
Leo Rigler
Leo George Rigler (1896-1979) was an American radiologist. Eponymously affiliated with Rigler sign; Rigler triad; Rigler notch sign; Hoffman-Rigler sign

Leo George Rigler (1896-1979) was an American radiologist. Eponymously affiliated with Rigler sign; Rigler triad; Rigler notch sign; Hoffman-Rigler sign
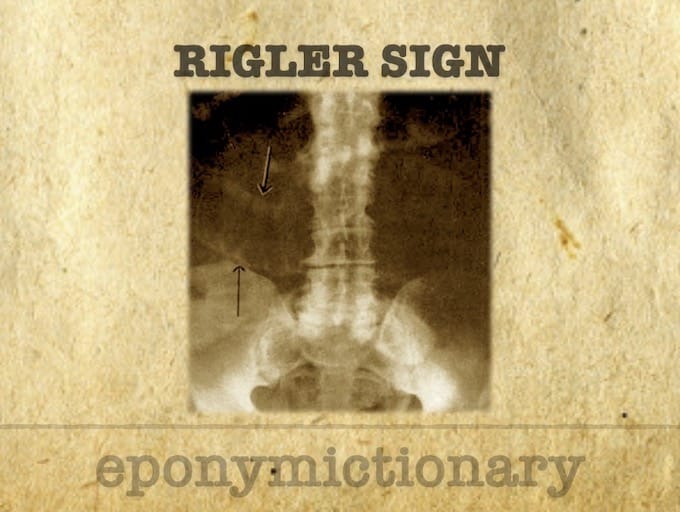
Radiological signs of pneumoperitoneum: history, diagnosis, and key eponyms including Rigler’s sign, Popper’s sign, football sign, and inverted V sign

John Brereton Barlow (1924-2008) was a South African cardiologist. Barlow described mitral valve prolapse (eponymously known as Barlow’s syndrome) in 1963

Herman Snellen (1834–1908): Dutch ophthalmologist who created the Snellen chart and standardized visual acuity testing, transforming eye care worldwide
Necrotizing fasciitis: life-threatening soft tissue infection, historically hospital gangrene, term coined by Ben J. Wilson in 1951

Charles Foix (1882–1927), French neurologist; defined brainstem vascular syndromes, Foix–Alajouanine syndrome, and helped shape modern cerebrovascular neurology.

Bamberger–Marie syndrome (hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy): clubbing, bone periostosis, and joint effusions—historically recognised as a paraneoplastic syndrome linked to lung disease.

Melvin Starkey Henderson (1883–1954), founding Mayo orthopaedist and ABOS president, co-described Reichel–Jones–Henderson syndrome (synovial chondromatosis).

Georges Charles Guillain (1876-1961) was a French neurologist. Multiple neurology-related eponyms including Guillain-Barré syndrome

Woldemar Mobitz (1889-1951) was a Russian-German physician. Applied mathematical approach to arrhythmias 1924 Mobitz Type I and II AV Block

Ernst Adolf Gustav Gottfried von Strümpell (1853-1925) was a German neurologist. Strümpell signs, Strümpell-Lorrain disease, Marie-Strümpell disease and Westphal-Strümpell pseudosclerosis.

William Henry Battle (1855–1936) English surgeon. Battle incision, Battle operation and Battle sign postauricular (mastoid) ecchymosis