Hypokalaemia
Hypokalaemia is defined as a serum potassium level of < 3.5 mmol/L. ECG changes generally do not manifest until there is a moderate degree of hypokalaemia (2.5-2.9 mmol/L). The earliest ECG manifestation of hypokalaemia is a decrease in T wave amplitude.
ECG features of hypokalaemia (K < 2.7 mmol/L)
- Increased P wave amplitude
- Prolongation of PR interval
- Widespread ST depression and T wave flattening/inversion
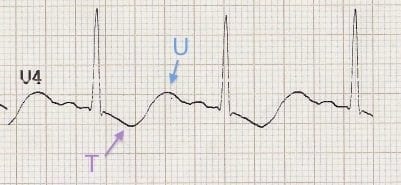
- Prominent U waves (best seen in the precordial leads V2-V3)
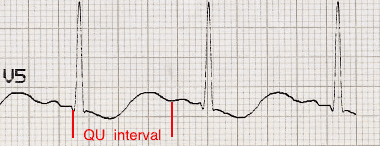
- Apparent long QT interval due to fusion of T and U waves (= long QU interval)
With worsening hypokalaemia…
- Frequent supraventricular and ventricular ectopics
- Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias: AF, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia
- Potential to develop life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, e.g. VT, VF and Torsades de Pointes
The push-pull effect
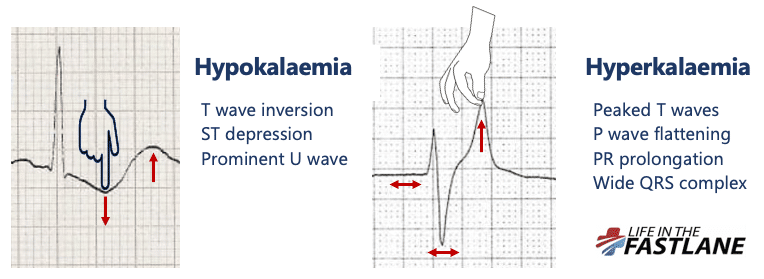
- Hypokalaemia creates the illusion that the T wave is “pushed down”, with resultant T-wave flattening/inversion, ST depression, and prominent U waves
- In hyperkalaemia, the T wave is “pulled upwards”, creating tall “tented” T waves, and stretching the remainder of the ECG to cause P wave flattening, PR prolongation, and QRS widening
Pathophysiology
Potassium is vital for regulating the normal electrical activity of the heart. Decreased extracellular potassium causes myocardial hyperexcitability with the potential to develop re-entrant arrhythmias.
| Degree of hypokalaemia | Potassium level (mmol/L) |
| Mild | 3.0 – 3.4 |
| Moderate | 2.5 – 2.9 |
| Severe | ≤ 2.4 |
Handy tips
- Hypokalaemia is often associated with hypomagnesaemia, which increases the risk of malignant ventricular arrhythmias
- Check both potassium and magnesium levels in any patient with an arrhythmia
- Replace potassium to ≥ 4.0 mmol/L and magnesium to ≥ 1.0 mmol/L to stabilise the myocardium and protect against arrhythmias – this is standard practice in most CCUs and ICUs
ECG Examples
Example 1
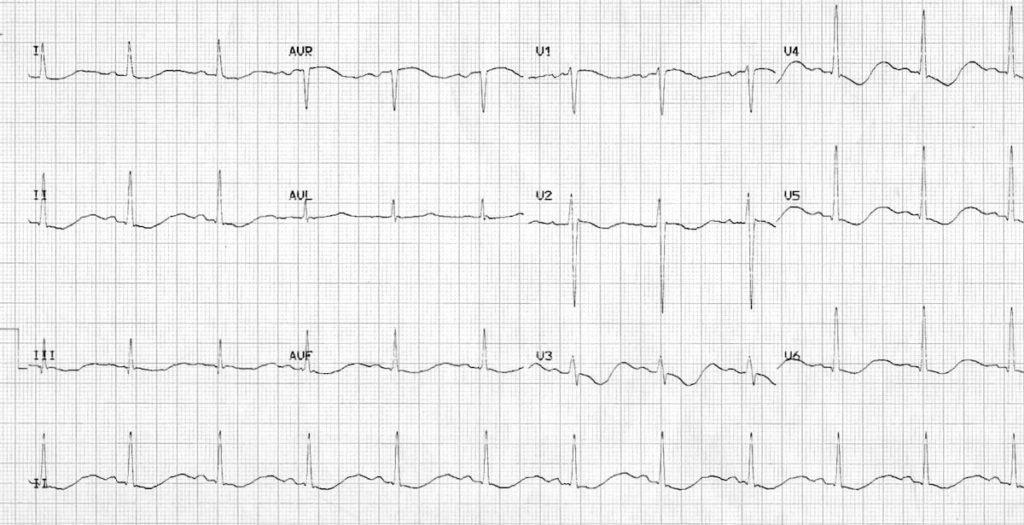
Hypokalaemia:
- Widespread ST depression and T wave inversion
- Prominent U waves
- Long QU interval
This patient had a serum K+ of 1.7
Example 2
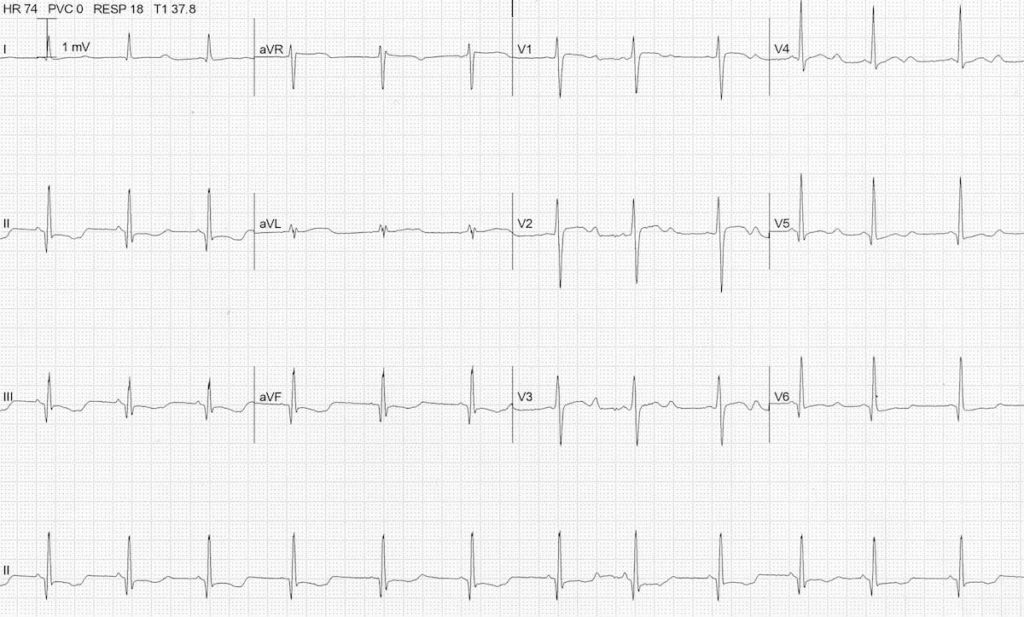
Hypokalaemia
- ST depression and T wave inversion best noted in inferior leads
- Prominent U waves
- Long QU interval
The serum K+ was 1.9 mmol/L.
Example 3
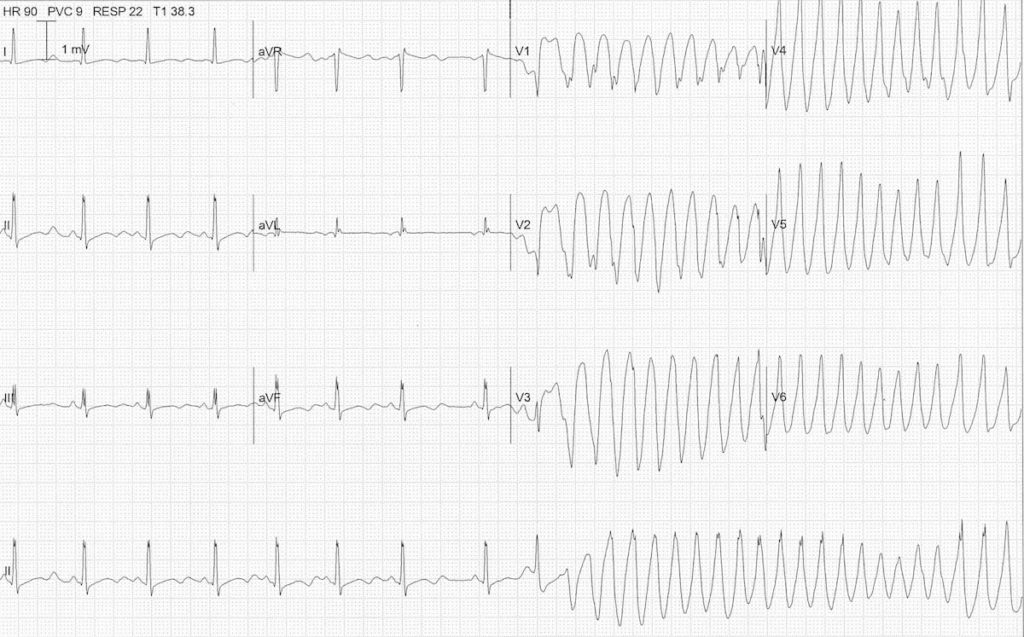
Hypokalaemia causing Torsades de Pointes
- Another ECG from the same patient
- Note the atrial ectopic causing ‘R on T’ (or is it ‘R on U’?) that initiates the paroxysm of TdP
Related Topics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

