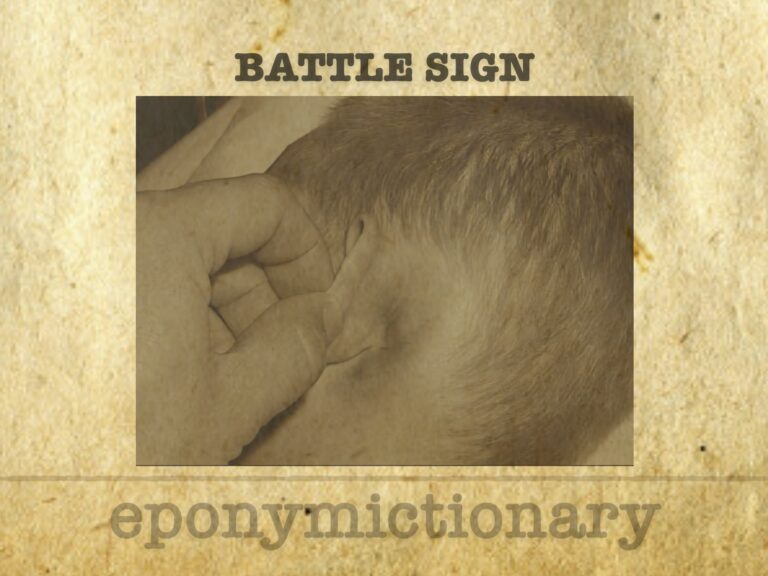
Battle Sign
Battle sign: mastoid ecchymosis indicating basilar skull fracture, described by W.H. Battle in 1890; it holds >75% PPV for posterior fossa injury.

Battle sign: mastoid ecchymosis indicating basilar skull fracture, described by W.H. Battle in 1890; it holds >75% PPV for posterior fossa injury.

Carl Gerhardt (1833–1902), German internist and paediatric pioneer, described Gerhardt’s sign and advanced diagnostics, paediatrics, and laryngology

Alfred Stieda (1869-1945) was a German Surgeon. Eponym: The Stieda fracture, Stieda tubercle, Pellegrini-Stieda disease (1908)
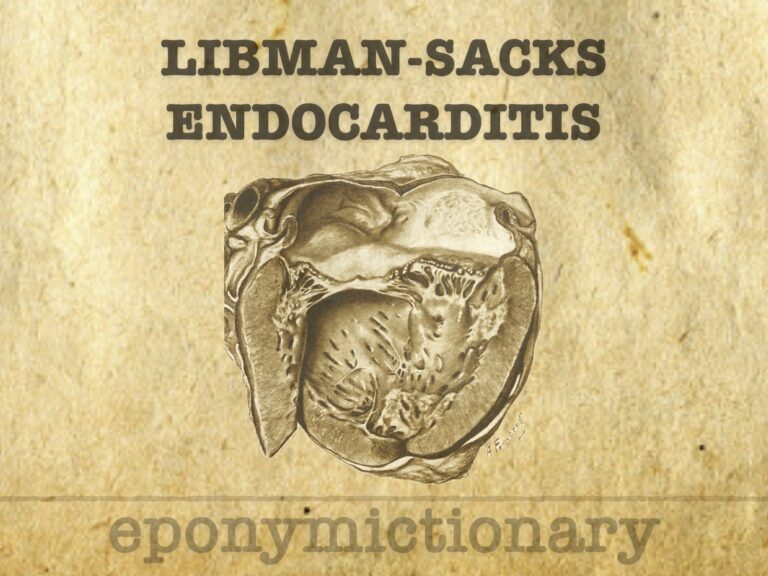
Libman–Sacks endocarditis is a sterile cardiac valve lesion linked to lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome, often detected via echocardiography

Benjamin Sacks (1896–1971), cardiac pathologist and co-describer of Libman–Sacks endocarditis, also a Hollywood advisor and Arizona frontier historian.

John Alsop (1931–), GP who coined "hand-foot-and-mouth disease" and published BMJ reports on outbreaks and ringworm in Birmingham, UK.

Sidney Yankauer (1872–1932), American ENT surgeon and inventor of the Yankauer suction catheter, pioneer in bronchoscopy and surgical airway care

Adolphe-Marie Gubler (1821-1879) was a French physician and therapeutic pharmacologist. Millard-Gubler syndrome (1856)
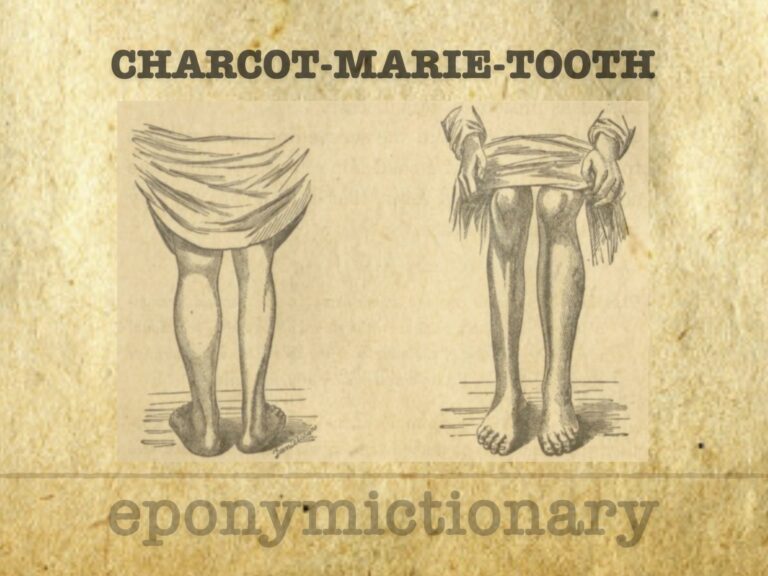
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is the most common inherited neuropathy, encompassing genetically diverse subtypes of peripheral nerve dysfunction.
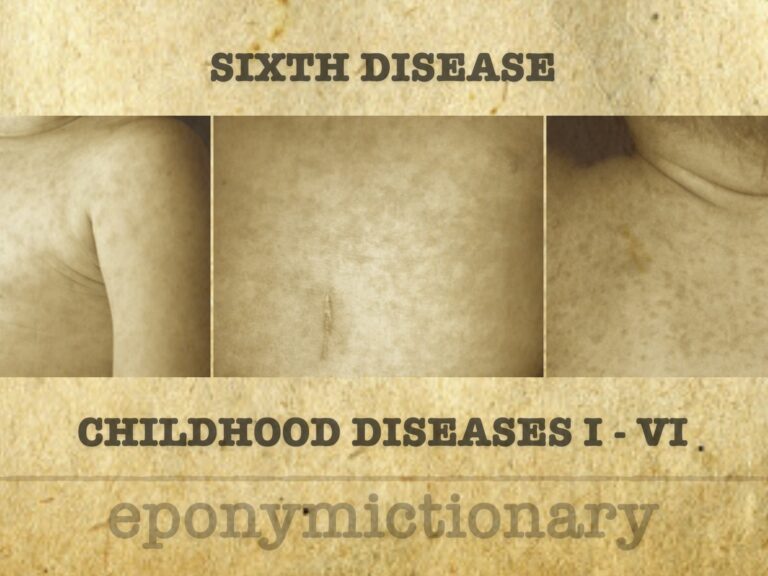
Common viral illness in infants caused by HHV-6. Roseola presents with high fever followed by sudden rash; also known as sixth disease or exanthem subitum.
Filatov-Dukes disease, or fourth disease, was a proposed childhood exanthem now largely dismissed as a misclassification of rubella or scarlet fever.
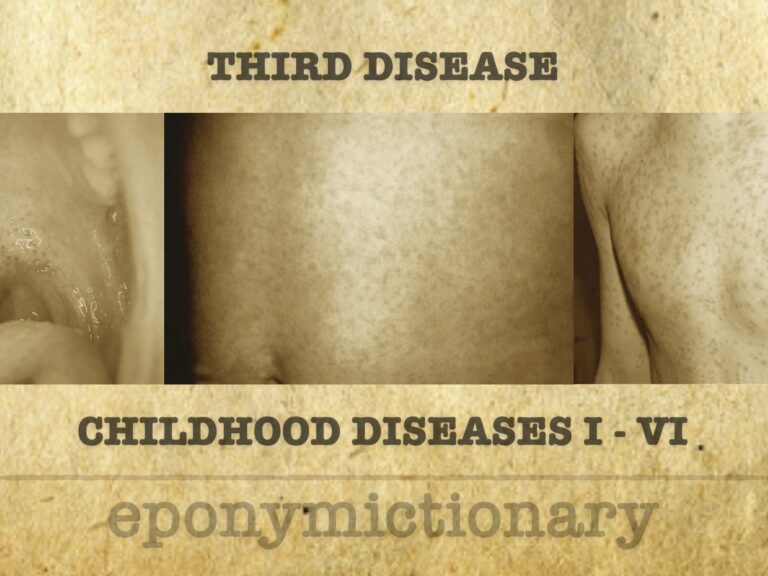
Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.