ECG Case 042
75-year old patient presenting with palpitations. Describe the ECG

Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
This is a typical example of atrial flutter with 2:1 AV block
- Narrow complex tachycardia at 150 bpm.
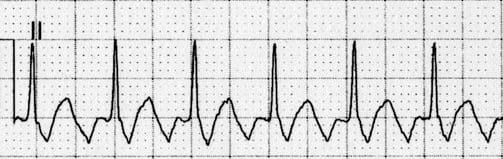
- Sawtooth flutter waves are seen in the inferior leads II, III, aVF.
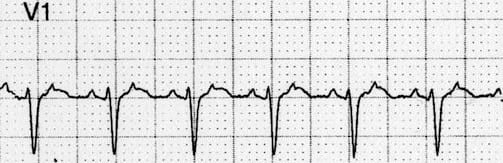
- Upright flutter waves in V1 appear either as pseudo-P waves or as notches in the T wave.
- There is a clear 2:1 relationship between the flutter waves (300 bpm) and QRS complexes (150 bpm).
Inverted flutter waves in lead II.
Upright flutter waves in V1.
CLINICAL PEARLS
Tips for Spotting Atrial Flutter
- Suspect flutter with 2:1 block in any patient with a regular NCT at 150 bpm.
- Scrutinise leads II and V1 for flutter waves.
- Flutter waves are typically sawtooth in lead II and resemble P waves in V1.
- Try turning the ECG upside down — this can make the flutter waves in lead II easier to see.
Inverting the ECG makes flutter waves in lead II easier to see

References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
