CT Case 101
A 46-year-old female presents with left iliac fossa pain and fevers.
She has a previous history of stage IV endometriosis and has had a prior total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (TAHBSO) for symptom management.
This presentation she has acute on chronic renal impairment with an eGFR of 19. On examination she is systemically well, afebrile and has tenderness in the left iliac fossa.
CT abdomen
Describe and interpret the CT scan
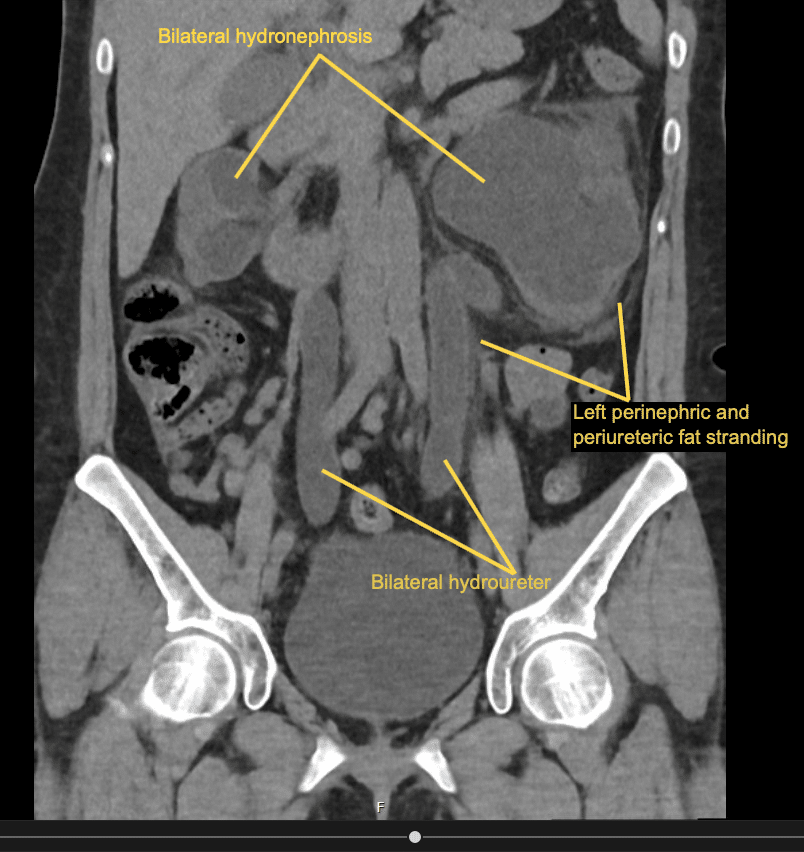
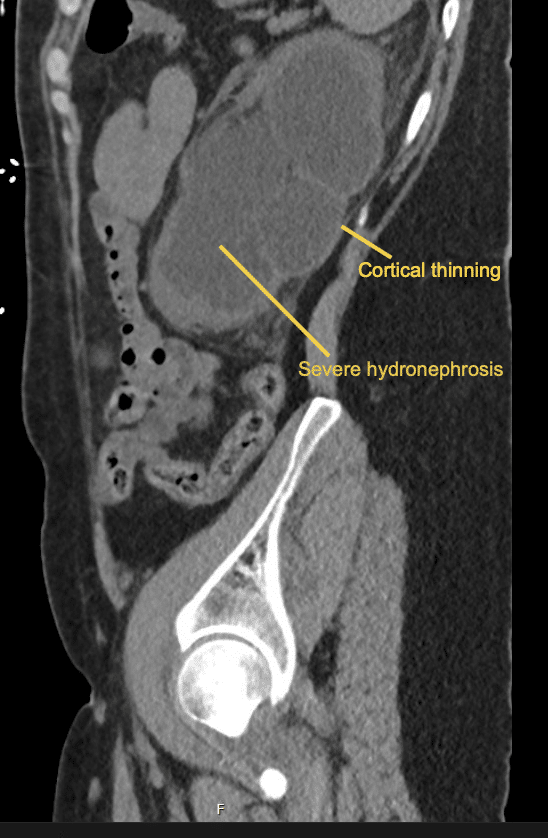
There is severe bilateral hydroureter and hydronephrosis.
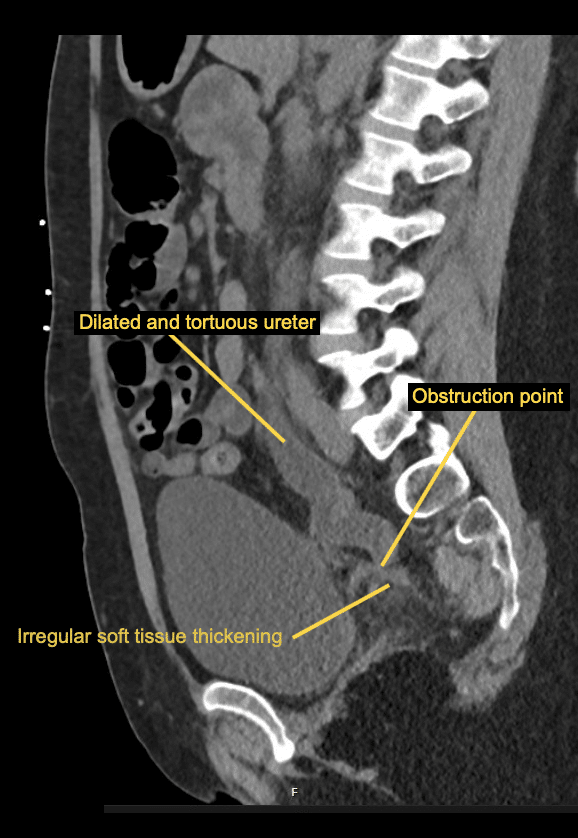
The point of obstruction is at the vaginal vault level where there is irregular soft tissue thickening suggesting scarring. Distal to this the ureters return to a normal calibre.
There is cortical thinning of the kidneys bilaterally, more severe on the left side.
There is left perinephric and periureteric fat stranding.
Clinical Pearls
Hydronephrosis is dilation of the renal collecting system due to obstruction along any part of the renal tract. Urinary obstruction can be broadly classified as intrinsic and extrinsic:
Common intrinsic causes;
- renal stones, malignancy, posterior urethral valves, BPH, neurogenic bladder, strictures
Common extrinsic causes;
- pregnancy, malignancy, retroperitoneal fibrosis
This case demonstrates a rare cause of urinary obstruction, secondary to fibrosis from severe endometriosis.
Principles of management include identification of the cause of obstruction and relieving it to prevent/limit renal damage.
Prolonged obstruction from hydronephrosis or hydroureter may result in tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis.
If there isn’t an option for relieving the obstruction, nephrostomy tubes can be placed for direct urinary drainage.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the endometrial cavity, it affects 10-20% of women and often goes undiagnosed.
The main location is in the pelvis. Extra-pelvic endometriosis has been found in lymph nodes and the GI tract. Rarely it can be located in the urinary tract, with a prevalence of 0.1-0.4% of all cases.
It is staged based on severity, with stage 4 being the most severe.
She underwent ureteric stent insertion for relief of obstruction.
References
- Wang P, Wang XP, Li YY, Jin BY, Xia D, Wang S, Pan H. Hydronephrosis due to ureteral endometriosis in women of reproductive age. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jan 15;8(1):1059-65.
TOP 100 CT SERIES
Provisional fellow in emergency radiology, Liverpool hospital, Sydney. Other areas of interest include paediatric and cardiac imaging.
Emergency Medicine Education Fellow at Liverpool Hospital NSW. MBBS (Hons) Monash University. Interests in indigenous health and medical education. When not in the emergency department, can most likely be found running up some mountain training for the next ultramarathon.
Dr Leon Lam FRANZCR MBBS BSci(Med). Clinical Radiologist and Senior Staff Specialist at Liverpool Hospital, Sydney
Sydney-based Emergency Physician (MBBS, FACEM) working at Liverpool Hospital. Passionate about education, trainees and travel. Special interests include radiology, orthopaedics and trauma. Creator of the Sydney Emergency XRay interpretation day (SEXI).







