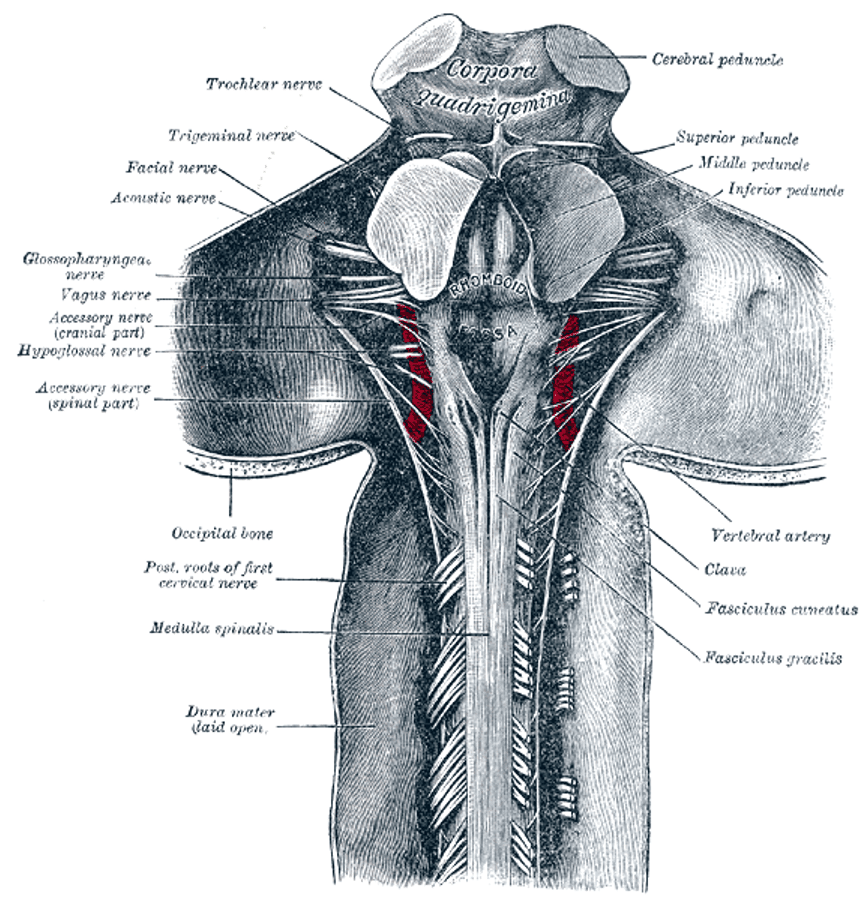
The accessory nerve has two roots: spinal and cranial (the latter generally considered part of the vagus nerve).
- Spinal root: Arises from C3–C4, ascends through the vertebral canal, and enters the skull via the foramen magnum.
- Cranial root: Arises from the nucleus ambiguus in the medulla, emerges as multiple fine rootlets, and joins the spinal root. The combined nerve exits the skull via the jugular foramen (with CN IX and X).
- The cranial root then separates to join the vagus nerve below its inferior ganglion and contributes to pharyngeal and recurrent laryngeal branches.
The spinal root:
- Passes behind the sternomastoid muscle.
- Emerges into the posterior triangle, running across levator scapulae and prevertebral fascia.
- Passes deep to the trapezius muscle and innervates it.
Innervation
| Muscle | Function |
|---|---|
| Sternomastoid | Turns head to opposite side |
| Trapezius | Elevates shoulder (shrug) |
Pathology
Isolated lesions are uncommon.
Causes include:
- Penetrating trauma
- Especially to the posterior triangle of the neck.
- Space-occupying lesions
- Tumours
- Aneurysms
- Abscesses
Other causes are rare.
Clinical Assessment
Trapezius
- Ask patient to shrug shoulders against downward pressure.
- Weakness indicates trapezius dysfunction.
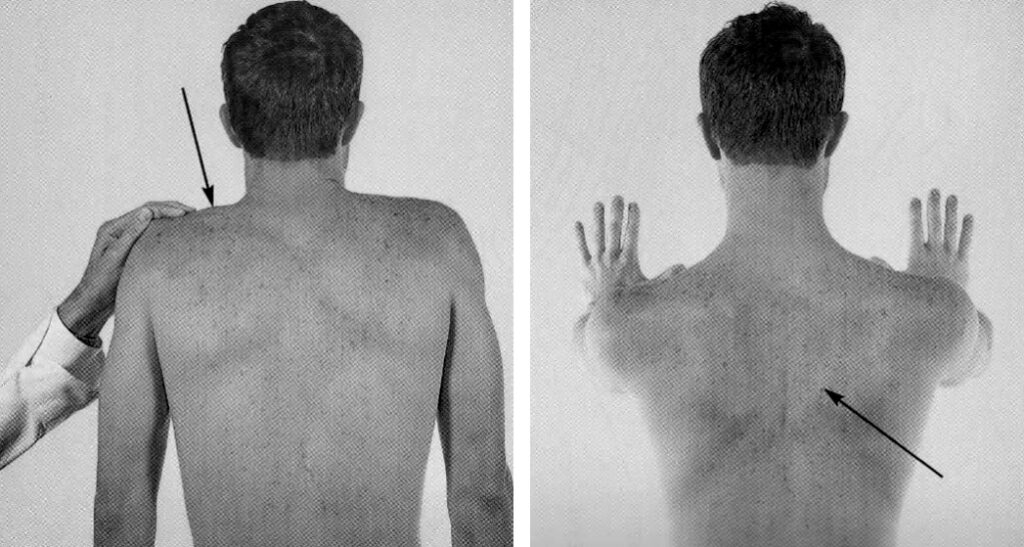
Right: The patient pushes the palms of the hands hard against a wall with the elbows fully extended. Arrow shows the lower fibers of trapezius.
Sternomastoid
- Ask patient to turn head against resistance applied to the mandible.
- Note: The right sternomastoid turns the head to the left.
Investigations
Blood Tests
- FBC
- CRP
- ESR
- U&Es / Glucose
Imaging
- CT / CT Angiogram: For mass lesion screening or suspected aneurysm.
- MRI: Most sensitive for detecting head and neck lesions.
Management
Management depends on the underlying cause of the lesion.
Appendix 1
Anatomy of the Eleventh cranial nerve
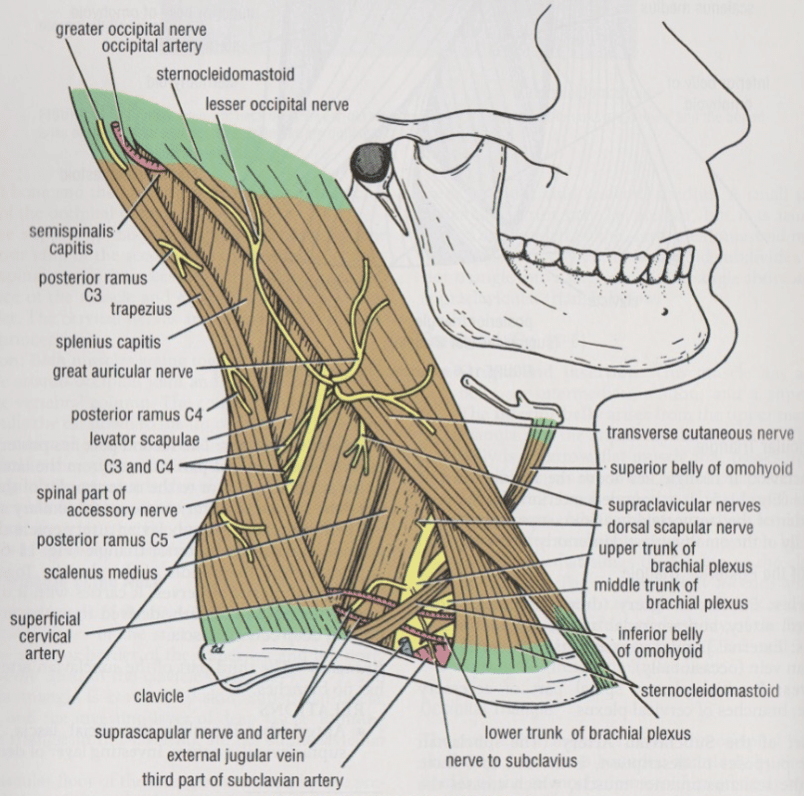
Appendix 2
References
Publications
- Brazis PW, Masdeu JC, Biller J. Localization in Clinical Neurology. 8e 2021
- Fuller G. Neurological Examination Made Easy. 6e 2019
- O’Brien M. Aids to the Examination of the Peripheral Nervous System. 6e 2023
FOAMed
- Coni R. Neuro 101: Cranial Nerves. LITFL
- Nickson C. The Brainstem Rules of Four. LITFL
- Ercleve T. The rule of 4 of the brainstem. LITFL
- Nickson C. Cranial nerve lesions DDx. LITFL
Fellowship Notes
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner
Educator, magister, munus exemplar, dicata in agro subitis medicina et discrimine cura | FFS |


