Twelfth Cranial Nerve Lesions
The hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) is a somatic motor nerve responsible for tongue movement.
Isolated lesions are rare and often occur alongside other lower cranial nerve pathologies.
Anatomy
Course
- Originates from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medial medulla oblongata.
- Exits the pre-olivary sulcus (between the olive and the pyramid).
- Leaves the skull via the hypoglossal foramen.
Innervation
The hypoglossal nerve innervates:
| Muscle Group | Muscles |
|---|---|
| Intrinsic | All intrinsic muscles of the tongue |
| Extrinsic | All extrinsic tongue muscles except palatoglossus (CN X) |
Pathology
Hypoglossal nerve lesions are usually associated with broader caudal cranial nerve pathology.
Causes
- Central (CNS) Lesions
- Vascular lesions of the medulla
- Neurological disorders:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Motor neurone disease
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Poliomyelitis
- Peripheral Lesions (posterior fossa / upper neck)
- Trauma at the skull base
- Mass lesions in the posterior cranial fossa:
- Tumours
- Abscesses
- Aneurysms
Clinical Assessment
1. Inspection
- Look for wasting or fasciculations of the tongue → suggests LMN lesion.
- Bilateral LMN lesions can result in dysarthria.
- Fasciculations may be unilateral or bilateral.
2. Movement
- Ask patient to protrude the tongue:
- Tongue deviates towards the weaker side in unilateral LMN lesion.
- Unilateral UMN lesions often cause no deviation, due to bilateral innervation.
- Bilateral UMN lesions → small, immobile tongue.
3. Bulbar Syndromes
- Pseudobulbar palsy: Bilateral UMN lesions (CN IX, X, XII)
- Bulbar palsy: Bilateral LMN lesions (CN IX, X, XII)
Investigations
Blood Tests
- FBC
- CRP
- ESR
- U&Es / Glucose
Imaging
- CT / CTA: Screens for mass lesions and aneurysms
- MRI: Most sensitive for detecting CNS, peripheral nerve, and head/neck lesions
Management
- Management is directed at the underlying cause where possible.
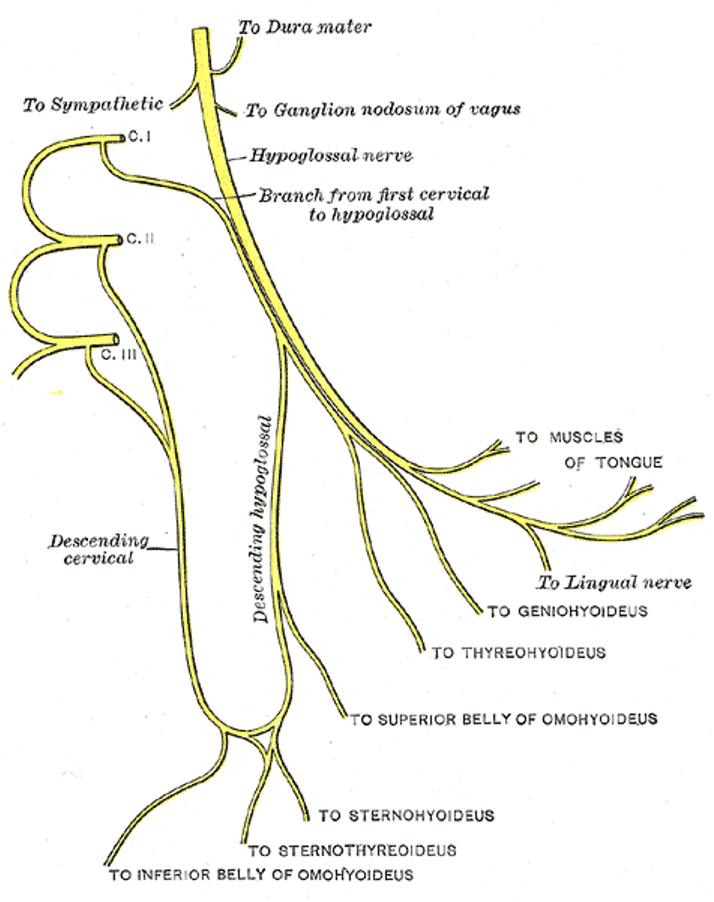
Appendix 1
Anatomy of the Twelfth cranial nerve
Appendix 2
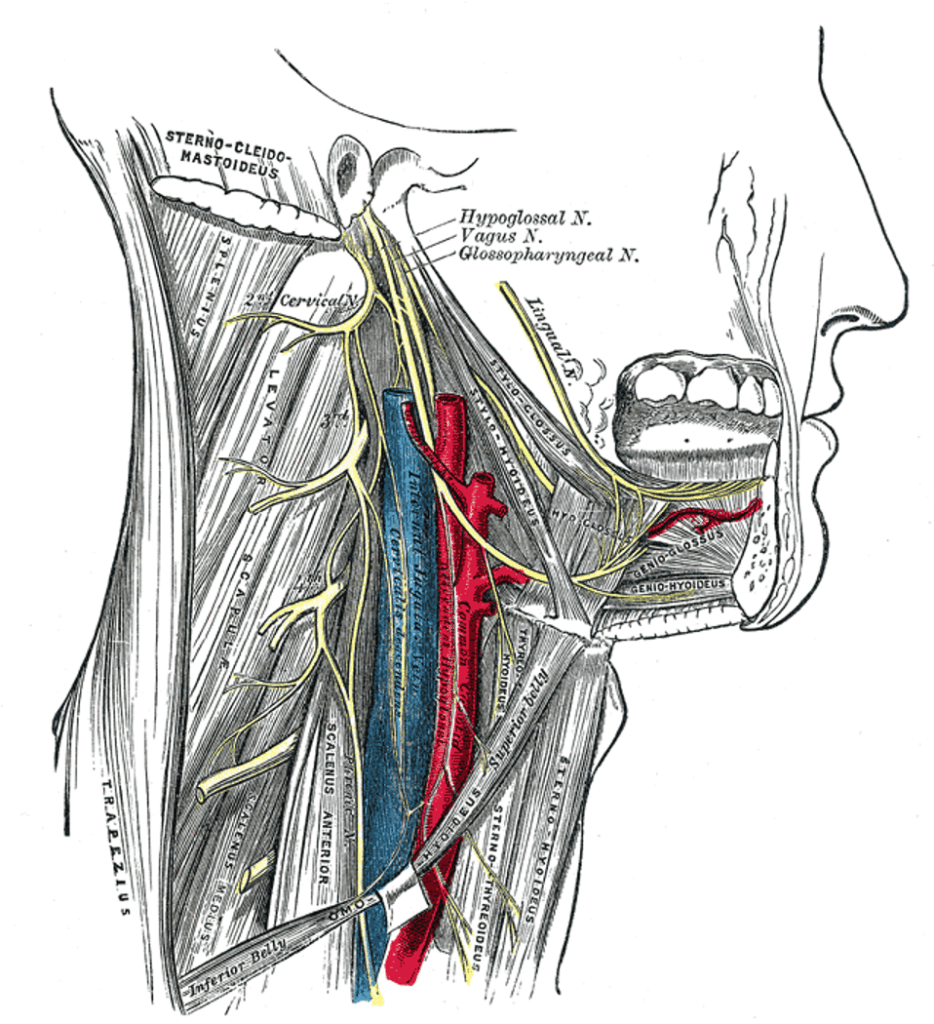
References
Publications
- Brazis PW, Masdeu JC, Biller J. Localization in Clinical Neurology. 8e 2021
- Fuller G. Neurological Examination Made Easy. 6e 2019
- O’Brien M. Aids to the Examination of the Peripheral Nervous System. 6e 2023
FOAMed
- Coni R. Neuro 101: Cranial Nerves. LITFL
- Nickson C. Bulbar and pseudobulbar palsy. LITFL
- Nickson C. Pseudobulbar and bulbar palsies. LITFL
- Nickson C. The Brainstem Rules of Four. LITFL
- Ercleve T. The rule of 4 of the brainstem. LITFL
- Nickson C. Cranial nerve lesions DDx. LITFL
Fellowship Notes
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner
Educator, magister, munus exemplar, dicata in agro subitis medicina et discrimine cura | FFS |


