
James Kernohan
James W. Kernohan (1896–1981), pioneer of glioma grading and the Kernohan notch, shaped modern neuropathology through diagnostic clarity and clinical insight.

James W. Kernohan (1896–1981), pioneer of glioma grading and the Kernohan notch, shaped modern neuropathology through diagnostic clarity and clinical insight.

Henry Woltman (1889–1964), Mayo Clinic neurologist, Kernohan-Woltman notch, stiff-man syndrome, and myxoedema reflex; leader in U.S. neurology

Woltman’s Sign is delayed reflex relaxation in hypothyroidism, often seen as a hung-up ankle jerk; a classic but non-specific clinical finding.

Léon Bouveret (1850-1929) was a French internal medicine physician. Eponymous terms Maladie de Bouveret (1889) and Bouveret Syndrome (1895)

Ludwig Georg Courvoisier (1843-1918) was a Swiss surgeon, academic, and naturalist best remembered for Courvoisier’s sign / law (1890)
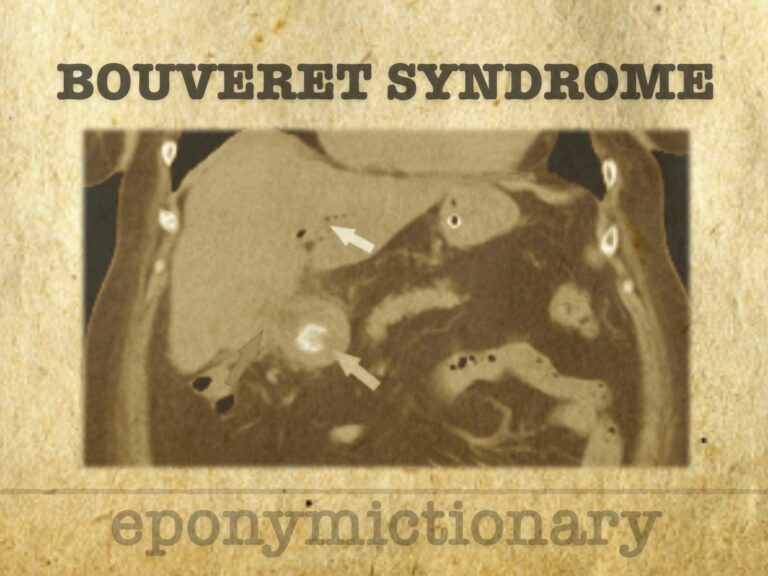
Bouveret syndrome: gastric outlet obstruction following passage of a gallstone from gallbladder to duodenum/pylorus via bilioenteric fistula

Sir Morell Mackenzie (1837–1892), pioneer of laryngology, founder of the Throat Hospital, author of the ‘laryngologist’s Bible’, and royal physician
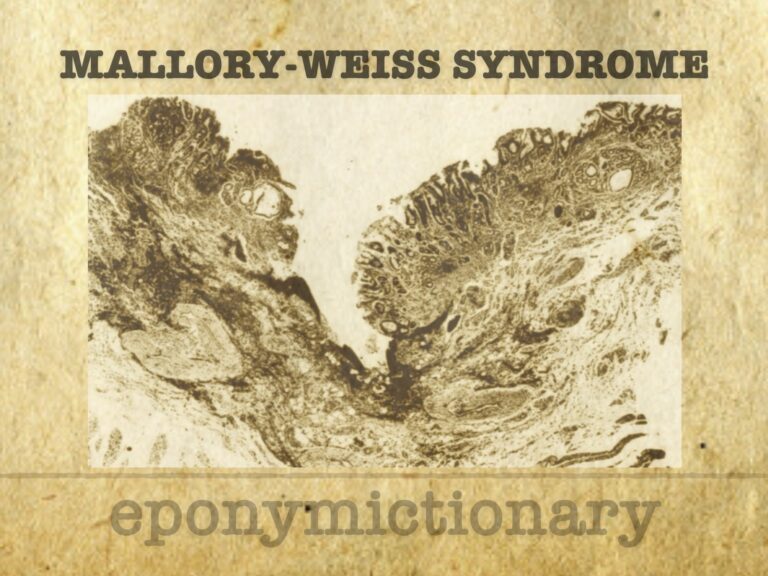
Mallory–Weiss syndrome: upper GI bleeding from gastroesophageal tears. History, key figures, first descriptions, diagnosis, and treatment.

Soma Weiss (1898-1942) was a Hungarian-born American physician. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome/lesion/tear and Charcot-Weiss-Baker Syndrome.

George Kenneth Mallory (1900–1986), American pathologist, co-described Mallory–Weiss syndrome and advanced cardiac, renal, and hepatic pathology

Philip R. Allison (1907–1974), pioneering thoracic surgeon, defined reflux oesophagitis, advanced Barrett’s oesophagus, and led Oxford surgery
Norman Barrett (1903–1979), thoracic surgeon, pioneer of oesophageal surgery, first repair of Boerhaave’s syndrome, and namesake of Barrett’s oesophagus.