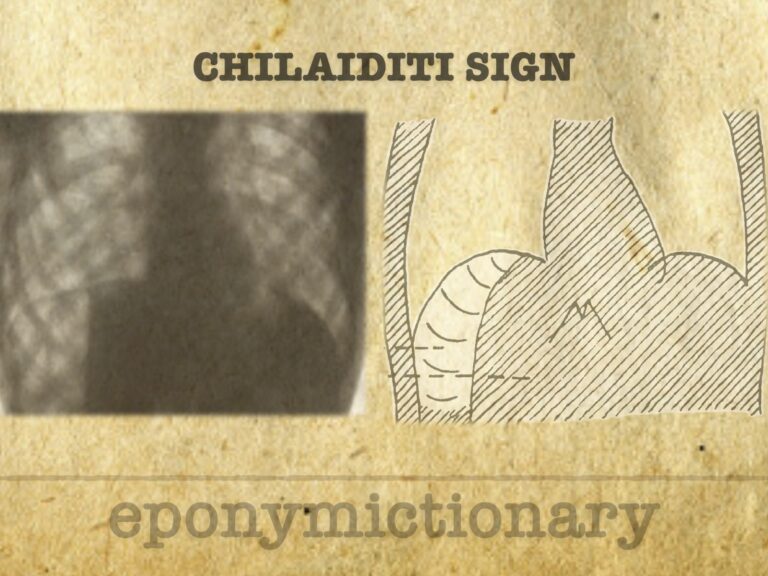
Chilaiditi syndrome
Chilaiditi sign: rare condition with bowel loops interposed between liver and diaphragm, with symptoms (syndrome). Must differentiate from free air.

Chilaiditi sign: rare condition with bowel loops interposed between liver and diaphragm, with symptoms (syndrome). Must differentiate from free air.

Saint’s Triad: coexistence of hiatal hernia, colonic diverticulosis, and gallstones—now linked to connective tissue disorders like herniosis.
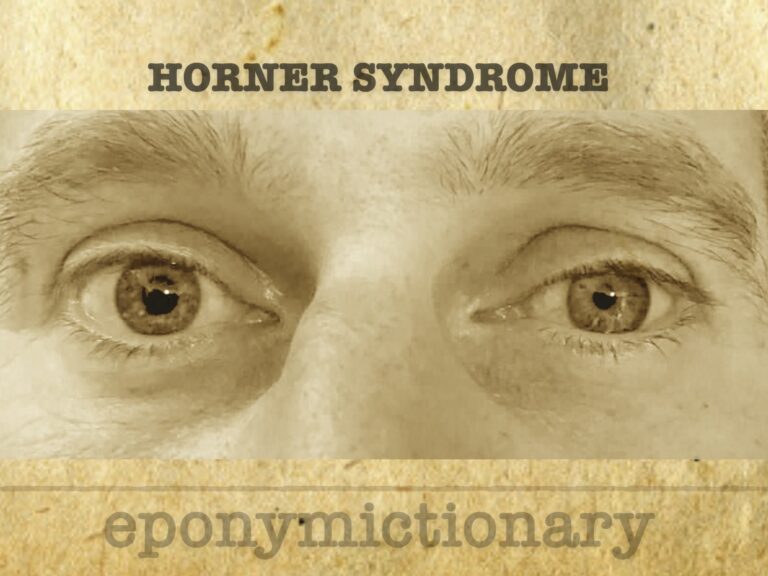
Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos
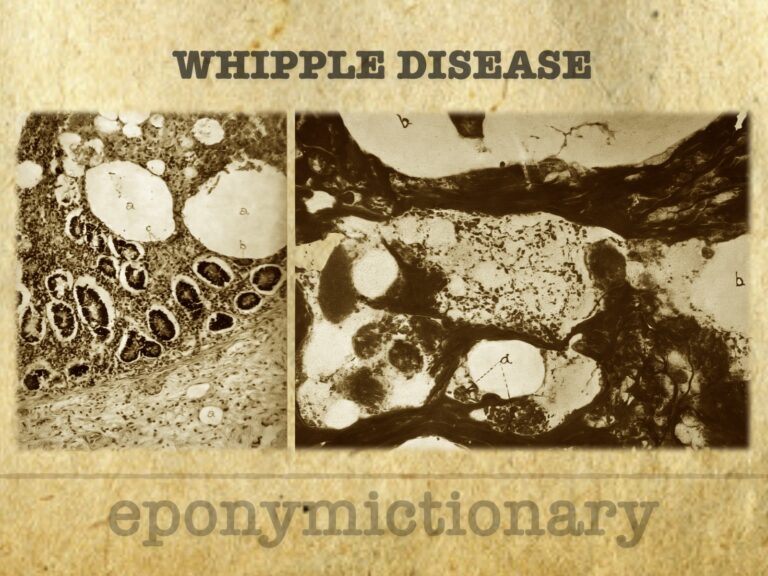
Whipple disease: rare systemic infection by Tropheryma whipplei. Explore its history, diagnosis, and treatment from 1907 discovery to present day
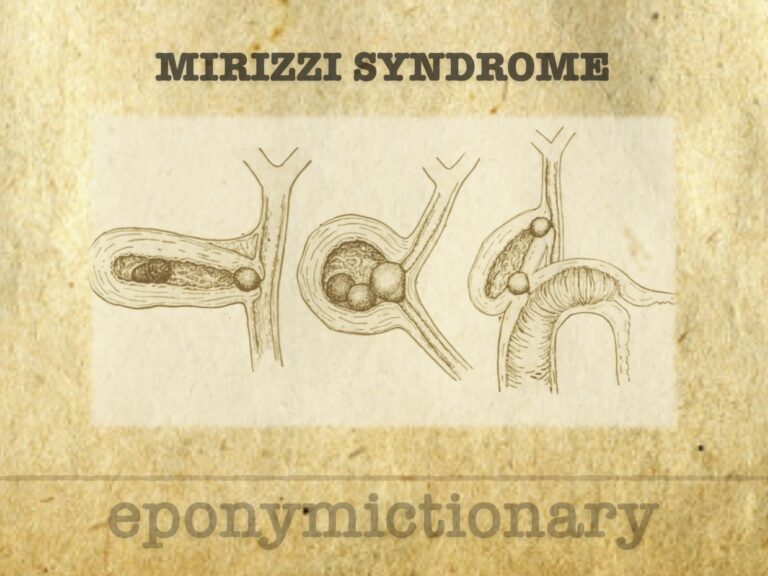
Mirizzi syndrome is a rare complication of gallstone disease involving bile duct compression or fistula formation, with evolving classifications from Mirizzi to Csendes and Beltrán
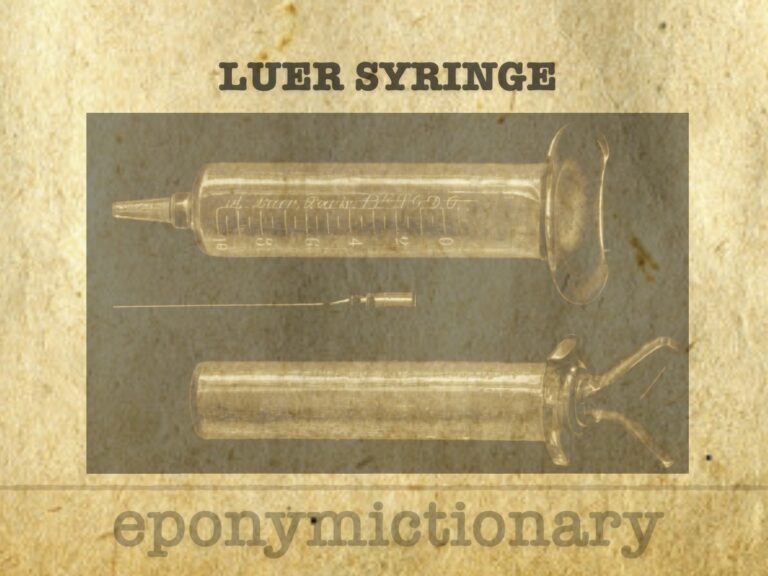
Lüer syringe (1894). Unique graduated all-glass hypodermic syringe. Invented by Jeanne Amélie Lüer; Patented by Wülfing-Lüer
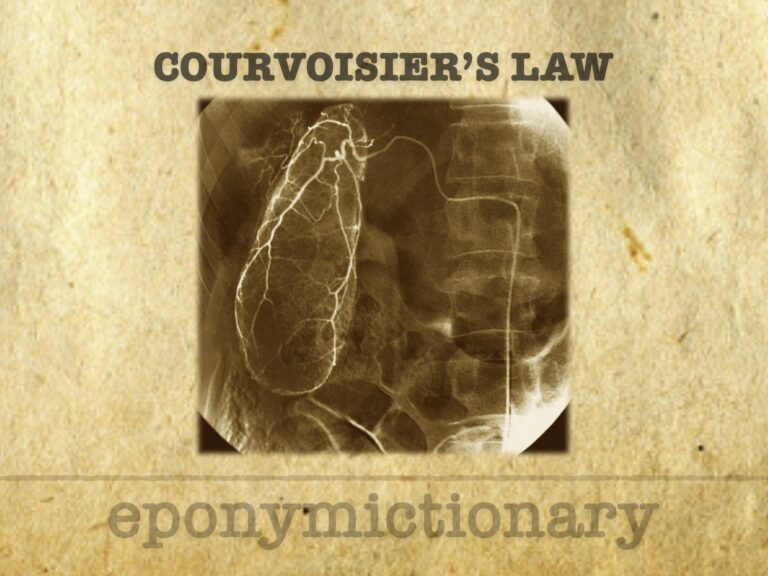
Courvoisier’s sign: palpable gallbladder with painless jaundice suggests malignant obstruction, not gallstones. A key clinical diagnostic clue.
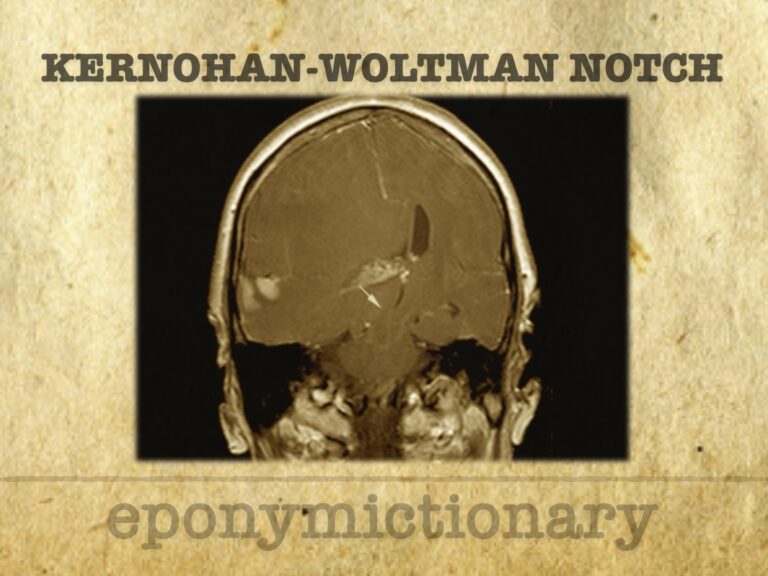
Kernohan-Woltman Notch Phenomenon (KWNP): false localising sign with mass effect and ipsilateral hemiparesis via contralateral peduncle compression.

Woltman’s Sign is delayed reflex relaxation in hypothyroidism, often seen as a hung-up ankle jerk; a classic but non-specific clinical finding.
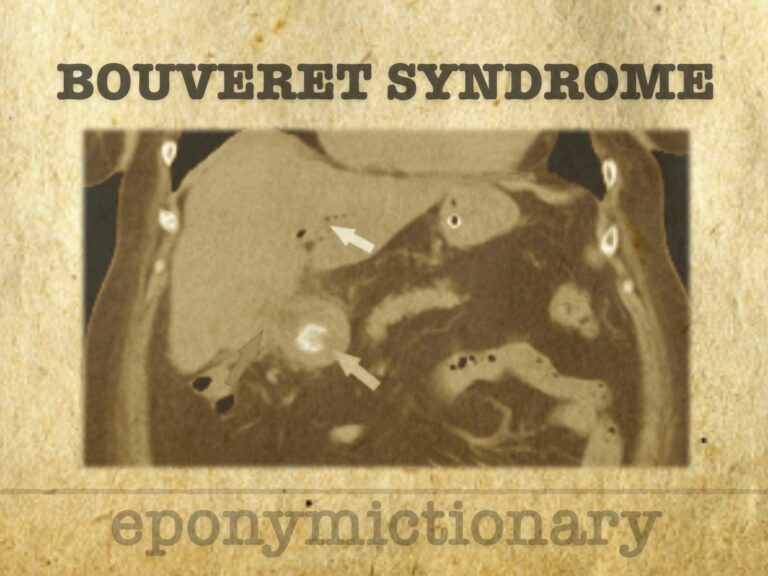
Bouveret syndrome: gastric outlet obstruction following passage of a gallstone from gallbladder to duodenum/pylorus via bilioenteric fistula
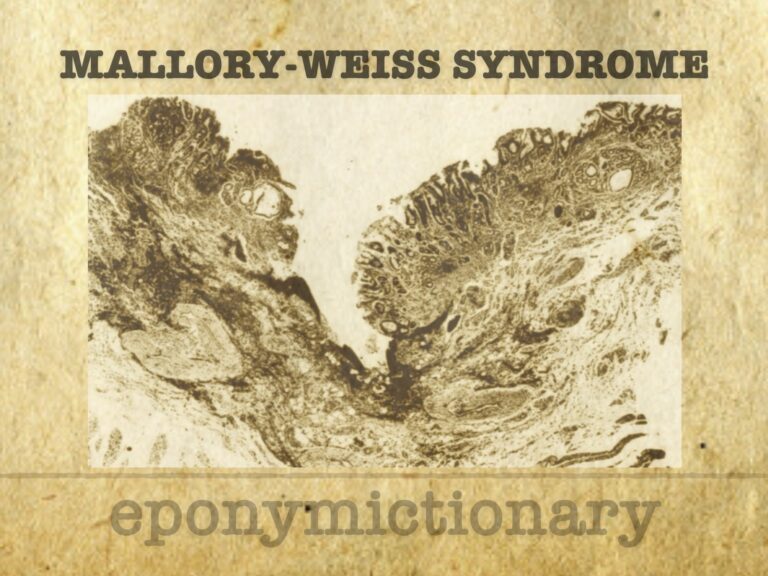
Mallory–Weiss syndrome: upper GI bleeding from gastroesophageal tears. History, key figures, first descriptions, diagnosis, and treatment.

The Weber and Rinne tuning fork tests differentiate conductive from sensorineural hearing loss using the principles of bone and air conduction.