Charles Hallpike

Charles Skinner Hallpike (1900-1979) was an English otologist.
Charles Skinner Hallpike was a pioneering British neuro-otologist who significantly advanced the understanding of inner ear disorders. Born in London on July 19, 1900, Hallpike was educated at Blundell’s School and studied medicine at University College London and University College Hospital Medical School, qualifying in 1926. He trained in pathology before turning to neurology and otology, developing a lifelong interest in the auditory and vestibular systems.
Hallpike held appointments at the National Hospital for Nervous Diseases (Queen Square), the Royal Ear Hospital, and the Institute of Laryngology and Otology. In collaboration with Hugh Cairns (1896–1952), he established novel experimental methods for investigating the inner ear, including the use of temporal bone histopathology. Their work laid the foundation for modern vestibular physiology.
In 1952, Hallpike and Margaret Dix published their seminal paper describing the Dix–Hallpike manoeuvre for diagnosing benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). He also contributed to the identification of Menière’s disease pathology and served as a founding figure in the field of neuro-otology.
He was elected Fellow of the Royal Society in 1964 and held numerous prestigious lectureships and editorial positions. Hallpike retired from clinical practice in 1965 but continued research and writing until his death on September 26, 1979.
Biography
- 1900 – Born July 19, in Murree, India
- 1924 – MRCS, MRCP
- 1926 – MB BS from University College Hospital Medical School
- 1929 – Bernhard Baron research fellow, Ferens Institute of Otology, Middlesex Hospital
- 1930s – Research with Hugh Cairns on vestibular system pathology
- 1931 – FRCS
- 1936 – Began role at Royal Ear Hospital
- 1938 – Developed international reputation following his original description of the pathology of Menière’s disease
- 1938-1965 he was a member of the Flying Personnel Research Committee and his knowledge of ear function in health and disease contributed much to the solution of aural problems in aviation
- 1942 – Hallpike and Fitzgerald developed bithermal caloric test
- 1944 – Aural physician and director of the Medical Research Council’s Otology Research Unit at the National Hospital, London
- 1947 – Hallpike and Dix, developed Peep-Show technique
- 1952 – Co-authored paper with Margaret Dix describing the Dix–Hallpike manoeuvre
- 1955 – Shambaugh Prize, Collegium Oto-Rhino-Laryngologicum Amicitiae Sacrum: CORLAS
- 1956 – Fellow of the Royal Society. FRS
- 1964 – Elected Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS)
- 1965 – Retired from clinical practice
- 1979 – Died September 26
Medical Eponyms
Dix-Hallpike Test (1952)
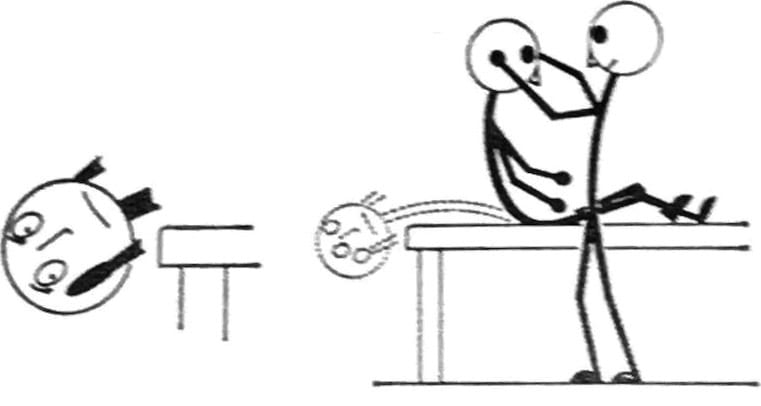
First described in 1952 by Margaret Dix (1902-1991) and Hallpike, this positional test is used to diagnose benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). The manoeuvre provokes nystagmus and vertigo by rapidly positioning the patient’s head to stimulate otolithic debris within the semicircular canals. It remains a fundamental diagnostic tool in vestibular assessment.
They described a clinical bedside manoeuvre in detail, “Lagerungs Manoeuvre”, known now as the Dix-Hallpike test, to provide an immediate diagnosis of BPPV
Key Medical Contributions
Peep-Show technique for pure tone audiometry (1947)
Diagnosing deafness in children under the age of six is challenging because pure tone audiometry sounds are meaningless to young children and require explanation beyond their understanding.
Dix and Hallpike aimed to solve this problem by designing an apparatus called the “Peep-Show”, to enable young children to reliably respond to sounds. The apparatus consisted of a lamp and loudspeaker, and a box containing hidden pictures.
The tester shows the child that when the lamp and loudspeaker activate, the child can make the pictures appear by pressing a switch. After the child does this several times, the lamp is removed, and now only the loudspeaker activates.
- A child who can hear the sound, will still press the switch when the sound occurs, to reveal the picture. A child who cannot hear the sound, will not.
The test allowed deafness to be identified and quantified in young children, enabling special education to commence at an early age.
Histopathology of Menière’s Disease Hallpike, alongside Cairns, provided histological evidence of endolymphatic hydrops in temporal bone studies of patients with Menière’s disease. Their 1938 paper was among the first to correlate pathological findings with the classic triad of vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus
Major Publications
- Hallpike CS, Cairns H. Observations on the pathology of Menière’s syndrome. Proc R Soc Med. 1938; 31(11): 1317–1336
- Dix MR, Hallpike CS. The peep-show: a new technique for pure-tone audiometry in young children. Br Med J. 1947; 2(4531): 719-23.
- Dix MR, Hallpike CS. The pathology symptomatology and diagnosis of certain common disorders of the vestibular system. Proc R Soc Med. 1952; 45(6): 341-54
- Dix MR, Hallpike CS. The pathology, symptomatology and diagnosis of certain common disorders of the vestibular system. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1952; 61(4): 987-1016.
- Hallpike CS. Ménière’s disease. Postgrad Med J. 1955; 31(357): 330-40
- Hallpike CS. The caloric tests. J Laryngol Otol. 1956; 70(1): 15-28.
- Cawthorne T, Dix MR, Hallpike CS, Hood JD The investigation of vestibular function. Br Med Bull. 1956;12(2):131-142.
- Hallpike CS. On the case for repeal of Ewald’s second Law. Some introductory remarks. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1961; 159: 7-14.
References
Biography
- Whitteridge D, Merton PA. Charles Skinner Hallpike. Biogr. Mems Fell. R. Soc. 1984; 30: 282-295
- Obituary. Charles Skinner Hallpike. Lancet. 1979 Oct 13;2(8146):805.
- Angell-James J. In memoriam Charles Skinner Hallpike. J Laryngol Otol. 1980;94(8):801-844.
Eponymous terms
- Baloh RW. Charles Skinner Hallpike and the beginnings of neurotology. Neurology. 2000 Jun 13;54(11):2138-46.
- Baloh RW. Vertigo: Five Physician Scientists and the Quest for a Cure. Oxford University Press. 2016: 121-200
Eponym
the person behind the name
Studied at Univerisity of Cambridge - BA MB BChir. British doctor working in emergency medicine in Perth, Australia. Special interests include primary care and emergency medicine.

