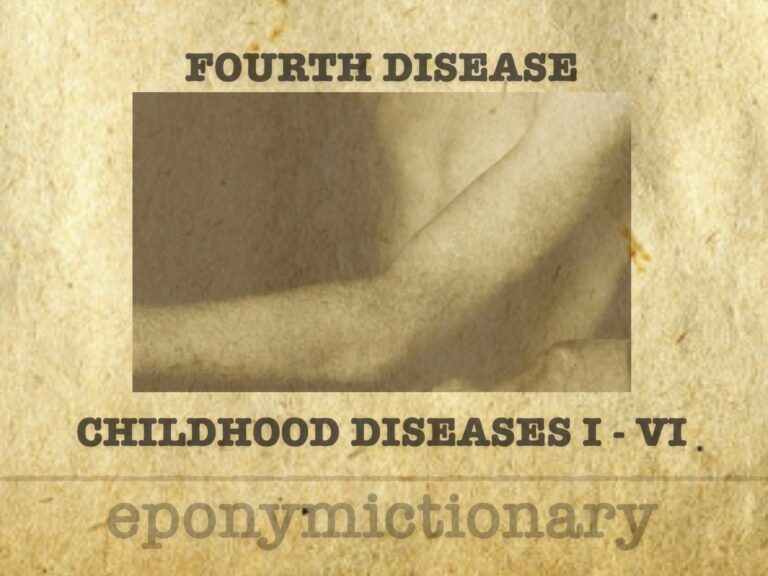
Fourth disease
Filatov-Dukes disease, or fourth disease, was a proposed childhood exanthem now largely dismissed as a misclassification of rubella or scarlet fever.

Filatov-Dukes disease, or fourth disease, was a proposed childhood exanthem now largely dismissed as a misclassification of rubella or scarlet fever.
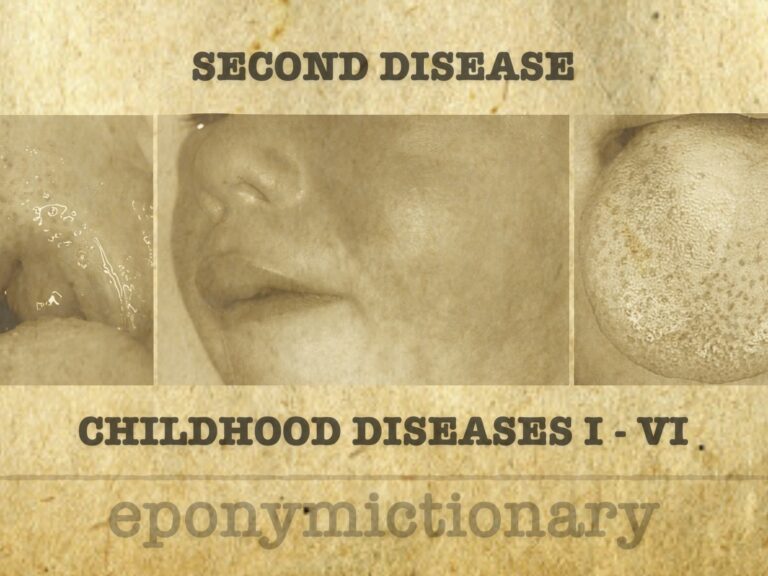
Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.
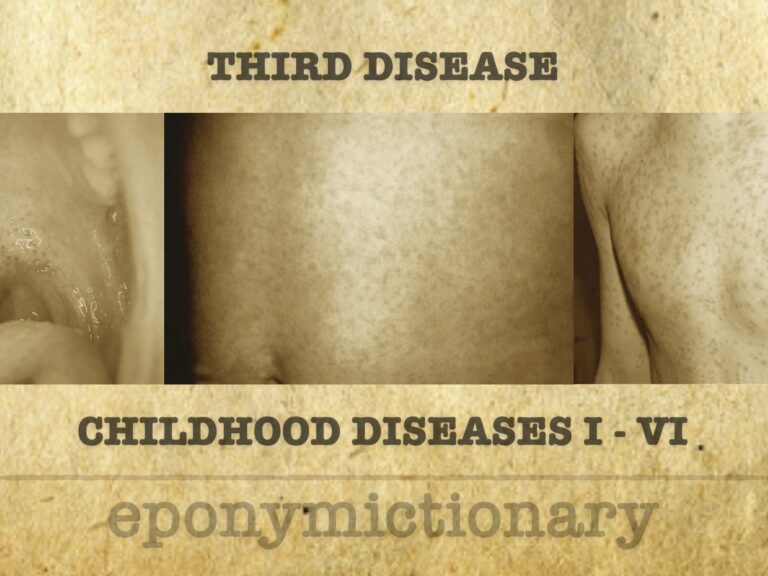
Scarlet fever (second disease). Contagious GABHS infection in kids under 10 with sore throat or rash; caused by S. pyogenes strains producing erythrogenic toxin.
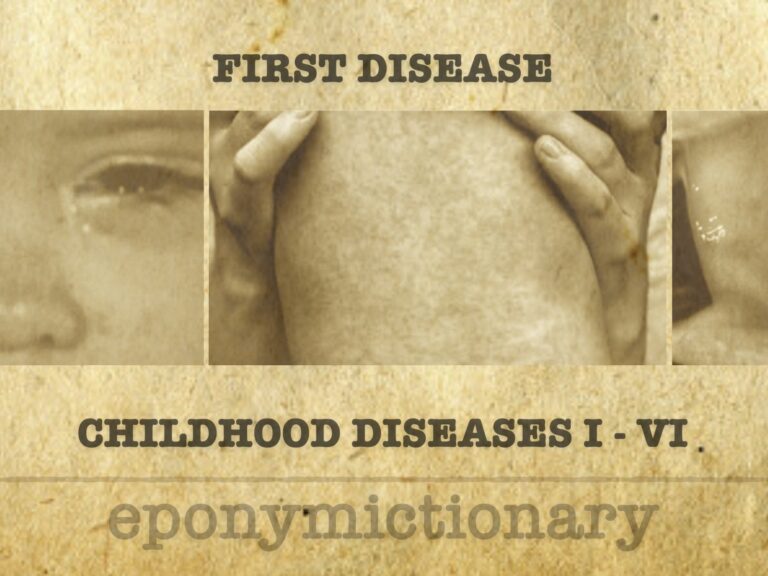
Measles (First Disease): classic childhood exanthem caused by Morbillivirus, with high infectivity, pathognomonic signs, and vaccine-preventable
Clement Dukes (1845–1925), English physician and school health reformer, proposed "Dukes' disease" and transformed adolescent medical care in public schools.
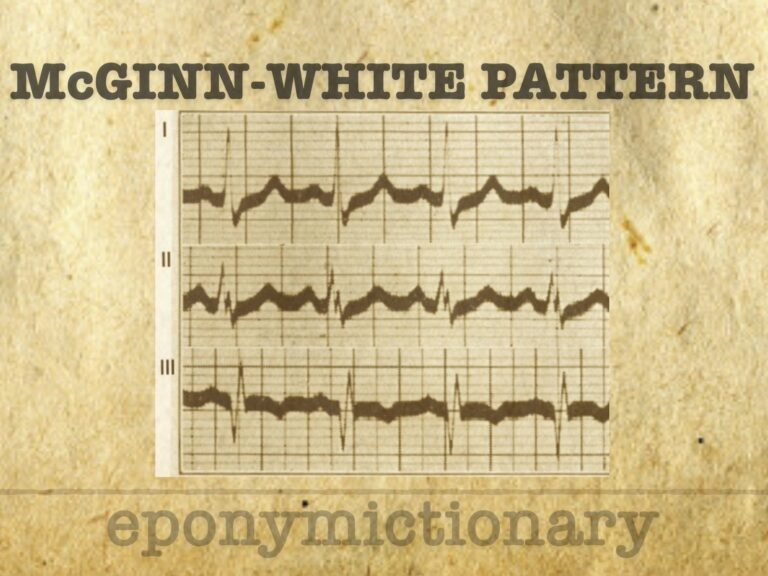
S1Q3T3 McGinn-White pattern indicates right heart strain and predicts severe PE outcomes. ECG sign of pulmonary embolism described in 1935.

Yvonne Edna Cossart (1934-2014) was an Australian virologist. In 1975, Cossart and her colleagues recognised parvovirus B19

James Ramsay Hunt (1874-1937) American neurologist. Renowned for his contributions to the field of neurology. Several conditions bear his name including Ramsay Hunt syndrome (1907)
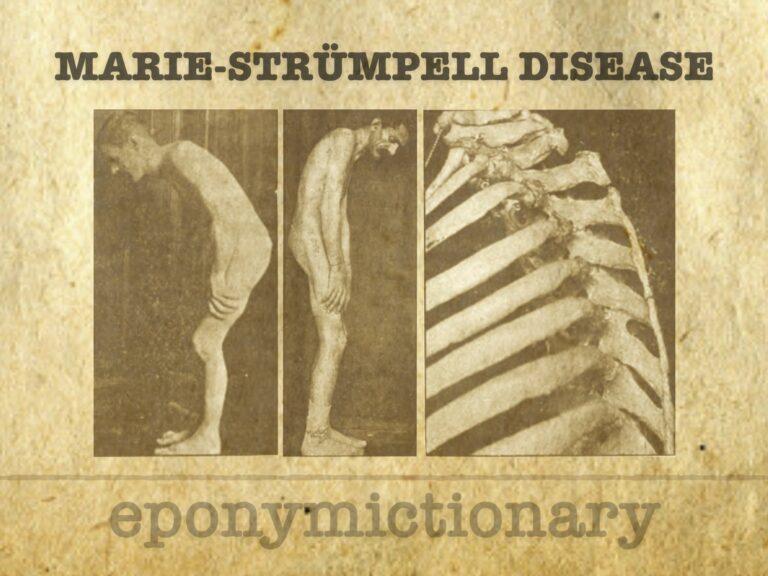
Marie-Strümpell disease (ankylosing spondylitis): a chronic inflammatory spinal arthritis with progressive axial fusion, first described by Pierre Marie and Adolf Strümpell in the late 19th century.

Sylvester McGinn (1904–1984); American cardiologist; McGinn-White sign (S1Q3T3) in pulmonary embolism; pioneer in Boston cardiac care and research.

Understand and identify prosthetic valves. Learn what can go wrong with prosthetic valves; how to assess their function and examine transcatheter valves

Mary Broadfoot Walker (1888 - 1974) was a Scottish physician. Mary Walker effect (1934); neostigmine and myasthenia gravis