Hawkins classification
Description
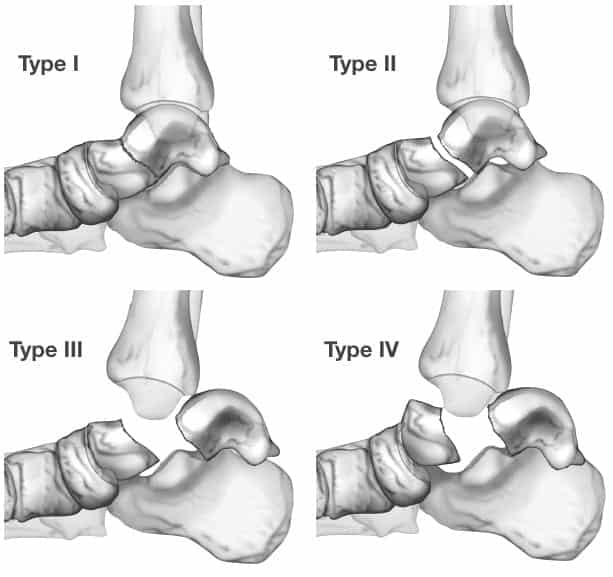
Hawkins classification: Classification system for talar neck fractures.
Classification system for vertical neck fractures of the talus, the commonest type of talus fracture. High energy injury usually associated with forced dorsiflexion and axial load. Associated with risk of avascular necrosis (AVN)
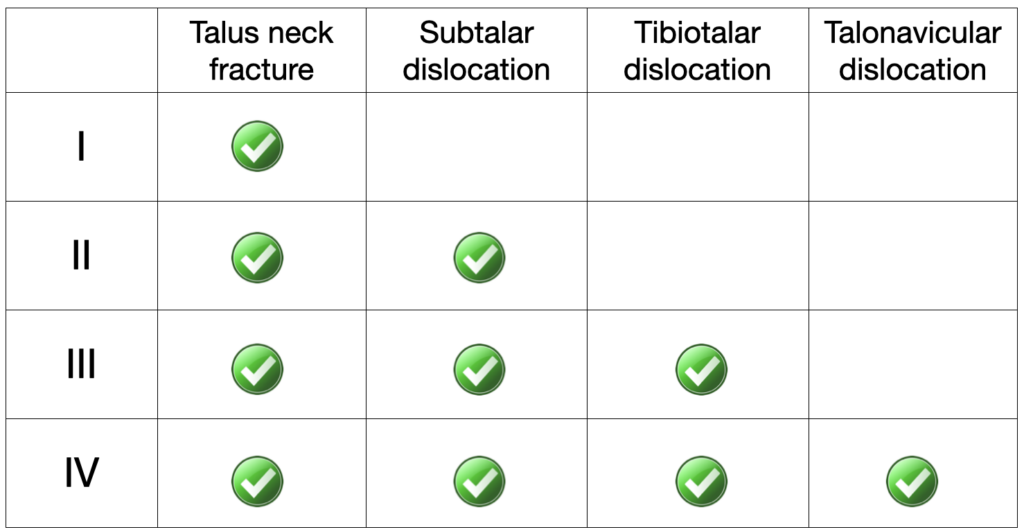
- Hawkins Type I: Nondisplaced talar neck fracture
- Hawkins Type II: Talar neck fracture with subtalar dislocation
- Hawkins Type III: Talar neck fracture with subtalar and tibiotalar dislocation
- Hawkins Type IV: Talar neck fracture with subtalar and tibiotalar and talonavicular dislocation
Leland G Hawkins (1933-1991) originally described Types I-III in 1970 with Canale and Kelly adding Type IV in 1978
History of talus fracture classification
1608 – Wilhelm Fabry first description of talus fracture in a report quoted as De admiranda pedis fractura.
…the Rev. Master Woolfbrand of Duisburg, a man strong and fleshy, in jumping from a bank three feet high so twisted and broke his right foot that the whole of the os tali was not only displaced but the ligaments by which it is bound to the other bones, being broken, it burst through the skin and hung out.
Fabricii G. De admiranda pedis fractura, Centuria II; Observatio LXVII 1682: 140
1818 – Astley Cooper wrote at length on fractures and dislocations of the astragalus (talus) in his treatise on dislocations and on fractures of the joints (1824)
1919 – Anderson HG was consulting surgeon to the Royal Flying Corps in the war of 1914-1918. He described eighteen cases of fracture and dislocation of the talus. He noted the association of injuries of the talus with the aircraft crash and named them collectively ‘Aviator’s Astragalus.’
…falls from a height on to the foot are common in civilian occupations but the calcaneum [os calcis] is usually broken, On the other hand, the aviator usually falls with his machine and strikes the ground at an angle. The sole of the foot rests on the rudder bar and with the impact the latter gets pressed into the instep just in front of the heel. There the astragalus takes most of the force and becomes the seat of fracture. Before the actual fracture occurs, the foot may be in a position of acute dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, or may be inverted.
Anderson 1919
1939 – Various attempts made to create a classification system such as Miller and Baker in the Southern Medical Journal
1952 – Coltart reported on 228 talus injuries treated by surgeons in the British Royal Air Force in an attempt to describe the variety of injuries that occur to the talus and surrounding joints. He described various talus fracture patterns, fracture-dislocation combinations, and isolated peritalar dislocations
1970 – Leland G Hawkins described injury patterns and avascular necrosis (AVN) rates in a series of 57 neck fractures of the talus in 55 patients from three different institutions. All 55 patients sustained forced dorsiflexion injuries, similar to the mechanism described as Aviator’s Astragalus by Anderson in 1919. Originally classified into three types (Types I-III)
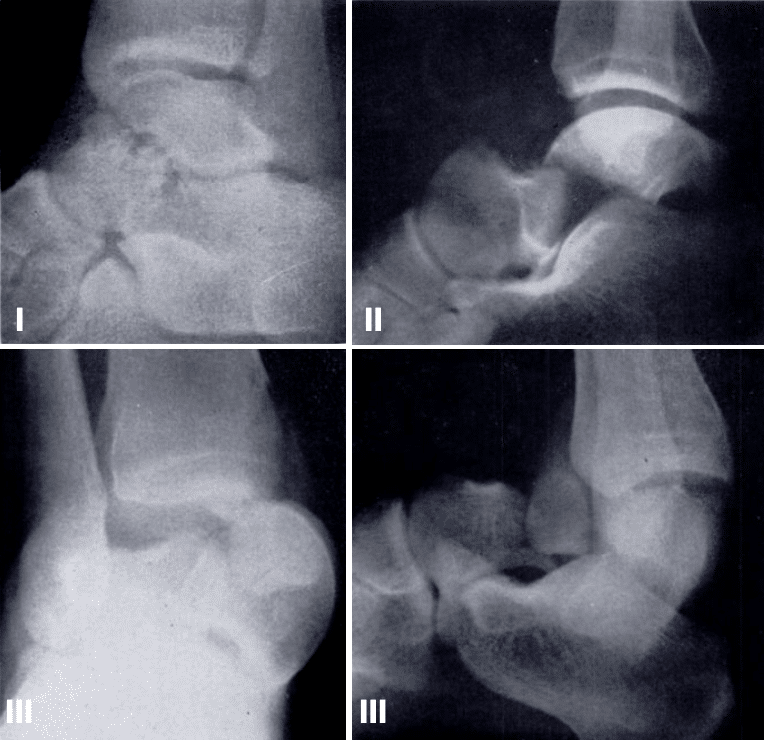
Group I: Non-displaced fracture of the neck of the talus in a 22 year-old involved in a motor-cycle accident. Note that the fracture line extends into the body of the talus. Group II: Fracture-dislocation of the neck of the talus; 33 year-old pilot who survived the crash of a small plane. Note the posterior dislocation of the body of the talus on the calcaneus.
Group III: Fracture-dislocation of the neck of the talus; 16 year-old involved in a motor-cycle accident. Note the vertical fracture of the medial malleolus and medial dislocation of the body which is wedged between the tibia amid calcaneus. Hawkins 1970
1978 – Canale and Kelly presented a series of 71 fractures with an average 13-year followup (range, 2.5–32 years) and an AVN rate of 52%. They added Type IV to Hawkins original classification. Fracture of the talar neck with dislocation of the body from the ankle or subtalar joint and additional dislocation / subluxation of the head of the talus from the talonavicular joint
Associated Persons
- Wilhelm Fabry (1560-1634)
- Sir Astley Paston Cooper (1768 – 1841)
- Leland G Hawkins (1933-1991)
Alternative names
- Aviator’s astragalus
- Astragalus fractures
References
Original articles
- Fabricii G. De admiranda pedis fractura, Centuria II; Observatio LXVII 1682: 140
- Cooper AP. Simple and Compound dislocations of the astragalus. In: A treatise on dislocations and on fractures of the joints. London. 1824: 334-354
- Anderson HG, Flack MW, Gotch OH. The Medical and Surgical Aspects of Aviation 1919:178-196
- Miller OL, Baker LD. Fracture and fracture-dislocation of the astragalus. Southern Medical Journal. 1939; 32(2):125–136.
- Coltart WD. Aviator’s astragalus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1952;34:545–566
- Canale ST, Kelly FB Jr. Fractures of the neck of the talus. Long-term evaluation of seventy-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60(2): 143-56.
Review articles
- Alton T, Patton DJ, Gee AO. Classifications in Brief: The Hawkins Classification for Talus Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473(9): 3046-9
- Day MA, Compton JT, Buckwalter JA 5th. Leland G. Hawkins, MD – His Life and Orthopaedic Legacy: Talus Fractures and the Hawkins Classification. Iowa Orthop J. 2018;38:1-8.
- McKennedy C. Hawkins classification – Eponym A Day. Instagram
- Eponymythology: Eponymous ankle and talus injuries. LITFL
[cite]
eponymictionary
the names behind the name