William Gissane
William Gissane (1898-1981) was an Australian born, British surgeon.
Gissane was the first clinical director and surgeon-in-chief of the Birmingham Accident Hospital, an experiment to improve the care of the injured by providing continuous cover by full-time consultant surgeons, under whose care the patient remained from admission to final discharge.
Gissane advocated for the prevention of injuries as well as good care for the injured. He assisted the then Austin Motor Company with the formation and development of their rehabilitation centre, and a mobile operating theatre based at the Accident Hospital. Gissane’s work on the reduction of road and industrial accidents brought him international recognition and had considerable influence over faults on car safety and seat belts.
Eponymously remembered for describing the Critical angle of Gissane to help determine the presence of a calcaneus fracture on lateral foot XR
Biography
- Born on April 26, 1898 Sydney, Australia
- 1917 – Royal Australian Artillery (RAA).
- 1925 – MB, University of Sydney (represented the university at rugby, cricket and boxing; becoming light heavyweight inter-university champion)
- 1927 – Emigrated to England; FRCS Edinburgh
- 1932 – MRCS, FRCS
- 1938 – Specialist in accident surgery in the London County Council Hospital Service greatly influenced by his visit to Lorenz Böhler’s clinic in Vienna
- 1941 – Clinical Director of the Birmingham Accident Hospital. The Accident Hospital (the ‘Birmingham experiment’) was an attempt to improve the care of the injured by providing continuous cover by full-time consultant surgeons, under whose care the patient remained from admission to final discharge.
- 1952 – Inaugural Joseph Henry Lecturer at the Royal College of Surgeons.
- 1959 – Sir Arthur Sims Commonwealth Travelling Professor
- 1959 – Honorary Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (Hon FRACS)
- 1961 – Robert Jones Lecturer at the Royal College of Surgeons
- 1964 – Honorary Professorship of Accident Surgery, University of Birmingham; Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (CBE)
- Died on April 1, 1981
Medical Eponyms
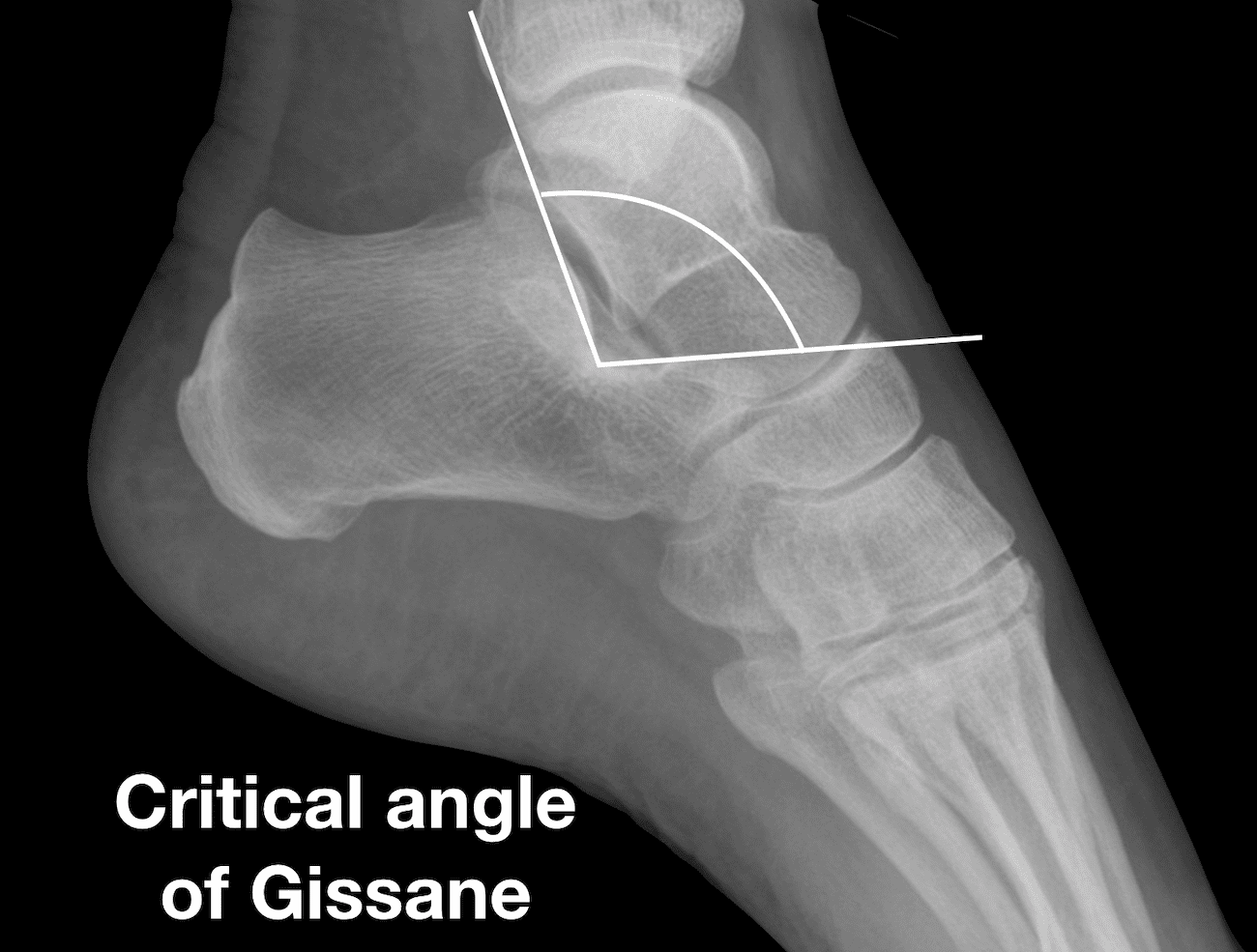
Gissane angle (1946)
Gissane Angle [aka *critical angle; critical angle of Gissane], like the Böhler angle, can be used to help determine the presence of a calcaneus fracture on a radiograph. The angle is measured on lateral foot radiograph formed by the intersection of the lines drawn along the downward (posterior facet) and the upward (anterior process) slopes of the calcaneal superior surface. Normal range (120-145°).
Major Publications
- Gissane W. Discussion on “Fractures of the os calcis” (Proceedings of the British Orthopaedic Association, 1946). J Bone Joint Surg Am 1947; 29: 254–255
- Gissane W. The stages of development and the organization of the Birmingham Accident Hospital. Postgrad Med J. 1963 Dec;39:683-7.
References
Biography
- London PS. Inaugural William Gissane Lecture: man and memorial. Injury. 1982; 14(3): 211-34
- Harrison SH. Accident surgery—the life and times of William Gissane. Injury. 1984; 16(3): 145-54
- Jackson DM. A birthday tribute to Professor William Gissane. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume. 60-B (2): 149
- Biography: Gissane, William (1898 – 1981). Plarr’s Lives of the Fellows Online. Royal College of Surgeons of England
- Bibliography. Gissane, William. WorldCat Identities
Eponymous terms
- Gomez A, Cadogan M. Eponymythology of foot injuries. LITFL
- Cadogan M. Critical angle of Gissane. Eponym A Day. Instagram
[cite]
Resident medical officer in emergency medicine MB ChB (Uni. Dundee) MRCS Ed. Avid traveller, yoga teacher, polylinguist with a passion for discovering cultures.