ECG Case 027
Elderly patient feeling generally unwell. PMHx of T2DM, hypertension, IHD, CCF, osteoarthritis. Describe the ECG.
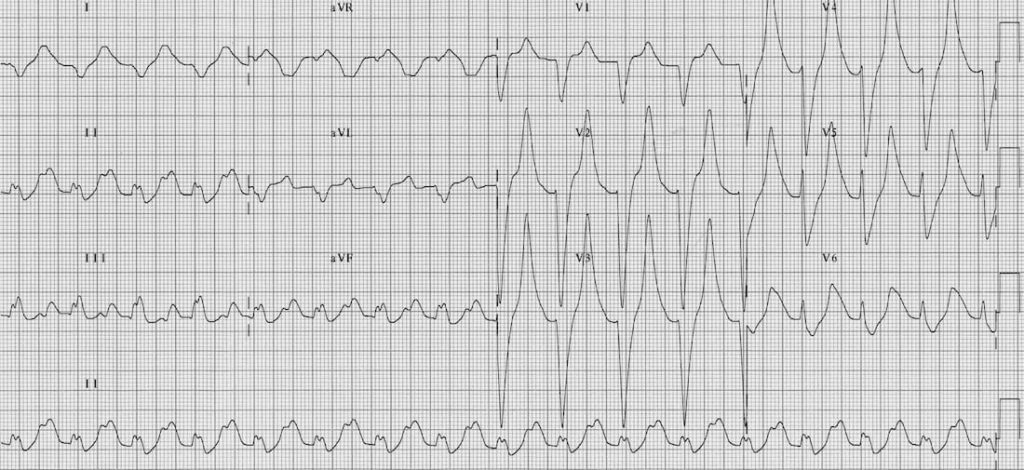
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Bizarre appearing complexes
- Marked T wave peaking in V2-6.
- Gross QRS prolongation (~200 ms)
- Some leads (I, aVR) are starting to take on a sine wave appearance
Diagnosis
The combination of…
- Bizarre complexes
- QRS prolongation
- Peaked T waves
- Sine wave appearance
… are all strongly suggestive of severe hyperkalemia.
This patient had a serum K of 9.2 mmol/L!
In this elderly patient with multiple medical problems, causes could include renal failure (e.g. due to diuretics, NSAIDs, intercurrent illness) or treatment with ACE-inhibitors, spironalactone or K-supplements.
CLINICAL PEARLS
The push-pull effect
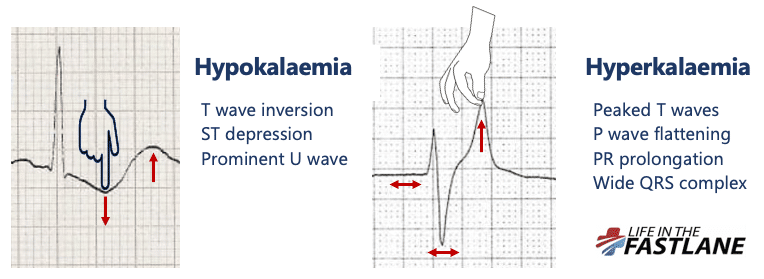
- Hypokalaemia creates the illusion that the T wave is “pushed down”, with resultant T-wave flattening/inversion, ST depression, and prominent U waves
- In hyperkalaemia, the T wave is “pulled upwards”, creating tall “tented” T waves, and stretching the remainder of the ECG to cause P wave flattening, PR prolongation, and QRS widening
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


What is the rhythm? Is it a 2:1 AT or sinus?