
Ladislas Meduna
Ladislas J. Meduna (1896–1964), pioneer of convulsive therapy, explored epilepsy-schizophrenia antagonism, CO₂ therapy, and oneirophrenia in psychiatry.

Ladislas J. Meduna (1896–1964), pioneer of convulsive therapy, explored epilepsy-schizophrenia antagonism, CO₂ therapy, and oneirophrenia in psychiatry.

Mary Broadfoot Walker (1888 - 1974) was a Scottish physician. Mary Walker effect (1934); neostigmine and myasthenia gravis
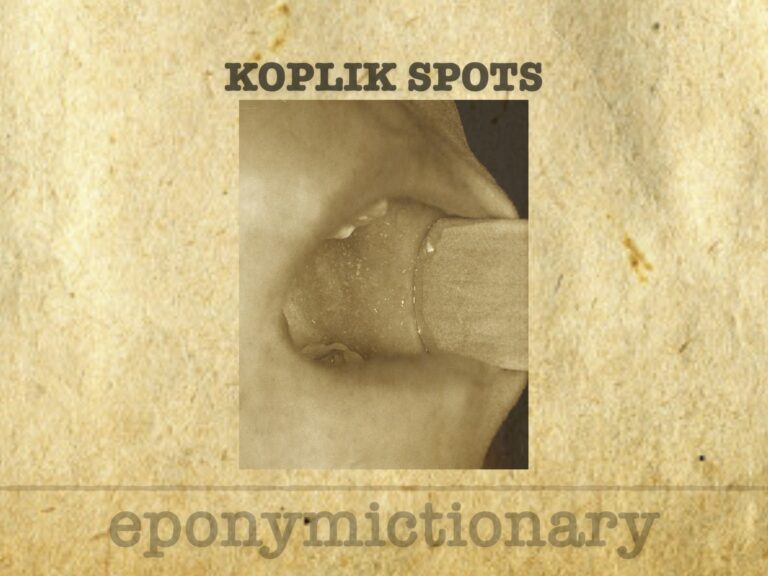
Koplik spots are pathognomonic buccal lesions in early measles, first described by Henry Koplik in 1896, aiding pre-rash diagnosis and outbreak control.

Henry Koplik (1858–1927), American pediatrician, discovered Koplik’s spots—an early diagnostic sign of measles—and pioneered infant health reform

Sir William Stokes (1839–1900), Irish surgeon and son of William Stokes, pioneered surgical techniques and served as RCSI professor and Queen Victoria’s surgeon

Jeremy Swan (1922–2005), Irish-born cardiologist, co-invented the Swan-Ganz catheter and led advances in cardiac catheterisation and haemodynamic monitoring

Frederick Forchheimer (1853–1913), U.S. paediatrician and educator, described Forchheimer spots and published landmark internal medicine textbooks

Nil Filatov (1847–1902), founder of Russian paediatrics, described key signs in measles, rubella, and mononucleosis; led Moscow’s first children’s hospital.

Louis Virgil Hamman (1877–1946), Johns Hopkins physician and diagnostician, described Hamman’s sign, Hamman syndrome, and Hamman-Rich syndrome

Raymond Garcin (1897–1971), French neurologist and Salpêtrière educator; described Garcin syndrome, “main creuse” sign, and led postwar French neurology.

Joseph Rouanet (1797–1865), French physician, first linked heart sounds to valve closure. His 1832 thesis laid foundations for modern cardiac auscultation.
Charles Edward Beevor (1854-1908) was an English neurologist. Beevor sign - indicating a spinal cord lesion between T10 and T12