ECG Case 006
30-year old patient presenting with generalised weakness.
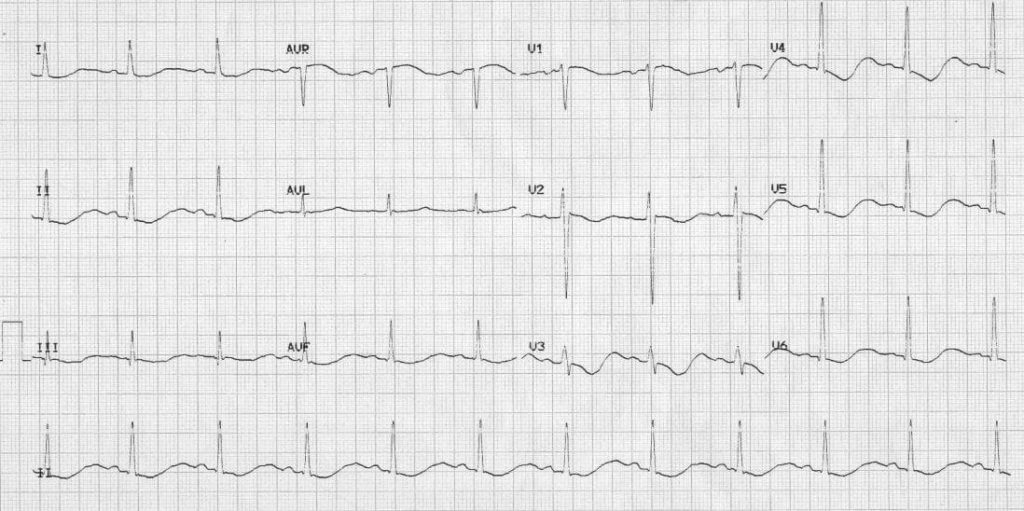
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
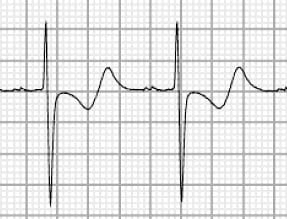
- The ECG shows widespread ST segment abnormalities
- There is a biphasic appearance to the ST segments and T waves, with initial negative deflection (= ST segment depression / T wave inversion) followed by a terminal positive deflection (= U wave)
- All these waves merge into each other and it is difficult to tell where one wave ends and the other begins
- There is gross prolongation of the QU interval (= time from onset of QRS complex to end of T/U wave)

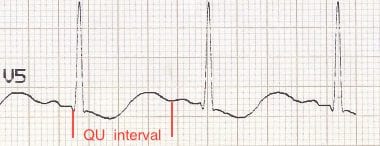
Diagnosis
The combination of…
- Widespread ST depression / T wave inversion
- Prominent U waves
- Long QU interval (> 500 ms)
…. is highly suggestive of severe hypokalaemia.
This patient had a serum K of 1.7 mmol/L in the context of decompensated Conn’s syndrome (primary aldosteronism).
CLINICAL PEARLS
The push-pull effect
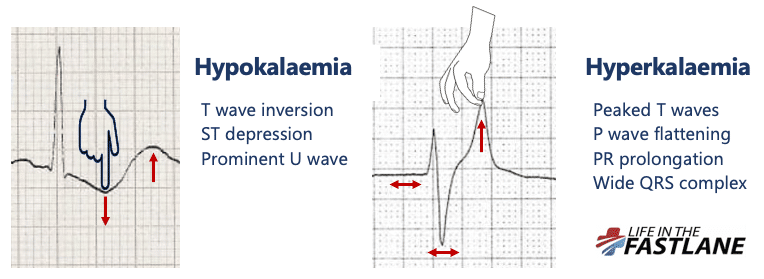
- Hypokalaemia creates the illusion that the T wave is “pushed down”, with resultant T-wave flattening/inversion, ST depression, and prominent U waves
- In hyperkalaemia, the T wave is “pulled upwards”, creating tall “tented” T waves, and stretching the remainder of the ECG to cause P wave flattening, PR prolongation, and QRS widening
Biphasic T waves: Wellens or hypokalaemia?
Biphasic T waves may be seen with both myocardial ischaemia (Wellens syndrome) and hypokalaemia.
The main differentiating factor (apart from the clinical picture) is the direction of the T waves:
- Wellens: – biphasic T waves go UP then DOWN.
- Hypokalaemia: – T waves go DOWN then UP.
Wellens Syndrome
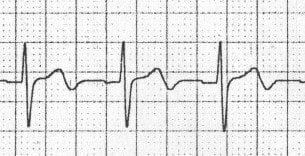
Hypokalaemia
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
