CXR Case 026
72 year old female presents with worsening cough and dypnoea. Inflammatory markers are normal.
Describe and interpret this CXR
CHEST X-RAY INTERPRETATION
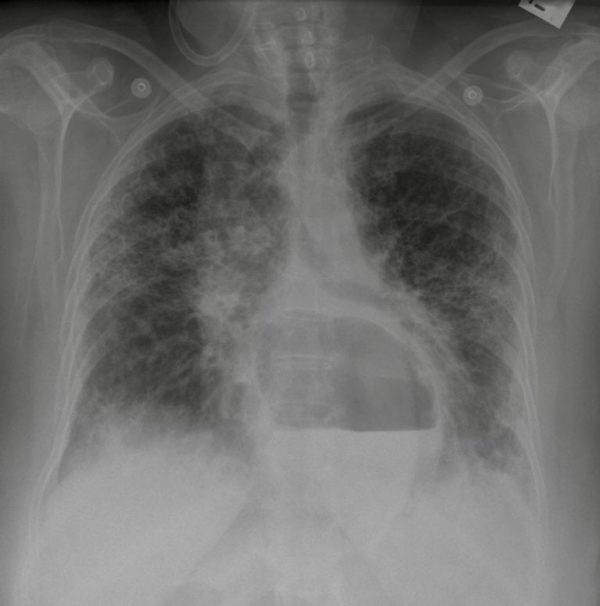
There are diffuse increased interstitial markings throughout both lungs without zonal distribution.
The reticular-nodular pattern is consistent with pulmonary fibrosis
*There is an air-fluid level overlapping the heart shadow, with absence of usual gastric air sinus. This is in keeping with a large hiatus hernia*
CLINICAL CORRELATION
This patient is at risk of aspiration, and given the context of unlikely infection, this is the most likely reason for the acute presentation.
*She has a background of pulmonary fibrosis which in this case is not caused by aspiration, but is a well recognized complication of pulmonary fibrosis.*
CLINICAL PEARLS
Acute aspiration of gastric contents causes a chemical pnuemonitis and the role of empirical antibiotics is controversial.
Many patients recover quickly over 24-48 hours. Supportive therapy and oxygenation may be required.
Should clinical and radiographic evidence of pneumonia develop, then antibiotics are indicated.
*In the community setting the most frequently isolated organisms are: S. Aureus, S. pneumoniae, Bacteroides sp., Fusobacterium and Prevotella sp.
* In the hospital setting, the spectrum differs: S. aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella sp., Proteus sp. and Pseudomonas aeroginosa.
Prof Fraser Brims Curtin Medical School, acute and respiratory medicine specialist, immediate care in sport doc, ex-Royal Navy, academic| Top 100 CXR | Google Scholar | ICIS Course ANZ