ECG Case 001
Middle-aged patient presenting with chest pain and diaphoresis. BP dropped to 80/50 following sublingual nitrates.
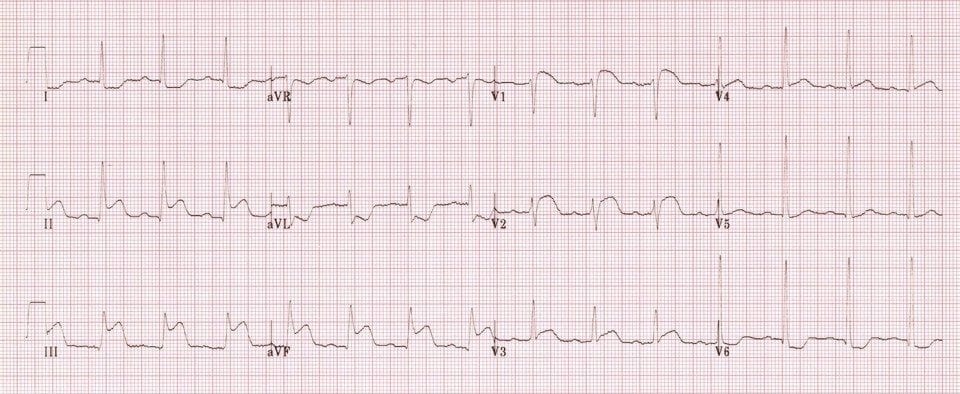
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
General:
- Sinus rhythm, rate 84bpm
- Normal axis
- 1st degree AV block (PR 220ms)
Signs of inferior STEMI:
- STE in inferior leads II, III, aVF
- Reciprocal STD in lateral leads I, aVL, V6
Signs of associated right ventricular infarction:
- STE in III > II
- STE in V1-2
This patient also had STE in V4R, confirming the diagnosis of RV infarction:
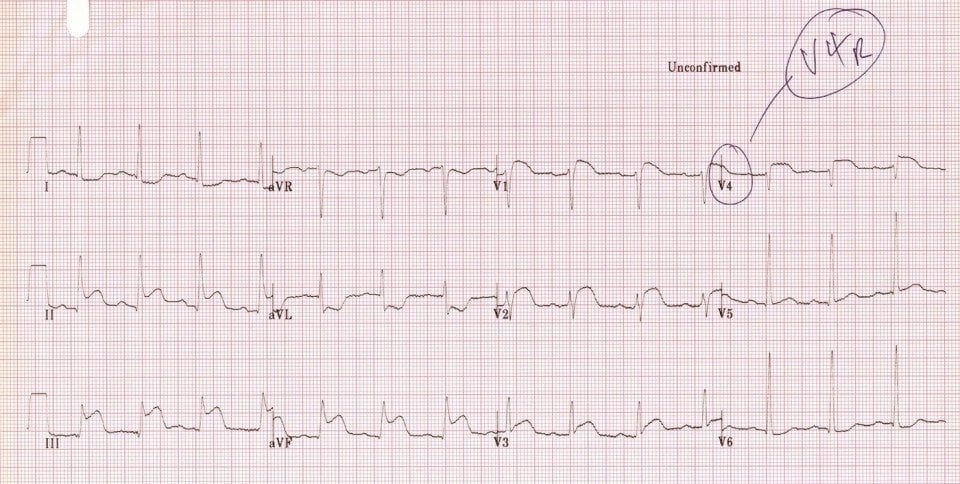
CLINICAL PEARLS
- RV infarction complicates 40% of inferior STEMIs
- Suggestive features include:
- ST elevation in V1, the only lead that looks directly at the RV
- ST elevation in III > II, as lead III is more rightward facing
- Diagnosis can be confirmed with right-sided leads
- These patients are preload sensitive and may have an exaggerated hypotensive response to nitrates
Read more about diagnosing RV infarction and how to record the V4R lead
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


Dr. Burns
I find a interesting aspect in the ecg: ST ELEVATION V2>V3>V4
It’s important to know the result of coronariogram. Please give us this date. Thanks
It seems to be an occlusion of a big dominant RCA with PDA rapping around the apex causing antero-inferior MI