ECG Case 004
20-year-old male presenting with seizures. BP 80/50.
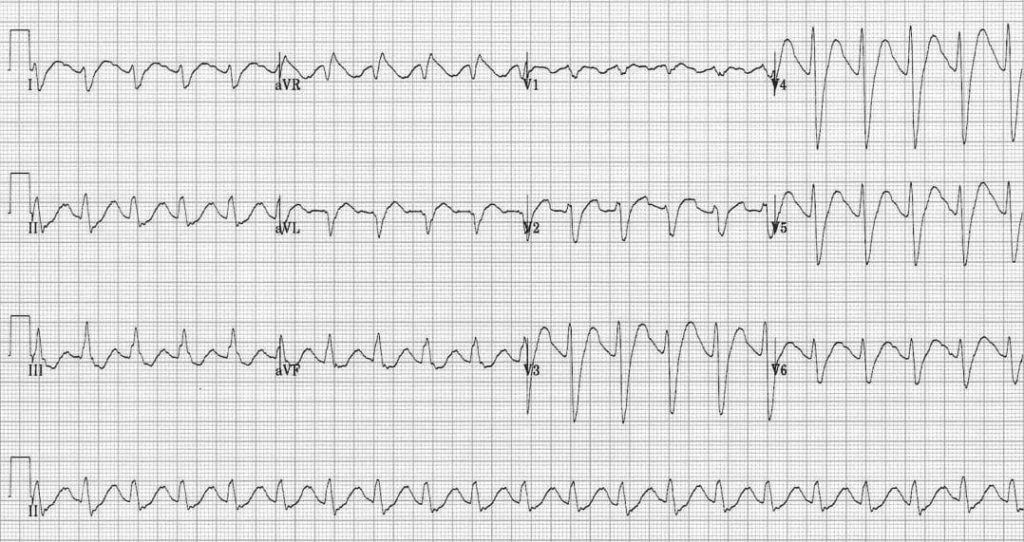
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Broad complex tachycardia, rate ~ 130 bpm
- The rhythm is likely sinus tachycardia with a 1st degree AV block — note the “camel hump” appearance to the T waves indicating a hidden P wave
- Interventricular conduction delay (QRS duration > 100ms, not typical LBBB / RBBB morphology)
- Right axis deviation
- Secondary R’ wave in aVR > 3 mm
What is the diagnosis?
Reveal answer
In the context of seizures and hypotension, the combination of…
- QRS broadening > 100 ms
- R’ wave in aVR > 3 mm
… is highly suggestive of poisoning with a sodium-channel blocking agent — e.g. tricyclic antidepressant.
The sinus tachycardia may be due to the anticholinergic effects of the TCA.
CLINICAL PEARLS
In the context of sodium channel blockade:
- A QRS duration > 100 ms is predictive of seizures
- A QRS duration > 160 ms is predictive of cardiotoxicity
This patient is already manifesting life-threatening toxicity and needs aggressive resuscitation, including:
- Serum alkalinisation with NaHCO3 to reverse pH-dependent toxicity
- Intubation and hyperventilation aiming for alkaline arterial pH (e.g. 7.45 to 7.55)
- Seizure management with benzodiazepines
- BP management with fluid boluses +/- pressors
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |

It looks to me more like a 2:1 AVB rather than a 1st degree. There are several leads but very clear in Lead II where it looks like a P wave right after the QRS morphology.
True, it resembles 2:1 block, though the PP interval varies.
My concern is different. Sinus rythm should have positive p waves in leads II, III, aVF and negative in aVR and this ECG in my opinion shows exactly the opposite. Could it be some ectopic atrial rythm than?