ECG Case 095
This ECG is from a middle aged male who presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. A ‘routine’ ECG was performed and is below.
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
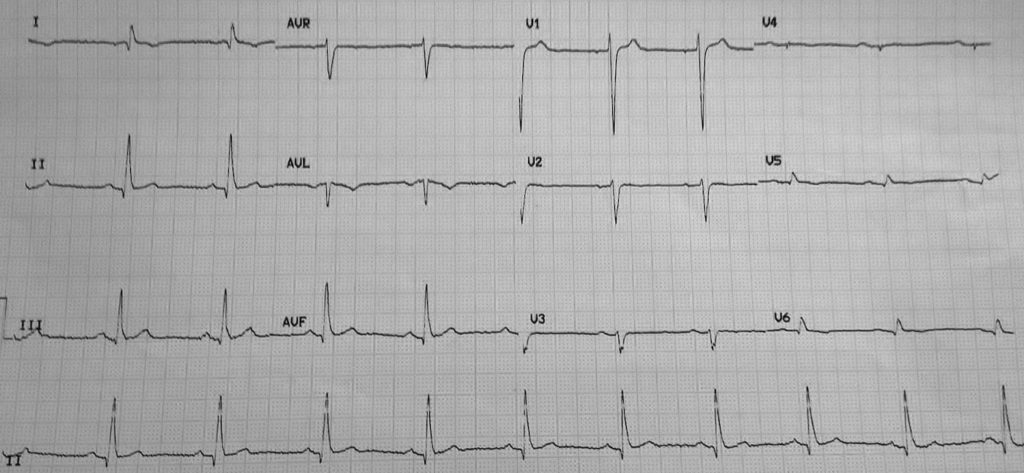
Rate:
- 60 bpm
Rhythm:
- Sinus rhythm
- Sinus arrhythmia
Axis:
- Normal
Intervals:
- PR – Normal (~200ms)
- QRS – Prolonged (120ms)
- QT – 440ms (QTc Bazett ~ 430 ms)
Segments:
- ST Elevation V1 (<1mm)
Additional:
- Lead I shows P and T wave inversion
- Lead aVR inverted P, QRS, and T wave
- Lead V1 higher overall voltage compared with other leads
- Lead V1 initial prominent R wave
- Leads V3-6 low voltage
- T wave inversion leads V5-6
Interpretation:
- Negative P wave in leads I and aVL with completely negative lead aVL should prompt consideration of LA/RA lead reversal.
- The low voltage lateral precordial leads, in conjunction with suspected lead reversal, should prompt consideration of dextrocardia.
- I only have limited information on this case but the patient had known dextrocardia.
CLINICAL PEARLS
Dextrocardia
Dextrocardia can occur in isolation (a.k.a situs solitus) in which only the position of the heart is changed, to sit in the right hemithorax with base to apex axis points to the right. This clinical picture has a high association with other congenital cardiac abnormalities.
Dextrocardia can also occur in conjunction with reversal of the thoracic and abdominal organs (a.k.a situs inversus) this has a lower association with congenital cardiac disease compared with isolated dextrocardia. The relevance of this in the setting of an acute presentation is remembering the abdominal organ position is altered e.g. the appendix will lie on the left. Kartagener syndrome is the combination of dextrocardia with situs inversus, chronic sinusitis, and bronchiectasis.
Dextrocardia may be mimicked by dextroposition which is an acquired condition in which the heart is displaced into the right hemithorax whilst the normal base to apex axis remains pointing to the left e.g. displacement due to large left pleural effusion.
Dextrocardia and the ECG
ECG features of dextrocardia are similar to a LA/RA lead reversal with the addition of precordial lead changes.
A LA/RA lead reversal results in the following ECG changes:
- Lead I becomes inverted
- Leads II and III switch places
- Leads aVR and aVL switch places
Unlike a lead reversal dextrocardia should manifest changes in the precordial leads which may include:
- Absent R wave progression
- Low voltage lateral precordial leads
- Leads V1 and V2 switch places
Interestingly in this ECG our patient has a normal axis, if the ECG was repeated with lead positions moved to account for the dextrocardia i.e RA lead on the left, LA lead on the right, and full right sided precordial leads (V1R-V6R) the resultant ECG would show a right axis deviation. An important clue to spotting a lead reversal (true or apparent) in a patient with an abnormal axis is the P and T wave morphology; in this ECG both leads I and aVR have P and T wave inversion.
Further Reading:
- ECG Library – Dextrocardia
- ECG Library – ECG Limb Lead Reversal
- ECG Library – Lead reversal: Left arm/right arm
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |