Austin Flint Murmur
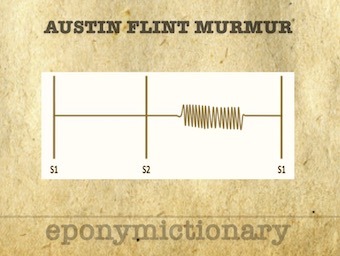
Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis

Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis

AI Tools for Learning - a review of a selection of tools - which ones work and which ones don’t, plus, the future of AI-assisted learning

The original hope was that using AI might allow us to create a single podcast episode in one afternoon. But things didn’t go quite the way we planned.

AI can work for Spotify's music DJ, so we wondered if it can also work for a cardiology podcast intended for clinicians. Here are the pros and cons we discovered.

A 45 year old woman with chronic alcoholic liver disease presents to the ED with exertional dyspnoea and is noted to have a SpO2 of 90% at rest despite having a normal chest examination and CXR.
Sir Thomas Lauder Brunton (1844-1916) was a Scottish physician

Cath lab activation for a 65yo male with sudden onset central crushing chest pain and some lower back pain with a STEMI pattern on ECG.

Julian Dobranowsk Medmastery help identify the features of cardiac failure on the chest X-ray. Evaluation of the three stages of failure

Pacemakers and the ECG: Learn to recognize failure to capture on an ECG or rhythm strip. Medmastery pacemeker essentials

Pacemaker essentials: Learn to recognize oversensing, its causes and how it is resolved (through decreasing sensitivity or the use of alternate algorithms).

Pacemaker essentials: How to recognize failure to sense, its causes and how it is resolved (increasing sensitivity or lead re-site).

Pacemaker essentials: Learn to recognize failure to capture, its causes, and how it is resolved (increasing output or lead resite).