
Chvostek sign
Chvostek sign is contraction of facial muscles provoked by lightly tapping over the facial nerve anterior to the ear as it crosses the zygomatic arch.

Chvostek sign is contraction of facial muscles provoked by lightly tapping over the facial nerve anterior to the ear as it crosses the zygomatic arch.

Corrigan pulse is the excessive visible arterial pulsations in aortic incompetence. Not to be confused with the palpated 'water-hammer pulse'.

Moschcowitz disease (1924) [aka *thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)]. Congenital syndrome characterised by thrombocytopenia, purpura, haemolytic anaemia, hyaline thromboses, renal failure and neurological symptoms.

Cotard syndrome: A rare condition characterized by nihilistic delusions, where a patient believes that they are dead, have missing organs, or have decaying or failing body parts.
Gilbert's syndrome: congenital, benign, chronic, intermittent hyperbilirubinemia. Fluctuating episodes of jaundice in the absence of any specific symptoms, with an excess of unconjugated bilirubin present in the urine.

Anton syndrome: Visual anosognosia or Anton-Babinski syndrome is a rare neurological condition related to cortical blindness. The patients deny their blindness and affirm adamantly that they are capable of seeing.
Heerfordt syndrome: a rare manifestation of sarcoidosis characterized by the presence of fever, facial nerve palsy, parotid gland enlargement, anterior uveitis, and low grade fever

Duroziez-type murmur observed with the patients arm subjected to various temperatures of water and by applying a subdiastolic pressure below the auscultation site, to help differentiate between aortic insufficiency and peripheral vasodilatation.

Description What is the actual eponymous medical sign/syndrome/repair/classification… History 1873 – Tilbury Fox (1836-1879) first to describe what is now generally designated as erysipeloid. In 1873 Fox briefly described two instances of an eruption clinically conforming with that disease. 1873…

Description Refetoff Syndrome: Thyroid hormone resistance is a rare syndrome in which thyroid hormone levels are elevated but the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level is not suppressed (or not completely suppressed as would be expected). History 1967 – first report…

McMurray test is used to evaluate individuals for tears in the meniscus of the knee. First described 1928 by Thomas Porter McMurray (1887-1949)
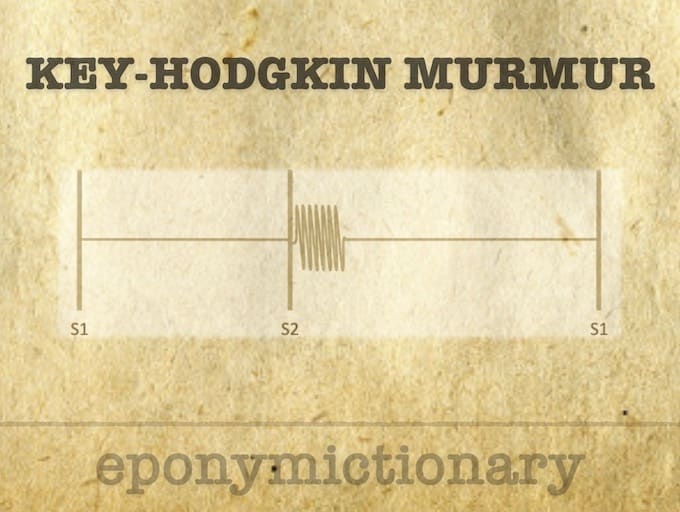
Key–Hodgkin murmur: diastolic murmur of aortic regurgitation with a raspy quality, likened to the sound of 'a saw cutting through wood'.