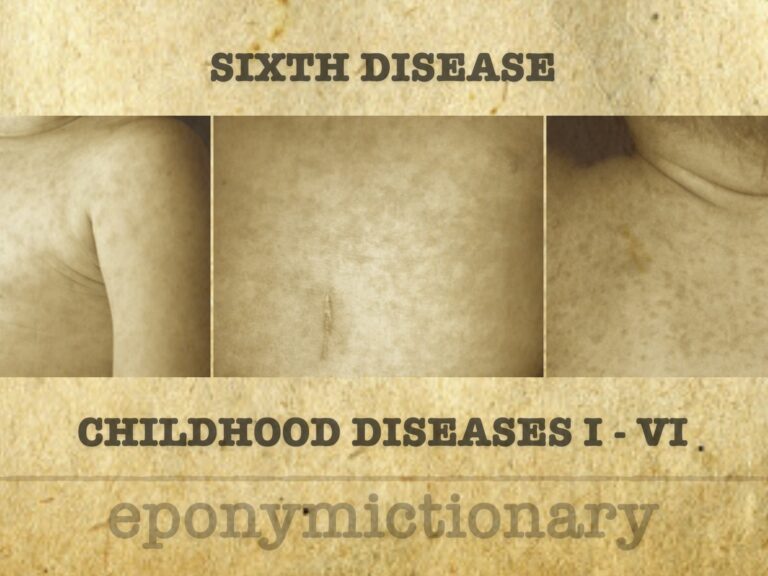
Sixth disease
Common viral illness in infants caused by HHV-6. Roseola presents with high fever followed by sudden rash; also known as sixth disease or exanthem subitum.

Common viral illness in infants caused by HHV-6. Roseola presents with high fever followed by sudden rash; also known as sixth disease or exanthem subitum.
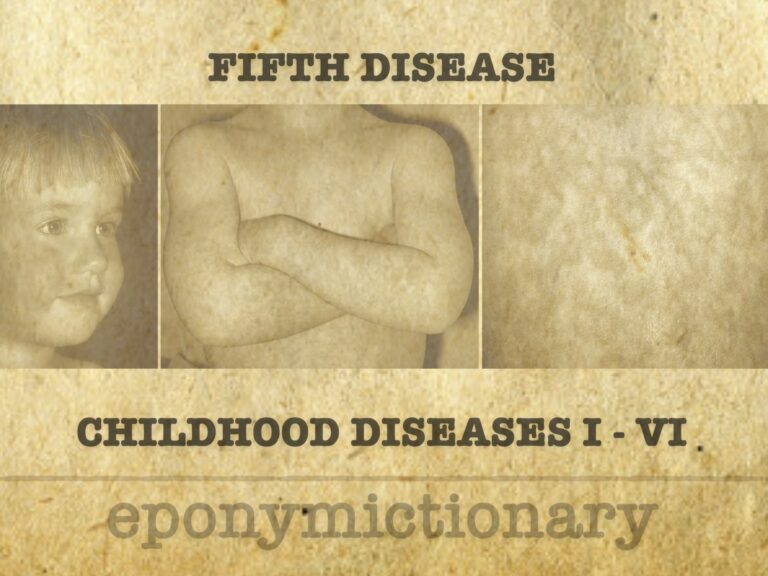
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease), is a common manifestation of infection in children characterized by low-grade fever, malaise, facial rash, and later by the spread of a lacy maculopapular rash involving the trunk and limbs.
Filatov-Dukes disease, or fourth disease, was a proposed childhood exanthem now largely dismissed as a misclassification of rubella or scarlet fever.
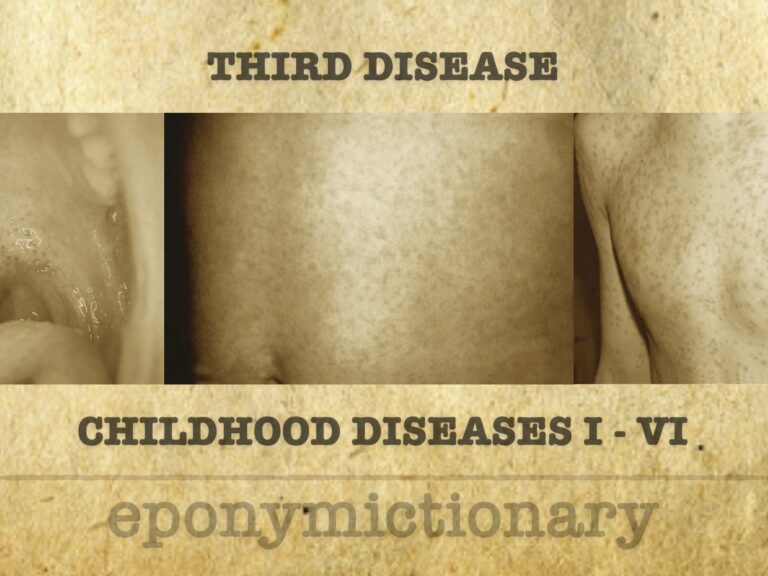
Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.
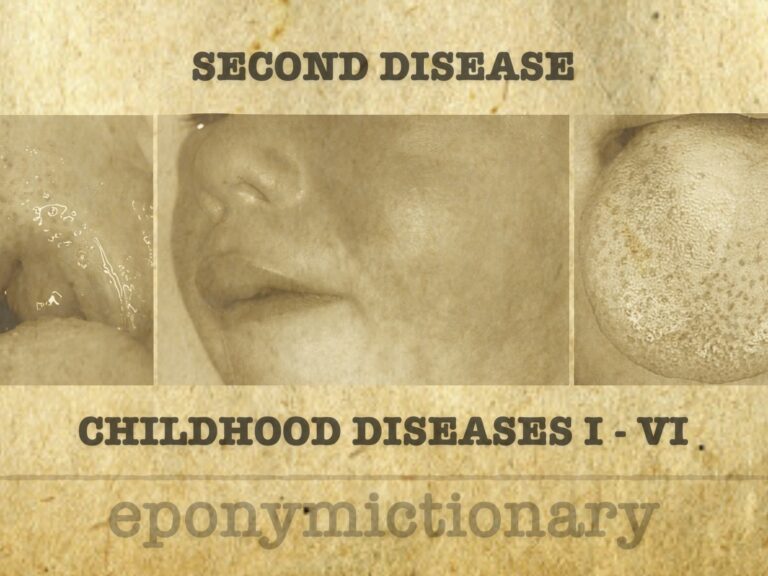
Scarlet fever (second disease). Contagious GABHS infection in kids under 10 with sore throat or rash; caused by S. pyogenes strains producing erythrogenic toxin.
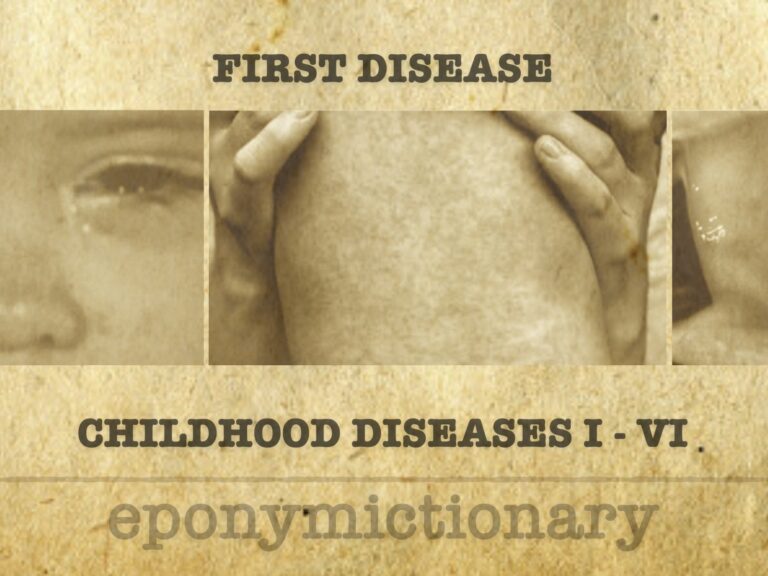
Measles (First Disease): classic childhood exanthem caused by Morbillivirus, with high infectivity, pathognomonic signs, and vaccine-preventable

Yvonne Edna Cossart (1934-2014) was an Australian virologist. In 1975, Cossart and her colleagues recognised parvovirus B19

Henry Koplik (1858–1927), American pediatrician, discovered Koplik’s spots—an early diagnostic sign of measles—and pioneered infant health reform
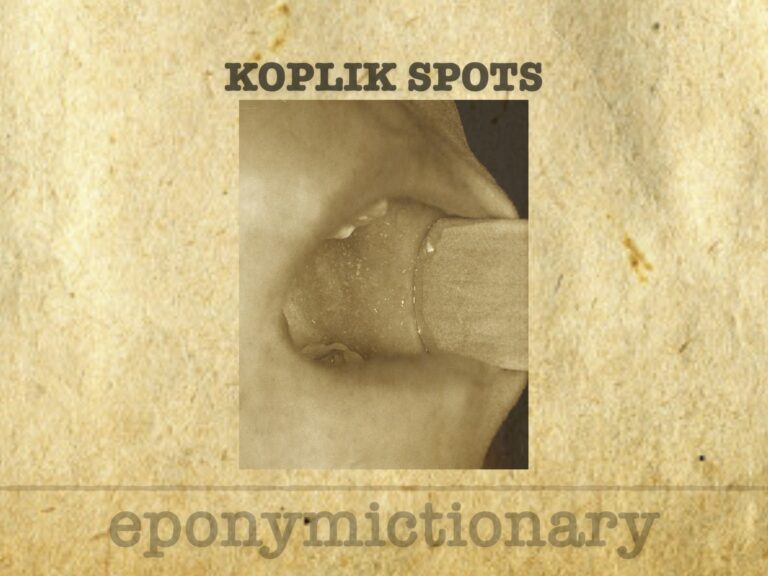
Koplik spots are pathognomonic buccal lesions in early measles, first described by Henry Koplik in 1896, aiding pre-rash diagnosis and outbreak control.

Nil Filatov (1847–1902), founder of Russian paediatrics, described key signs in measles, rubella, and mononucleosis; led Moscow’s first children’s hospital.

Melioidosis is a severe infectious disease caused by the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei. It is widespread in Southeast Asia and Northern Australia, with increasing recognition in other tropical and subtropical regions. It presents with a wide range of clinical manifestations, from localized infections to severe sepsis and septic shock.

CCC entry for fusariosis / Fusarium infections (infectious disease)