Horner Syndrome
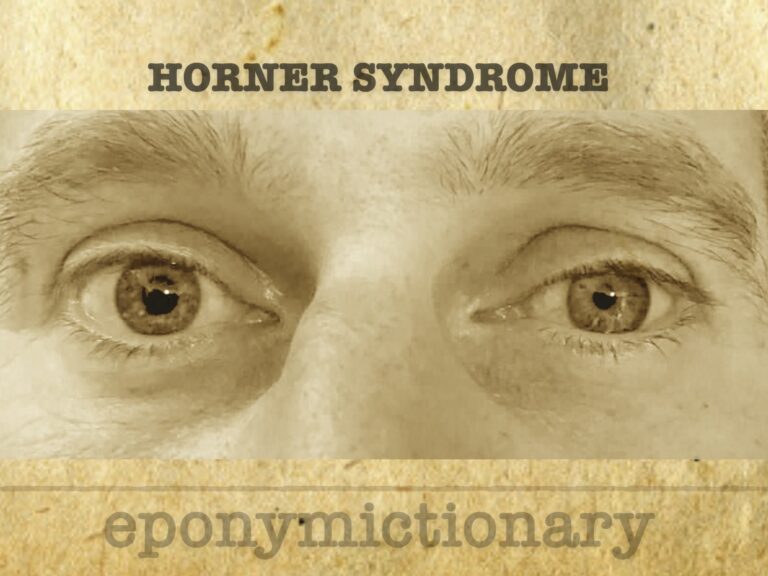
Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos

Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos

Henry Khunrath Pancoast (1875 – 1939) was an American radiologist. The Pancoast tumour and Pancoast syndrome is named after him

Pancoast Tumour is a primary bronchogenic carcinoma which arises in the apex of the lung at the superior pulmonary sulcus.

Silas Weir Mitchell (1829–1914), American neurologist and Civil War doctor, pioneered causalgia, phantom limb, rest cure, and erythromelalgia

Horner syndrome is a neurological disorder caused by disruption to sympathetic innervation to the eye, presenting with ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis

Lateral medullary (Wallenberg) syndrome is a rare brainstem stroke due to vertebral or PICA occlusion, presenting with vertigo, dysphagia, and cranial nerve signs.

Swiss ophthalmologist Johann Friedrich Horner (1831–1886), eponym of Horner's syndrome, advanced ophthalmic surgery and neuroanatomical diagnostics

Claude Bernard (1813–1878), French physiologist, pioneered experimental medicine, homeostasis, and glucose metabolism. Father of modern physiology.
Wallenberg Syndrome: neurological disorder with a variety of symptoms associated with posterior circulation ischaemic stroke. [AKA lateral medullary syndrome or posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome]

You are asked to review a 65 year-old man who is comatose (GCS 3) with small pupils (2 mm bilaterally). He has a history of diabetes mellitus and bipolar disorder. He was discharged from hospital yesterday, following a surgical procedure.

Horner Syndrome = unilateral interruption of ascending cervical sympathetic innervation eye and face.

Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos