
William Macewen
Scottish surgeon Sir William Macewen (1848–1924) pioneered neurosurgery, bone grafting, and antiseptic technique, transforming modern surgical practice

Scottish surgeon Sir William Macewen (1848–1924) pioneered neurosurgery, bone grafting, and antiseptic technique, transforming modern surgical practice

Emergency Procedure, instruction and discussion: Serratus Anterior Plane (SAP) Block; a technique most often used for rib fracture pain
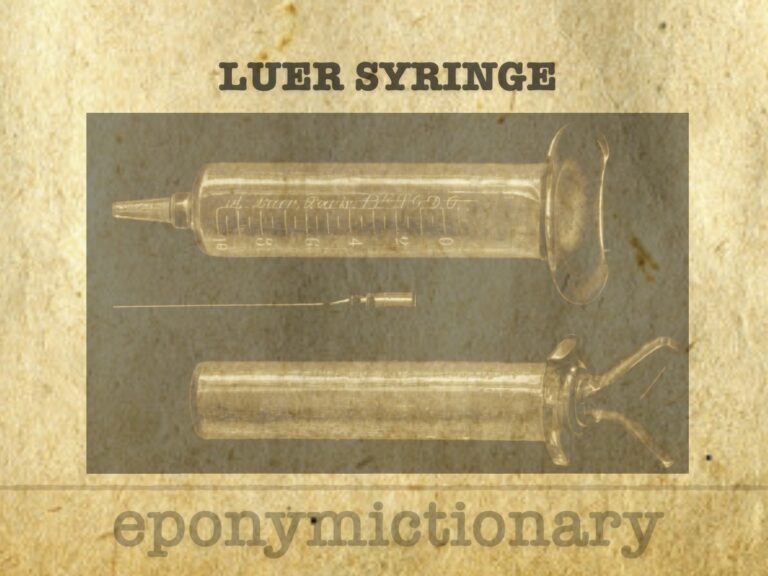
Lüer syringe (1894). Unique graduated all-glass hypodermic syringe. Invented by Jeanne Amélie Lüer; Patented by Wülfing-Lüer
Courvoisier’s sign: palpable gallbladder with painless jaundice suggests malignant obstruction, not gallstones. A key clinical diagnostic clue.
Kernohan-Woltman Notch Phenomenon (KWNP): false localising sign with mass effect and ipsilateral hemiparesis via contralateral peduncle compression.

James W. Kernohan (1896–1981), pioneer of glioma grading and the Kernohan notch, shaped modern neuropathology through diagnostic clarity and clinical insight.

Henry Woltman (1889–1964), Mayo Clinic neurologist, Kernohan-Woltman notch, stiff-man syndrome, and myxoedema reflex; leader in U.S. neurology

Woltman’s Sign is delayed reflex relaxation in hypothyroidism, often seen as a hung-up ankle jerk; a classic but non-specific clinical finding.

Léon Bouveret (1850-1929) was a French internal medicine physician. Eponymous terms Maladie de Bouveret (1889) and Bouveret Syndrome (1895)
history of gallstone ileus: from early autopsy reports to surgical breakthroughs, tracing its clinical evolution from Courvoisier to Clavien

Ludwig Georg Courvoisier (1843-1918) was a Swiss surgeon, academic, and naturalist best remembered for Courvoisier’s sign / law (1890)
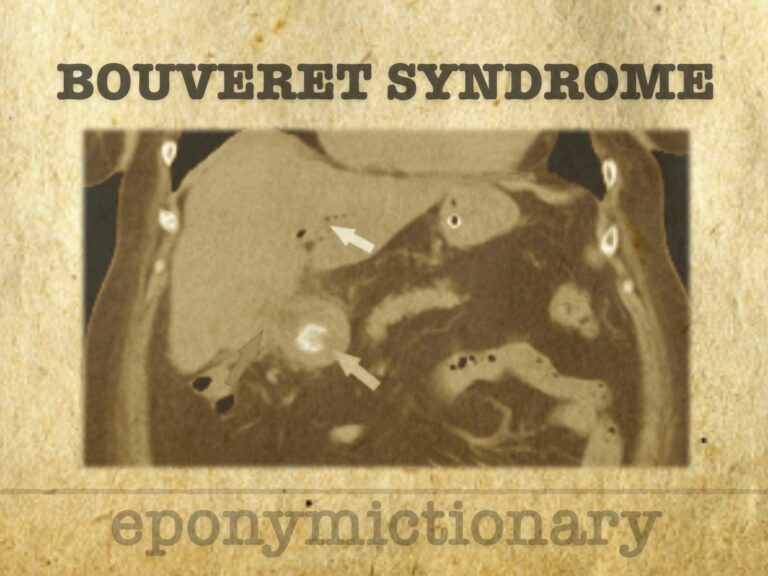
Bouveret syndrome: gastric outlet obstruction following passage of a gallstone from gallbladder to duodenum/pylorus via bilioenteric fistula