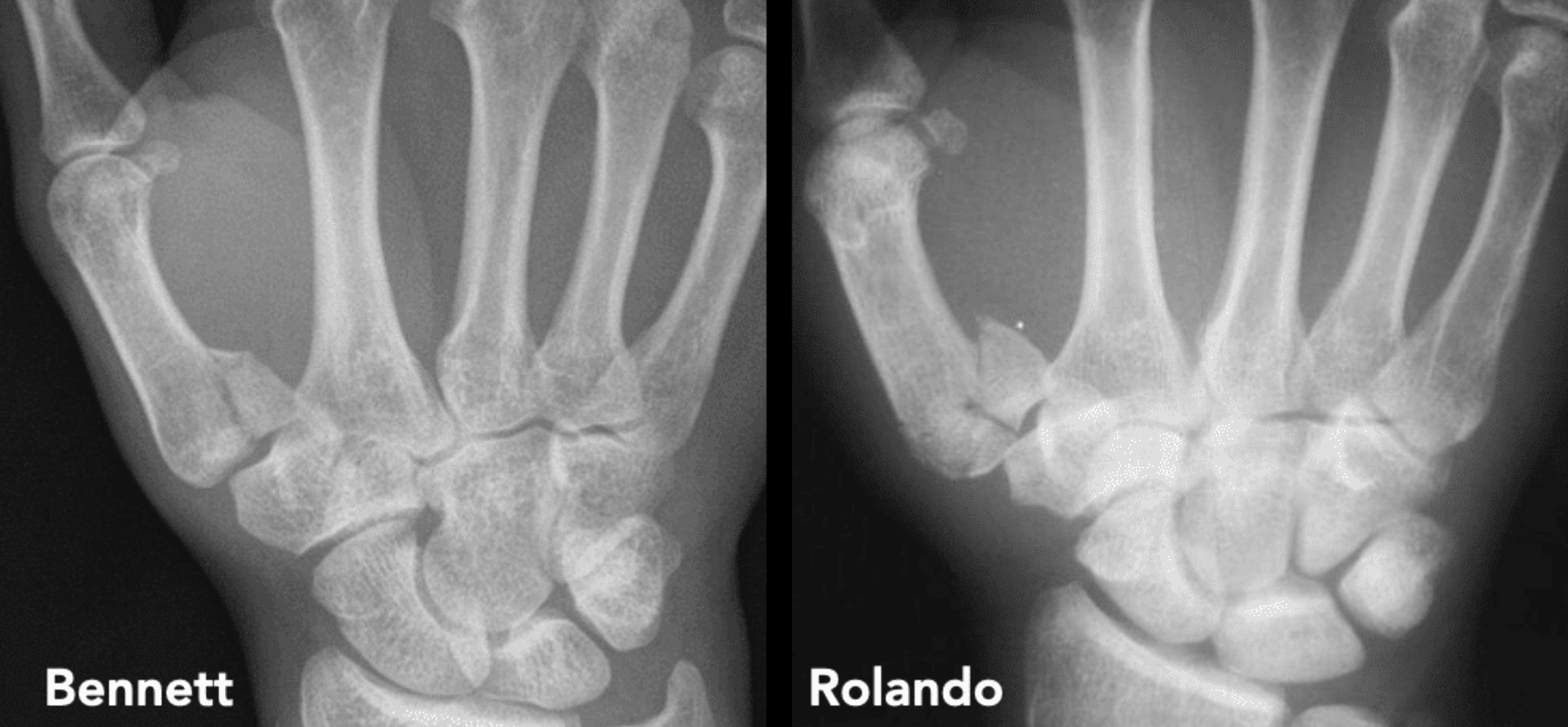
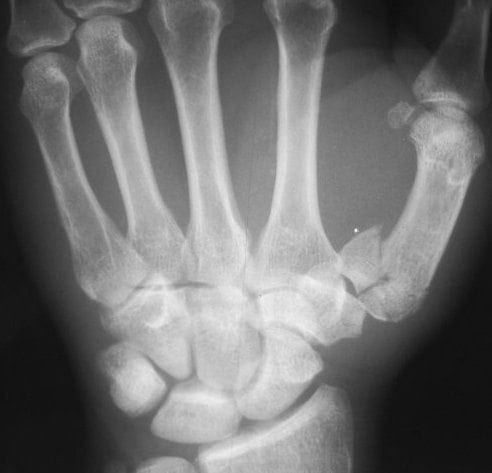
Rolando fracture
Rolando fracture: Comminuted T- or Y-shaped intra-articular three-part fracture through the base of the first metacarpal (thumb) first described in 1910 by Silvio Rolando (1873-1949).
Since Rolando’s original report of the Y pattern intra-articular fracture, the eponymous fracture has now come to include all multi-fragmentary intra-articular base of thumb metacarpal fractures.
Now more commonly referred to as an ‘intra-articular thumb metacarpal base fracture with three or more segments‘ or a comminuted Bennett fracture. This is an unstable injury that requires surgical reduction and fixation. Current treatment is an external fixator accompanied by the tension band wiring.
NOTE: Comminuted two-part base of first metacarpal fracture known eponymously as Bennett fracture, first described by Edward Hallaran Bennett in 1882
Imaging
- Routine views of the thumb adequately define the nature of the fragment(s).
- CT scans may be performed as part of the definitive management work-up.
History of the Rolando fracture
1910 – Silvio Rolando publishes ‘Fracture de la base du premier metacarpien’ in which he reports the outcomes and treatment of twelve thumb metacarpal fractures in port workers. Two cases involved the diaphysis and in the other ten, the metacarpal base. Of the base fractures, two were extra-articular fractures; five Bennett fractures; and three were Y pattern intra-articular fractures. It was these previously undescribed Y pattern fractures that became the focus of his paper and the basis of hi eponym.
Anatomy and Mechanism
Toutes les fois donc que la violence exercée au long de l’axe longitudinal du métacarpe agit plus intensément ou plus longuement, elle ourrait entraîner aussi la fracture du procès articulaire plus résistant, c’est-à-dire du procès dorsal. Dans ce cas-là il se produit une fracture en Y par laquelle l’extrémité supérieure du premier métacarpien reste partagé en trois fragments, dont deux, correspondant à la base, sont respectivement dorsal et palmaire, et l’autre correspond au corps de l’os.
Dans les trois cas de fractures en Y, le facteur étiologique est représenté dans un cas par un coup de poing fortement vibré contre la tête de l’adversaire, le pouce étant replié et serré dans la paume de la main; dans les deux autres cas par chute sur le côté radial de la main avec le pouce en adduction.
Rolando 1910; 33: 303–304
When trauma occurs to the long axis of the metacarpal, it can cause a fracture of the dorsal process. In this case, a Y shaped fracture is produced by which the proximal first metacarpal is divided into 3 fragments of which 2 parallel the base, dorsal and palmar respectively, and the other corresponds to the body of the bone.
In the 3 cases of Y fractures, the etiologic factor is represented in 1 case by a blow with a closed fist, very strongly against the head of the adversary with the thumb folded and held into the palm of the hand, in the other 2 cases by a fall on the radial side with the thumb in adduction.
Rolando 1910; 33: 303–304
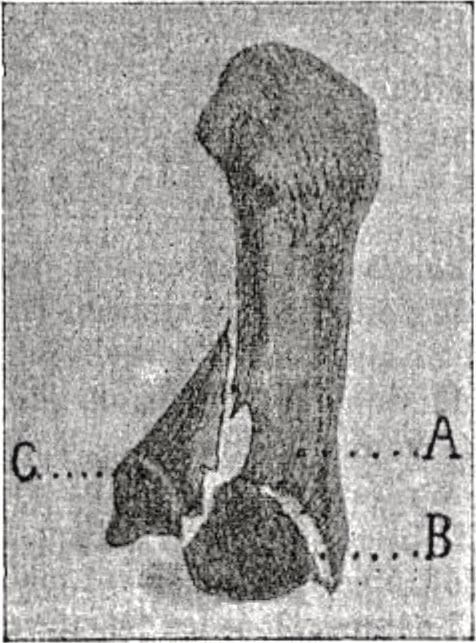
Prognosis
Le pronostic est défavorable au point de vue fonctionnel toutes les fois que de telles fractures, (principalement quand les fragments en sont mobiles et le déplacement remarquable) sont abandonnées à elles-mêmes, ou n’ont pas reçu un traitement convenable.
The prognosis is unfavorable from the functional point of view whenever this fracture (principally when the fragments are mobile and there is noticeable displacement) is left to itself or has not received the appropriate treatment
Treatment
Rolando abducted and extended the thumb to reduce the fracture. He immobilised the thumb in traction, by applying two small bands of diachylon on the dorsal and palmar sides of the thumb followed by a plaster cast to the thumb and wrist. As Rolando suspected a ‘considerable tendency for the displacement to recur’ he recommended cast immobilisation for 3 weeks.
Il résulte de mes observations qu’il existe un type de fracture de la base du premier métacarpien, qui n’avait pas encore été décrit à ce que je sache. Cette fracture, que j’ai observé trois fois sur dix cas de fracture de la base, est consécutive à une violence qui agit suivant l’axe longitudinal du métacarpe; elle possède une forme en Y, ne peut pas se distinguer de la fracture de Bennett sans l’intervention radioscopique, et, comme celle-là, elle exige un traitement spécial.
Rolando 1910; 33: 304
I have found that there exists a type of fracture of the base of the first metacarpal that has not yet been described as far as I know. This fracture that I have noticed in 3 cases of 10 of base fractures follows an injury acting along the longitudinal axis of the metacarpal. It has a Y form and cannot be distinguished from a Bennett’s fracture without radiographic studies, and like the Bennetts’s fracture, it has to have a special kind of treatment.
Rolando 1910; 33: 304
Associated Persons
- Silvio Rolando (1873-1949)
- Edward Hallaran Bennett (1837–1907)
Alternative names
- Rolando’s fracture
- Intra-articular thumb metacarpal base fracture with three or more segments
References
Original articles
- Rolando S. Fracture de la base du premier metacarpien et principalement sur une variété non encore décrite. La Presse Médicale 1910; 33: 303–304. [Translated Meals RA. Fracture of the base of the first metacarpal and a variation that has not yet been described. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006 Apr;445:15-8]
Review articles
- Proubasta IR. Rolando’s fracture of the first metacarpal. Treatment by external fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992 May;74(3):416-7
- Howard FM. Fractures of the basal joint of the thumb. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987 Jul;(220):46-51.
- Edmunds JO. Traumatic dislocations and instability of the trapeziometacarpal joint of the thumb. Hand Clin. 2006 Aug;22(3):365-92
- Sood A, Granick MS. Rolando fracture. Eplasty. 2014 Jun 6;14:ic16
- Feletti F, Varacallo M. Rolando Fractures. 2021 Jul 18. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022
- Vajuhudeen Z. Rolando Fracture. Radiopaedia
- Cadogan M. Rolando fracture. Eponym A Day. Instagram
[cite]