
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis: autoimmune disruption of post-synaptic acetylcholine receptors at NMJ; up to 80% of functional receptors loss; typically young woman; may have thymus hyperplasia; prevalence = 14.2 cases per 100,000

Myasthenia Gravis: autoimmune disruption of post-synaptic acetylcholine receptors at NMJ; up to 80% of functional receptors loss; typically young woman; may have thymus hyperplasia; prevalence = 14.2 cases per 100,000

Myopathy versus Neuropathy

Neurology Literature Summaries

Non-Convulsive Status Epilepticus (NCSE) is a persistent change in the level of consciousness, behaviour, autonomic function, and sensorium from baseline associated with continuous epileptiform EEG changes, but without major motor signs

Critical illness is associated with a spectrum of neurological failure (largely under-reported), including polyneuropathy, encephalopathy and long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness (LTCI-CI)

Septic encephalopathy is brain dysfunction mediated by the septic inflammatory response, independent of other co-existent causes such as liver or renal dysfunction

Encephalitis an acute encephalopathy due to an inflammatory cause
Underlying causes are numerous and may be infectious or non-infectious, many of which lack effective therapies

Stroke Thrombolysis: thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke is a controversial intervention; it is supported by a number of guidelines and in general is viewed favourably by the neurological community

Tenecteplase is a tissue plasminogen activator used as a thrombolytic medication in: Acute Ischaemic Strokes, Acute Myocardial Infarction, PE
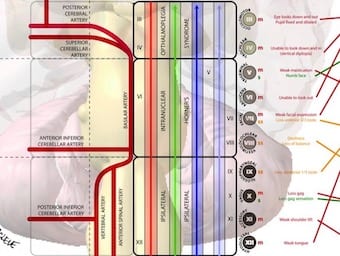
A ferocious spider lives in the brain. His name is Willis!

Sidney Weinstein (1922 - 2010) was and American neuroscientist and neuropsychologist. Semmes-Weinstein monofilament test and the Weinstein Enhanced Sensory Test

Douglas Moray Cooper Lamb Argyll Robertson (1837–1909) was a Scottish surgeon and ophthalmologist. Eponym: Argyll Robertson pupils