
Bornholm disease
Acute, transient viral myositis involving intercostal and abdominal muscles associated with Coxsackievirus B. Eponym: Ejner Sylvest (1930)

Acute, transient viral myositis involving intercostal and abdominal muscles associated with Coxsackievirus B. Eponym: Ejner Sylvest (1930)

Eponymythology: heart murmur eponyms and named cardiac murmurs. Related eponyms, the person behind their origin, their relevance today, and modern terminology.

Echocardiography basics and the differences between 2D imaging, M-mode, pulsed wave Doppler, continuous wave Doppler, and tissue Doppler imaging.

William Cec. Dabney (1849–1894) described epidemic chest pain (“Devil’s Grip”) and championed medical education, licensure, and public health in Virginia
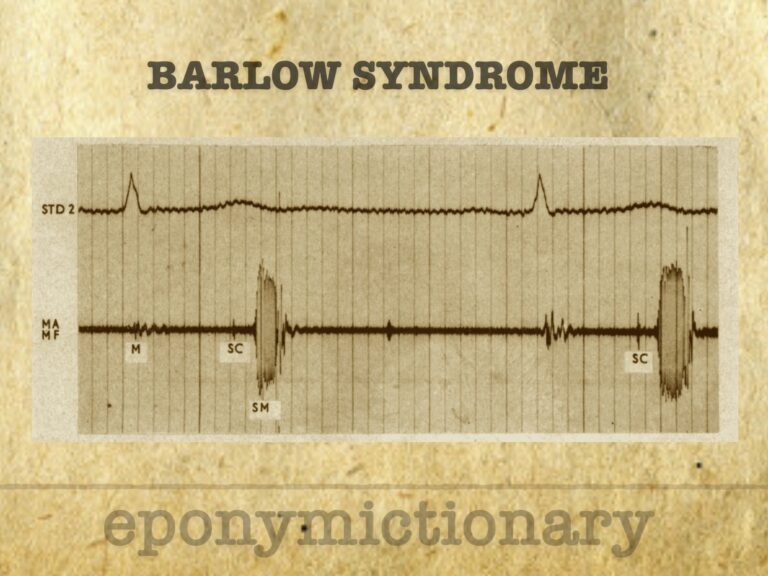
Barlow syndrome (primary billowing mitral leaflet syndrome (BMLS)). Auscultatory findings of late systolic murmur with non-ejection ('mid-late') systolic click
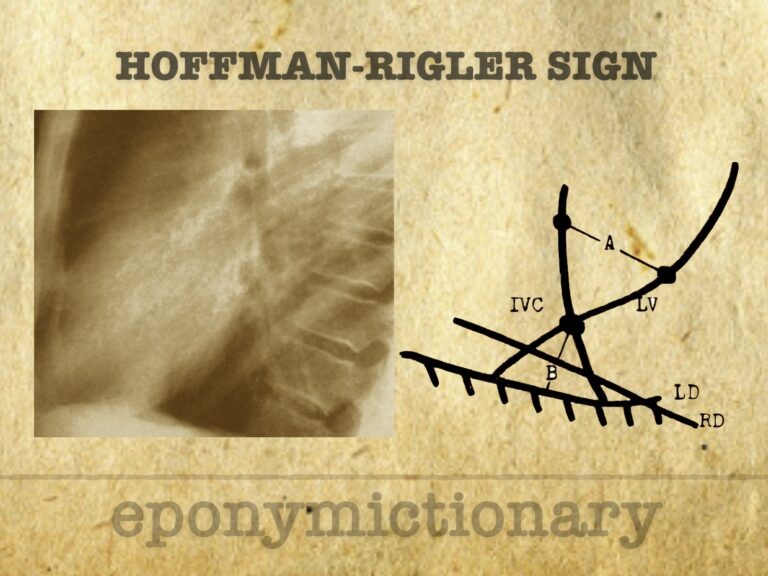
Radiographic sign of left ventricular enlargement on lateral chest X-ray, based on LV extension behind the IVC; described by Hoffman and Rigler in 1965

John Brereton Barlow (1924-2008) was a South African cardiologist. Barlow described mitral valve prolapse (eponymously known as Barlow’s syndrome) in 1963

Woldemar Mobitz (1889-1951) was a Russian-German physician. Applied mathematical approach to arrhythmias 1924 Mobitz Type I and II AV Block

Carl Gerhardt (1833–1902), German internist and paediatric pioneer, described Gerhardt’s sign and advanced diagnostics, paediatrics, and laryngology
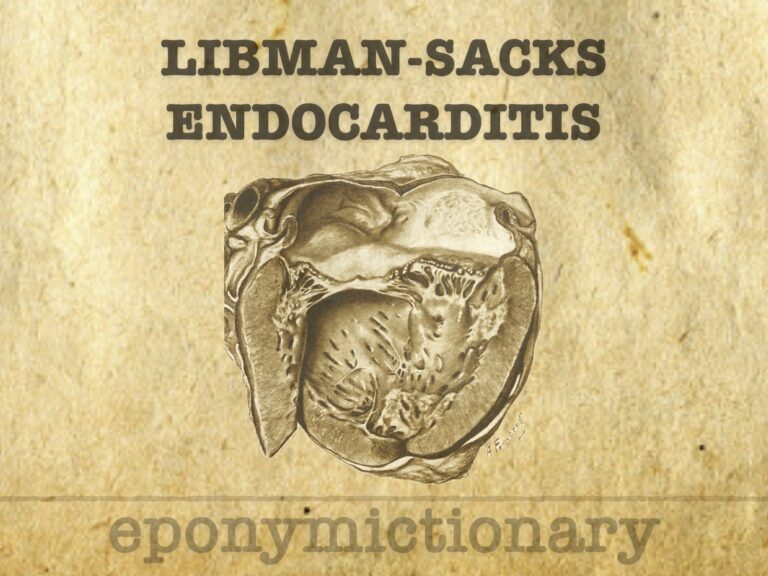
Libman–Sacks endocarditis is a sterile cardiac valve lesion linked to lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome, often detected via echocardiography

Benjamin Sacks (1896–1971), cardiac pathologist and co-describer of Libman–Sacks endocarditis, also a Hollywood advisor and Arizona frontier historian.
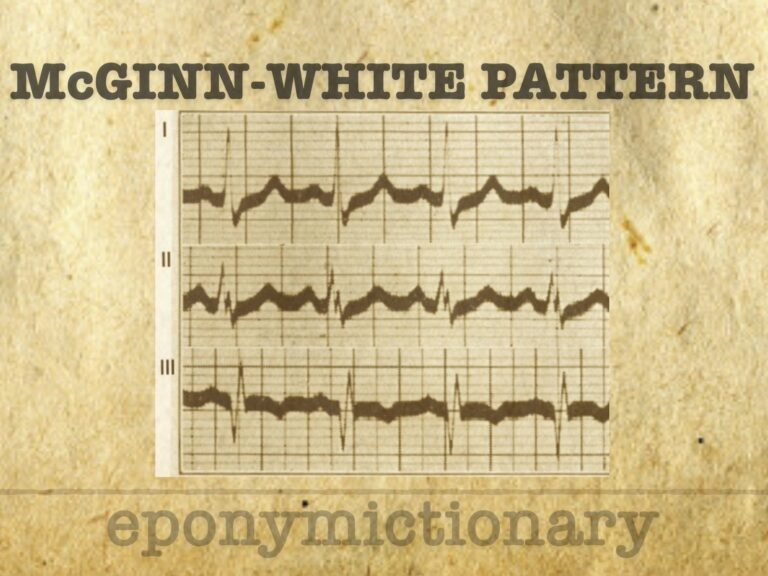
S1Q3T3 McGinn-White pattern indicates right heart strain and predicts severe PE outcomes. ECG sign of pulmonary embolism described in 1935.