
FFS: Vestibular Neuronitis
Vestibular neuronitis causes acute peripheral vertigo. Corticosteroids improve recovery. Differentiation from central causes is key in ED.

Vestibular neuronitis causes acute peripheral vertigo. Corticosteroids improve recovery. Differentiation from central causes is key in ED.

Vestibular migraine presents as episodic vertigo with or without headache. Diagnosis is clinical and often made by a neurologist after excluding other causes

Margaret Dix (1911–1991), British neuro-otologist who co-developed the Dix–Hallpike test, reshaped diagnosis of vertigo and advanced vestibular science

Charles S. Hallpike (1900–1979), British neuro-otologist, co-devised the Dix–Hallpike manoeuvre, clarified Menière’s disease pathology, and pioneered vestibular physiology.

Network Five Emergency Medicine Journal Club Episode 16 - Neurology reviewing papers from vertigo, GBS to status epilepticus.

Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is one of the most common forms of peripheral vertigo. Whilst its name may not be the most imaginative or succinct, it accurately describes the syndrome

Menière’s disease is a condition characterized by the triad of episodic vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss, caused by endolymphatic hydrops of the labyrinthine system of the inner ear.

Prosper Menière (1799 - 1862) was a French otorhinolaryngologist. Maladie de Menière, Menière's disease (1861)

John Epley (1930–2019), pioneer of the Epley maneuver for BPPV, revolutionized vertigo care and developed the Omniax Chair for vestibular diagnosis
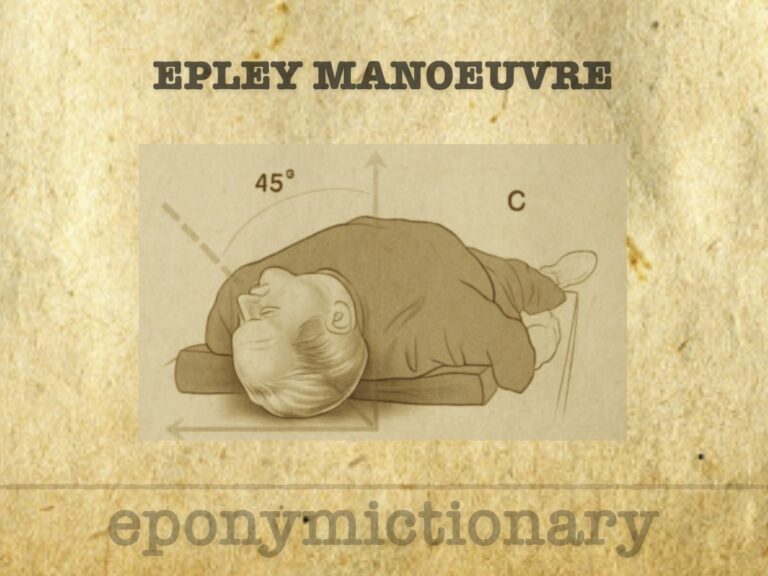
Epley maneuver: Particle repositioning maneuver for the treatment of BPPV - with the aim of moving the canaliths out of the posterior semicircular, back into the utricle.

A 50 year-old woman sees the world spin round when she hangs up her washing. Can you make the diagnosis and effect a cure?
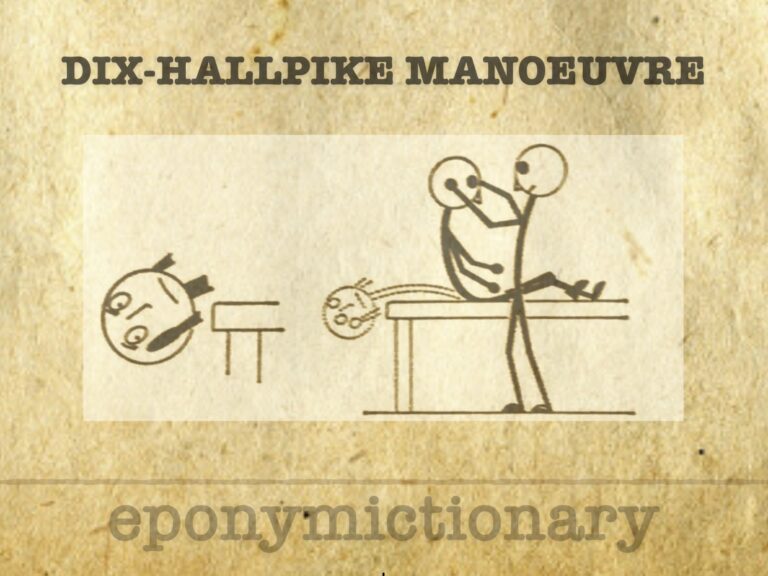
The Dix-Hallpike manoeuvre is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of posterior semicircular canal BPPV, first described by Dix and Hallpike in 1952