John Call Dalton Jr
John Call Dalton Jr (1825 – 1889) was an American physiologist.
First full-time professor of physiology in the United States, and ‘possibly’ America’s first experimental neurophysiologist. Dalton introduced the experimental method of teaching physiology by demonstration of animals that had ablative lesions operated under ether anaesthesia.
He defended the humane use of animals as the ‘sole means of learning’ about the ‘vital function of life while life was going on’, anda that ‘all his seemingly cruel experiments could be carried out under the beneficent influence of anesthesia’
…these sciences have to do with the phenomena of life; and there is no way of learning what the vital phenomena are, except by examining them while life is going on. Experiments upon the living body are, for the physiologist, what experiments in chemistry are for the chemist
Experimentation on Animals (1875)
Dalton was an erudite medical educator and in 1878 his complete series of physiology lectures was published verbatim in the Boston Medical and Surgical Journal (now the NEJM)
Biography
- Born 2 February 1825 in Chelmsford, Massachusetts
- 1840 – 1844 Graduated A.B. Harvard College
- 1844 – 1847 Graduated MD, Harvard University
- 1847 – 1850 – Studied in Europe with Claude Bernard (1813 – 1878)
- 1851 – American Medical Association Prize essay for “On the Corpus Luteum” attracting the attention of Austin Flint (1812 – 1886) and Frank Hamilton (1813 – 1886) of the University of Buffalo
- 1851 – Professor of Physiology and Medical Jurisprudence, University of Buffalo. Dalton secured funds for equipment and animals to provide demonstration lectures to students of physiology
- 1855 – Professor of Physiology, College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York City
- Dean of the College of Physicians and Surgeons
- 1884 – President of the College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York
- 1885 – $500,000 donation of land and money from William H. Vanderbilt to build laboratories for instruction in physiology, pathology, and chemistry
- Died 12 February 1899
Key Medical Contributions
In 1854 Dalton devised a method to directly observe the larynx of dogs during inspiration. He proved widening of the glottis was due to contraction of the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles; and by cutting the inferior laryngeal nerve he substantiated their innervation. Transection of both pneumogastric (vagus) nerves led to laboured breathing and death secondary to pulmonary oedema [On the movements of the glottis in respiration]
The Cerebellum
In 1859 (published 1861) Dalton confirmed the 1824 observations of Jean-Pierre-Marie Flourens (1794 – 1867), that partial destruction of the cerebellum in pigeons caused acute ataxia without weakness.
When the injury has been moderate in extent, so that the pigeon can still stand and walk, though imperfectly, there is often a very close and ludicrous resemblance to the effects of intoxication — the movements being still quite natural in force and rapidity, but their harmony and certainty being lost.
Dalton 1861: 84
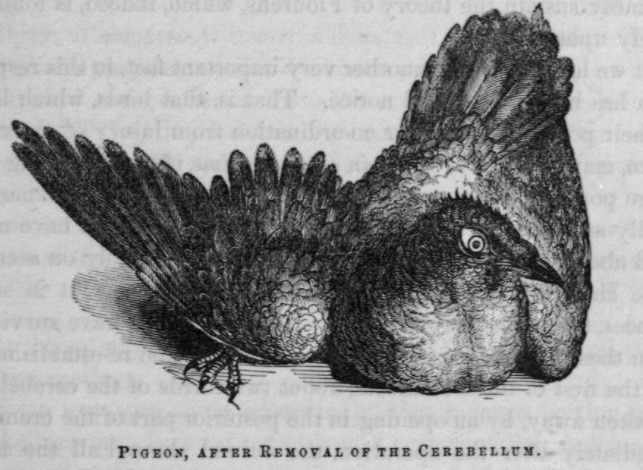
Cerebellar ablation was performed under ether anaesthesia to control bleeding and prevent pain to the pigeons. By increasing the size of the cerebellar lesions Dalton observed progressive degrees of incoordination in his pigeons. The pigeons recovered coordination, could eat unassisted, push away rival pigeons from their food, and fly at around 16 days following surgery. At this point, the pigeons with sacrificed, and the brains dissected. Dalton saw no regrowth of the remaining cerebellum to account for the recovery of function. Dalton concluded:
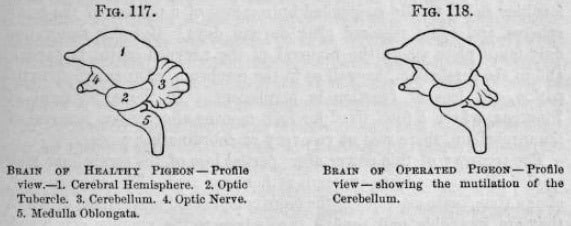
…the permanent loss of a portion of the cerebellum does not permanently impair the power of muscular co-ordination. If, therefore, we are still to believe that the power of co-ordination resides in the cerebellum as a nervous centre, we must admit that, after the removal of a part of this ganglion, the remaining portions gradually become enabled to supply its place.
Dalton 1861: 88
Major Publications
- Dalton JC Jr. On the Corpus Luteum of Menstruation and Pregnancy. 1851 [AMA Prize essay]
- Dalton JC Jr. On the movements of the glottis in respiration. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1854; 28: 75–79.
- Dalton JC Jr. Introductory address delivered at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York. 1855
- Dalton JC Jr. Anatomy of the placenta. 1858
- Dalton JC Jr. A treatise on human physiology. 1859
- Dalton JC Jr. On the cerebellum as the centre of co-ordination of the voluntary movements. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1861; 61: 83–88.
- Dalton JC Jr. A Treatise on Physiology and Hygiene: For Schools, Families, and Colleges. 1868
- Dalton JC Jr. Spontaneous generation. 1872
- Dalton JC Jr. Galen and Paracelsus. 1873
- Dalton JC Jr, Arnold JWS, Flint A, Beard GM, Mason JJ. Motor centres in the cerebral convolutions: their existence and localization. 1874
- Dalton JC Jr. The origin and propagation of disease. 1874
- Dalton JC Jr. Experimentation on Animals as a Means of Knowledge in Physiology, Pathology and practical medicine. 1875
- Dalton JC Jr. On the form and topographical relations of the corpus striatum. Brain 1880; 3(1): 145–159.
- Dalton JC Jr. The experimental method in medical science. 1882
- Dalton JC Jr. Doctrines of the circulation; a history of physiological opinion and discovery, in regard to the circulation of the blood. 1884
- Dalton JC Jr. Topographical anatomy of the brain. 1885
- Dalton JC Jr. History of the College of Physicians and Surgeons in the City of New York. 1888
Physiology lecture series
Delivered at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York as recorded by P. Brynberg Porter MD
- Porter PB. Lectures on the physiology of the spinal cord. Part I. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal 1878; 68: 355–360.
- Porter PB. Lectures on the physiology of the spinal cord. Part II. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal 1878; 68: 428–435.
- Porter PB. Lectures on the physiology of the spinal cord. Part III. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal 1878; 68: 459–465.
- Porter PB. Lectures on the physiology of the spinal cord. Part IV. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal 1878; 68: 487-494
References
- Bibliography. Dalton, John Call 1825-1889. WorldCat Identities
- Obituary. John C. Dalton MD. The Medical Record 1889; 35: 186–187.
- Peters JC. Dr. Dalton and the New York Pathological Society. The Medical Record 1889; 35: 262–263.
- John Call Dalton, M.D., U.S.V. 1892
- John C. Dalton, Jr. (1825-1899) experimental physiologist. JAMA. 1968; 203(3): 221-222.
- Fine EJ, Manteghi T, Sobel SH, Lohr LA. John Call Dalton, Jr., MD: America’s first neurophysiologist. Neurology. 2000; 55(6): 859-864.
- John Call Dalton Jr. In: History of Science in United States: An Encyclopedia 2001
- Fine EJ, Ionita CC, Lohr L. The History of the Development of the Cerebellar Examination. Seminars in Neurology 2002; 22(4): 375-384

