
Name that murmur
Eponymythology: heart murmur eponyms and named cardiac murmurs. Related eponyms, the person behind their origin, their relevance today, and modern terminology.

Eponymythology: heart murmur eponyms and named cardiac murmurs. Related eponyms, the person behind their origin, their relevance today, and modern terminology.
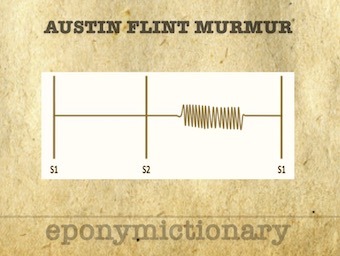
Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis
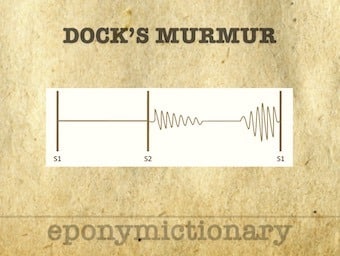
Dock’s murmur: Early diastolic murmur when there is a severe stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery. 1967 William Dock

Thomas Hodgkin (1798 – 1866) was an English physician and pathologist. Eponym: Hodgkin disease (1832); Key-Hodgkin murmur (1827)

George Alexander Gibson (1854 – 1913) was a Scottish physician. Eponymously affiliated with the Gibson murmur (1906)

Still's Murmur ejection systolic murmur first described in 1909 by English pediatrician Sir George Frederic Still KCVO (1868 – 1941)

The Cabot-Locke murmur is an early diastolic murmur found in patients with severe anaemia. The murmur resolves with treatment of the anaemia. There is no functional valvular abnormality present.

Graham Steell murmur: soft, blowing, decrescendo early diastolic murmur of pulmonary incompetence caused by pulmonary hypertension
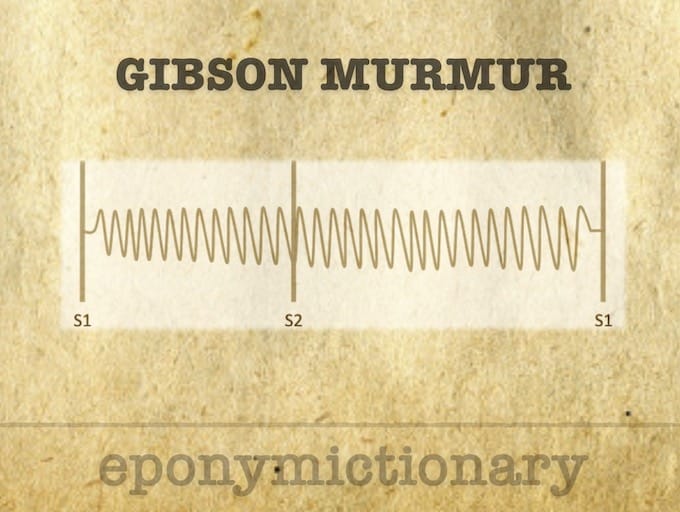
Gibson murmur (machinery murmur) associated with patent ductus arteriosus. Eponymously affiliated with George Alexander Gibson (1906)

David Abramson Rytland (1909 - 1991) was an American physician and cardiologist. Rytand murmur (1946), Rytand's law (1951)

Duroziez-type murmur observed with the patients arm subjected to various temperatures of water and by applying a subdiastolic pressure below the auscultation site, to help differentiate between aortic insufficiency and peripheral vasodilatation.
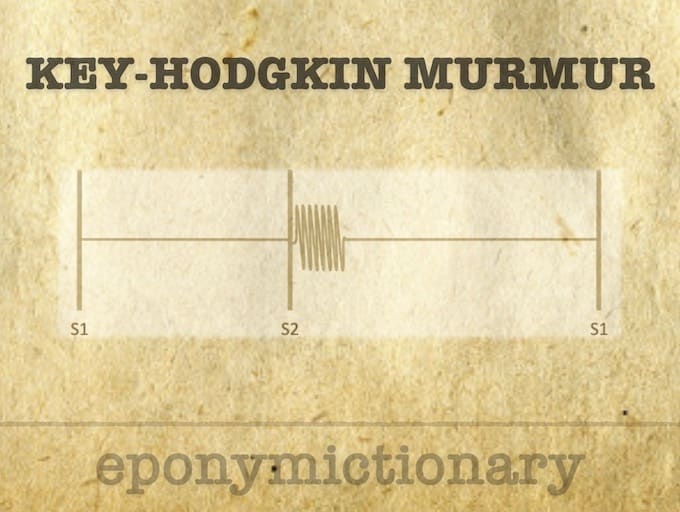
Key–Hodgkin murmur: diastolic murmur of aortic regurgitation with a raspy quality, likened to the sound of 'a saw cutting through wood'.