
Robert Graves
Robert James Graves (1796–1853): Irish physician, pioneer of bedside teaching, described Graves’ disease, reformed fever care, and influenced modern clinical medicine.

Robert James Graves (1796–1853): Irish physician, pioneer of bedside teaching, described Graves’ disease, reformed fever care, and influenced modern clinical medicine.

Charles Heber McBurney (1845 – 1913) was an American surgeon. Most famous for McBurney's point (1889) and McBurney's incision (1894) Medical Eponym.

John Hay (1873-1959) English physician first to record second degree atrioventricular (AV) block now better known as Mobitz type II AV block

Jean Lenègre (1904–1972), French cardiologist, defined Lenègre’s disease and pioneered cardiac electrophysiology, catheterization, and bundle branch pathology

Maurice Lev (1908–1994), pathologist and teacher, defined Lev’s disease and advanced cardiac conduction and congenital heart pathology through over 500 publications
Robert Adams (1791–1875), Dublin physician, first described Adams–Stokes syndrome and pioneered clinical-pathological correlation in heart disease

John Cheyne (1777–1836), Irish physician, co-described Cheyne-Stokes respiration, advanced clinical neurology, and linked pupils to brain injury

American neurologist Francis Xavier Dercum (1856–1931), first described Dercum’s disease; pioneer in neurology, psychiatry, and medical education.
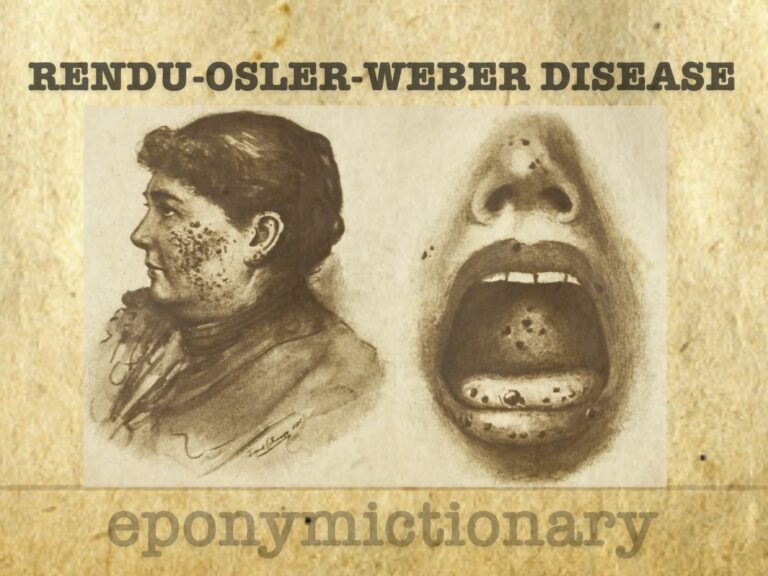
Rendu-Osler-Weber disease (aka Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterised by epistaxis, cutaneous telangiectasia, and visceral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
Josef Thurner (b. 1927), Austrian pathologist and co-eponym of May–Thurner syndrome; led pathology in Salzburg and published widely on venous disease.
Robert May (1912–1984), pioneer of scientific phlebology; co-described May–Thurner syndrome and the May perforating vein, advancing venous diagnostics.

Overview of Dercum's disease: rare painful adipose‑tissue disorder, epidemiology, treatment strategies, and eponym history.