
Cope’s Sign
Cardio-biliary reflex (“Cope sign”): gallbladder disease causing vagal bradycardia or AV block that mimics cardiac events, often with normal troponin.

Cardio-biliary reflex (“Cope sign”): gallbladder disease causing vagal bradycardia or AV block that mimics cardiac events, often with normal troponin.
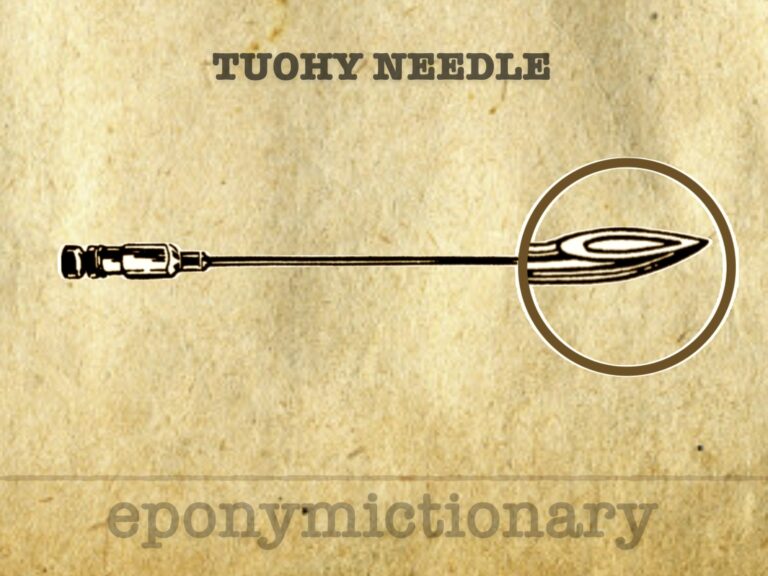
Tuohy needle: directional neuraxial needle enabling continuous spinal and epidural catheter techniques, based on the original Huber-point design.

Lauge-Hansen classification of ankle injuries (1950) - predictable fracture patterns defined by injury mechanism and resultant radiological findings
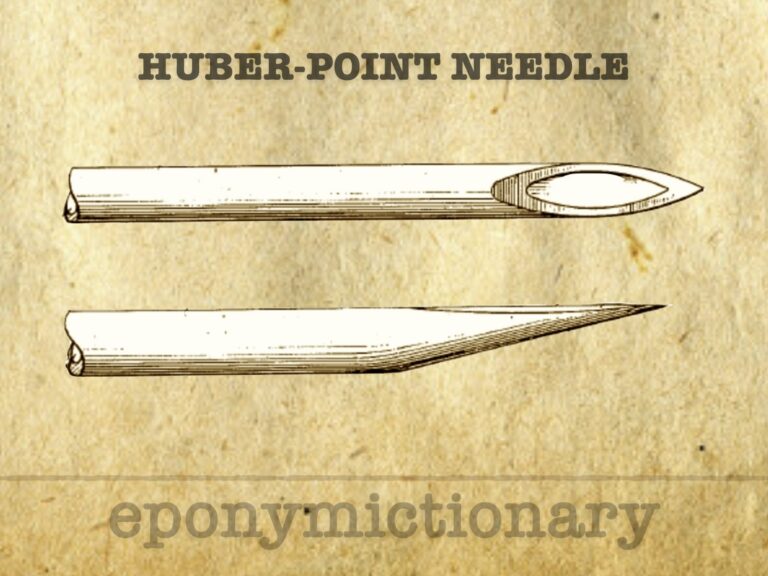
Hypodermic needle (needle which enters the skin) Originally described in 1946 by Ralph Huber. More commonly known as the Tuohy Needle
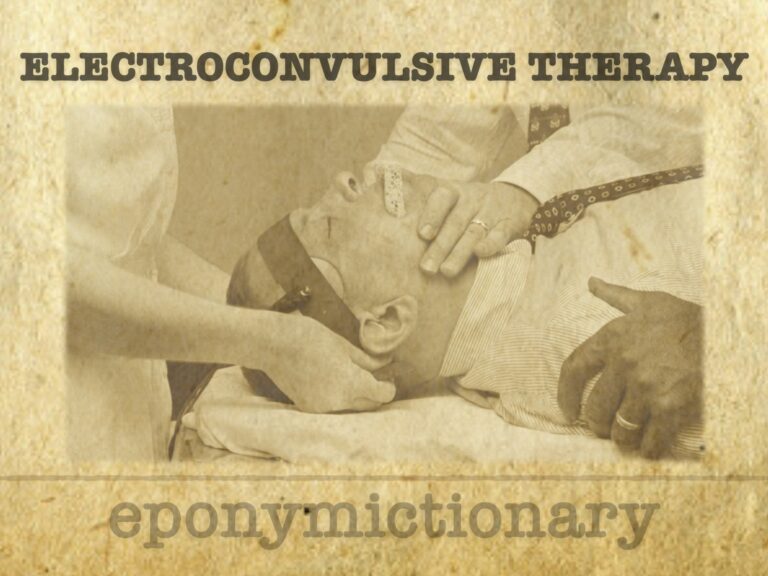
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): history, pioneers, modern use, efficacy, and controversy, one of psychiatry’s most enduring treatments.

Stigler’s Law of Eponymy: no discovery is named after its true originator. Explore its history, Merton’s roots, and modern scientific misattribution.
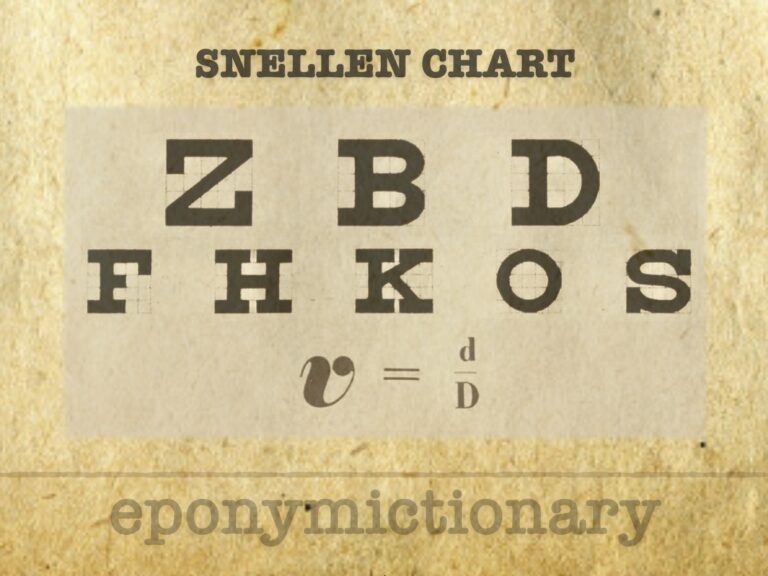
Snellen chart: history of visual acuity testing from Hooke to ETDRS, with key milestones, optotype design, and contributions from Snellen, Donders, Sloan
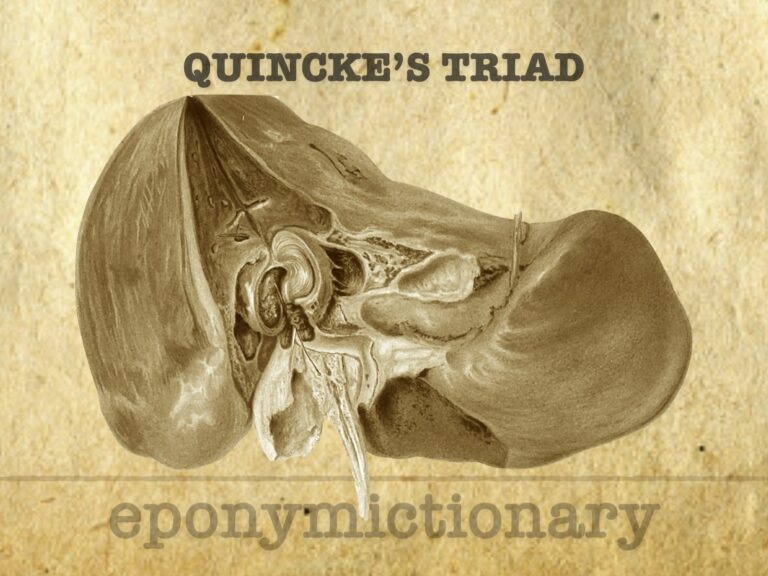
Quincke's Triad describes hemobilia via the triad of GI bleeding, biliary colic, and jaundice; first detailed by Heinrich Quincke in 1871, named retrospectively in 1975

Romberg’s sign: a classic neurological test detecting proprioceptive loss by demonstrating postural instability with eyes closed.

Howship-Romberg sign: pain and paraesthesia along the distribution of the obturator nerve (medial thigh to knee); a clinical indicator of obturator nerve compression, commonly due to an obturator hernia
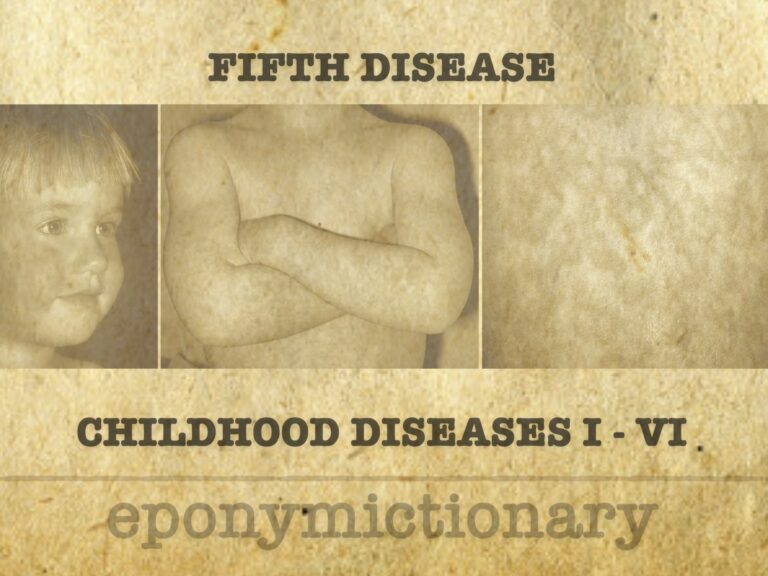
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease), is a common manifestation of infection in children characterized by low-grade fever, malaise, facial rash, and later by the spread of a lacy maculopapular rash involving the trunk and limbs.

Meigs syndrome: Triad of ascites with hydrothorax in association with benign ovarian tumor, that is cured after tumor resection. Described in 1934 by Joe Vincent Meigs (1892-1963)