CT Case 014
A 55yo lady presents with a two day history of subjective fevers and left flank pain. She has a past medical history including recurrent pyelonephritis and anaemia.
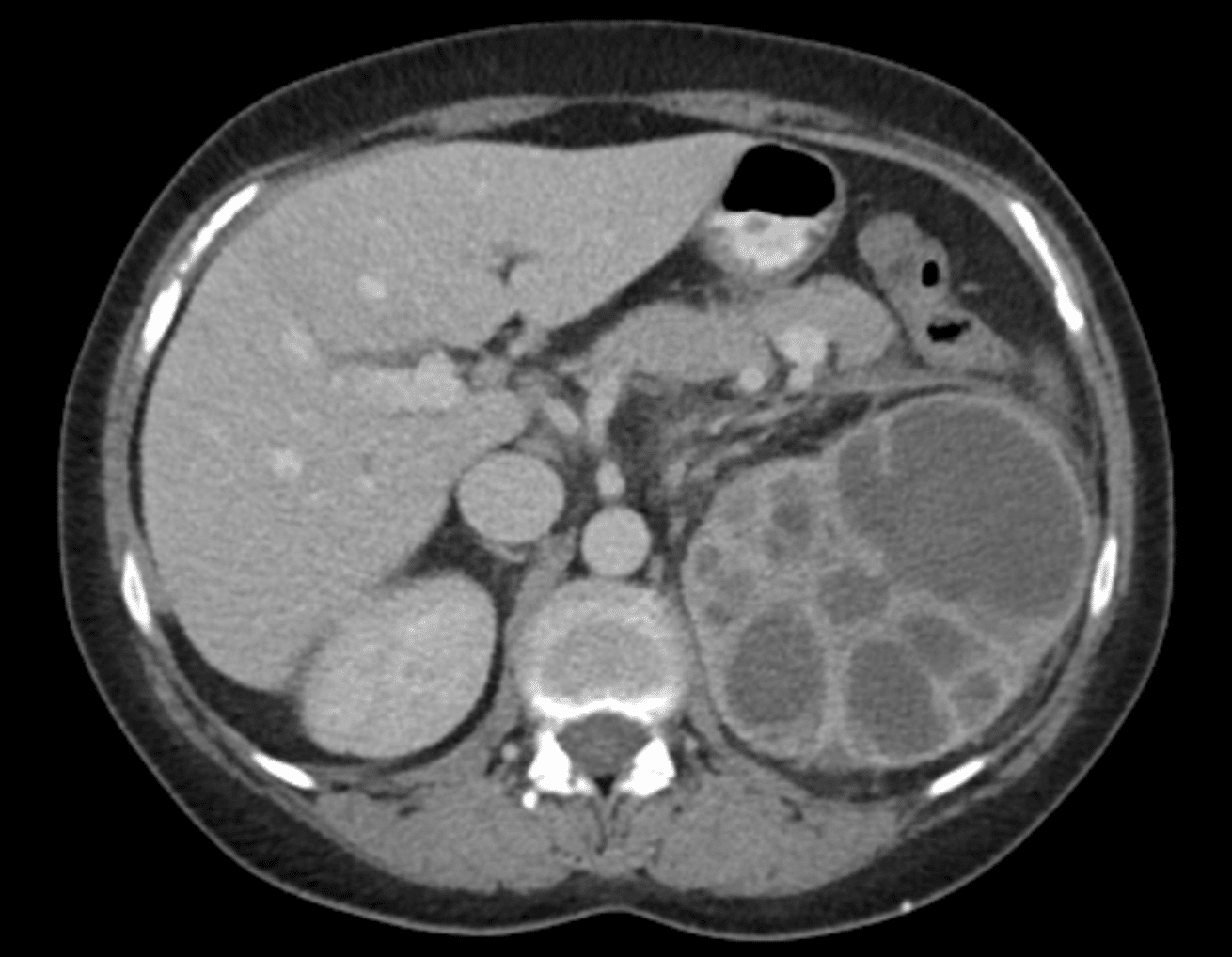
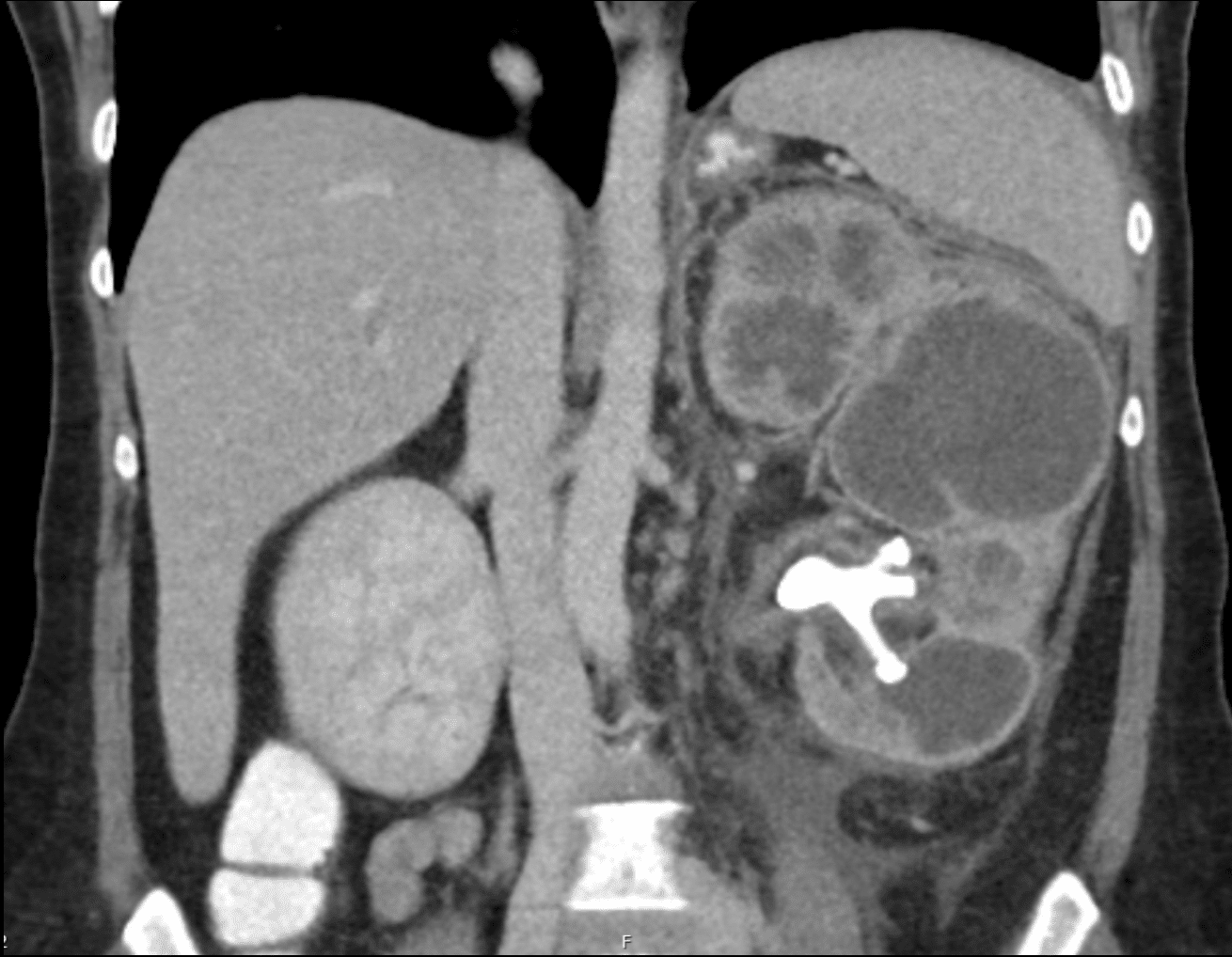
Describe and interpret the CT images
CT Abdomen INTERPRETATION
This CT abdomen shows significant left renal tract abnormalities including
- very enlarged kidney
- extensive perinephric and periureteric fat stranding
- staghorn calculus in the inferior pole of the kidney
- extremely dilated calyces with very little remaining parenchymal tissue
- gas within the renal parenchyma


CLINICAL CORRELATION
This CT shows xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGP).
Never heard of XGP before? Fear not, neither had I until this case!
This is an unusual variant of chronic pyelonephritis.
Often it occurs in the setting of recurrent infection due to obstructing calculi (note the presence of a staghorn calculi in this patient). Due to persistent infection and inflammation, granulomatous tissue (which contains macrophages filled with lipids) replace the normal renal tissue.
This causes almost complete destruction of the kidney.
The CT appearance is called a ‘bear paw sign’. It describes the clusters of necrotic lipid-filled tissue surrounded by a thin layer of renal parenchyma.
This appearance can be confused for that of a renal cell carcinoma, and in fact the two pathologies can co-exist.
The presence of fat stranding and gas within the renal parenchyma are consistent with active infection.
After a course of antibiotics to control the infection, our patient underwent nephrectomy. This is the recommended treatment to remove the non-functional kidney, prevent ongoing infection and also to ensure any cases with co-existing renal cell carcinoma are identified.

REFERENCES
- Dyer RB, Chen MY, Zagoria RJ. Classic signs in uroradiology. Radiographics. 2004 Oct;24 Suppl 1:S247-80.
- Tan WP, Papagiannopoulos D, Elterman L. Bear’s Paw Sign: A Classic Presentation of Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. Urology. 2015 Aug;86(2):e5-6.
- Jha SK, Aeddula NR. Pyelonephritis Xanthogranulomatous. StatPearls
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: renal infections LITFL
[cite]
TOP 100 CT SERIES
Sydney-based Emergency Physician (MBBS, FACEM) working at Liverpool Hospital. Passionate about education, trainees and travel. Special interests include radiology, orthopaedics and trauma. Creator of the Sydney Emergency XRay interpretation day (SEXI).
Dr Leon Lam FRANZCR MBBS BSci(Med). Clinical Radiologist and Senior Staff Specialist at Liverpool Hospital, Sydney
Emergency Medicine Education Fellow at Liverpool Hospital NSW. MBBS (Hons) Monash University. Interests in indigenous health and medical education. When not in the emergency department, can most likely be found running up some mountain training for the next ultramarathon.



