Marie-Strümpell disease
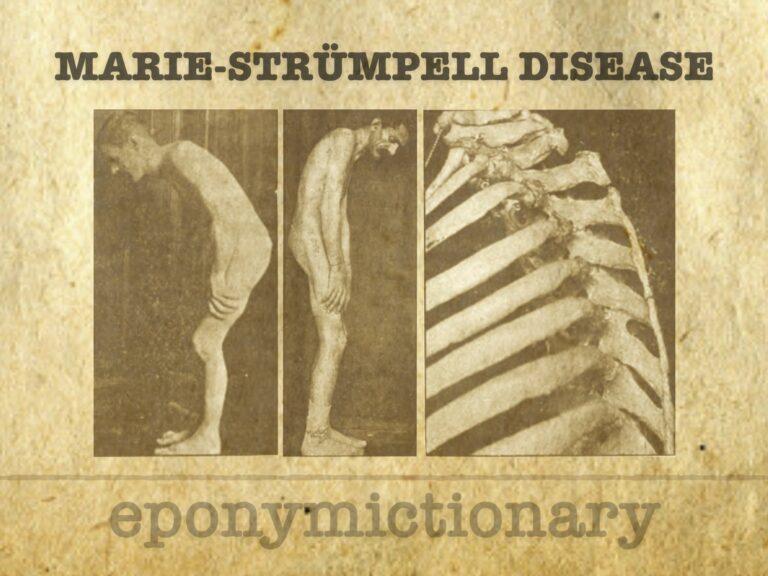
Marie-Strümpell disease (ankylosing spondylitis): a chronic inflammatory spinal arthritis with progressive axial fusion, first described by Pierre Marie and Adolf Strümpell in the late 19th century.

Marie-Strümpell disease (ankylosing spondylitis): a chronic inflammatory spinal arthritis with progressive axial fusion, first described by Pierre Marie and Adolf Strümpell in the late 19th century.
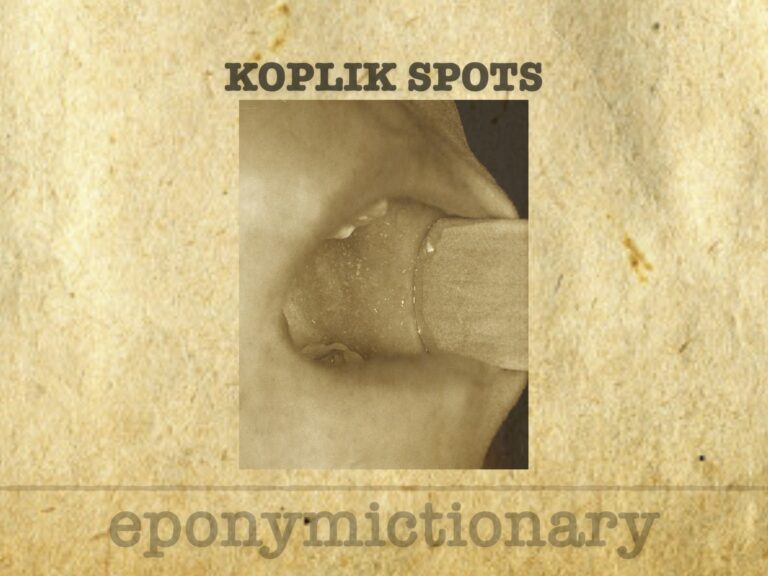
Koplik spots are pathognomonic buccal lesions in early measles, first described by Henry Koplik in 1896, aiding pre-rash diagnosis and outbreak control.
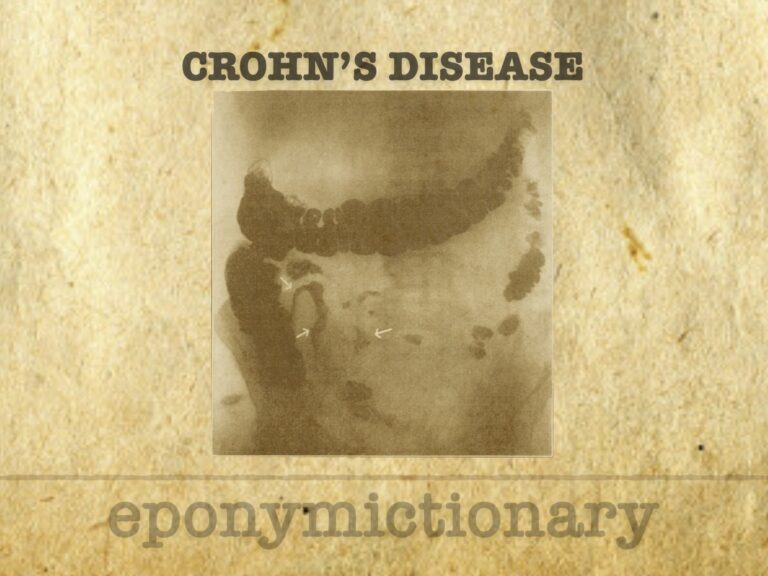
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the GI tract, Crohn’s disease was first defined in 1932 but described decades earlier by Dalziel and others

EGPA (Churg–Strauss syndrome): rare ANCA-associated vasculitis with asthma, eosinophilia, and systemic granulomatous inflammation of small vessels
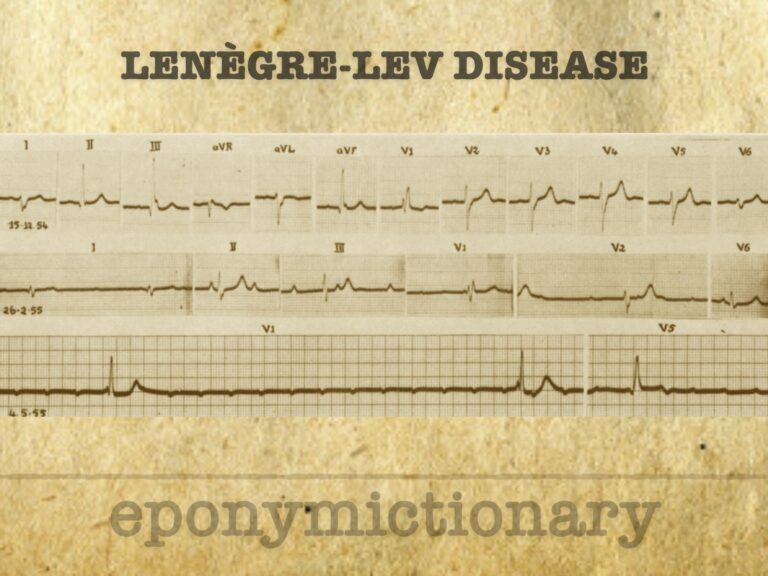
Acquired fibrous degeneration of the left and right bundle branches, eventually manifesting as permanent complete atrioventricular (AV) dissociation with cardiac pauses and Adams-Stokes attacks

Stokes-Adams syndrome is an abrupt, transient loss of consciousness due to a sudden but pronounced decrease in the cardiac output

Cheyne-Stokes respiration is a cyclical breathing pattern of apnoea and hyperpnoea, seen in heart failure, brain injury, and end-of-life settings.
May–Thurner syndrome (MTS). Venous compression syndrome causing left-sided iliofemoral DVT, first anatomically defined by May and Thurner in 1957.
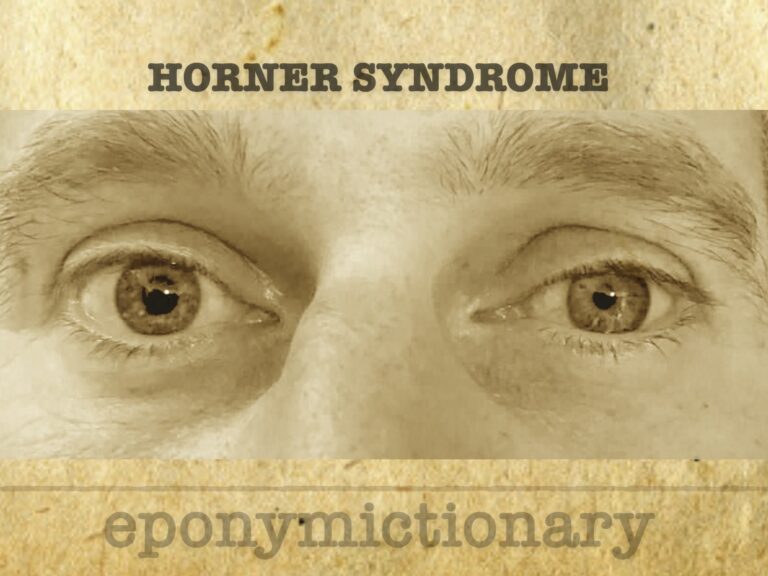
Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos

Janeway lesions; painless, haemorrhagic macules of the palms/soles linked to infective endocarditis. Edward Gamaliel Janeway (1899)

Guillain-Barré syndrome is the most common and severe acute inflammatory paralytic neuropathy. The classical description of GBS involves rapidly progressive bilateral weakness, usually starting in the distal lower extremities and ascending proximally.

Bell’s palsy: Acute idiopathic unilateral paralysis of the facial nerve. Named after Sir Charles Bell and his description in 1827