ECG Case 052
Middle-aged patient presenting with central chest pain. Now asymptomatic. Interpret the ECG.
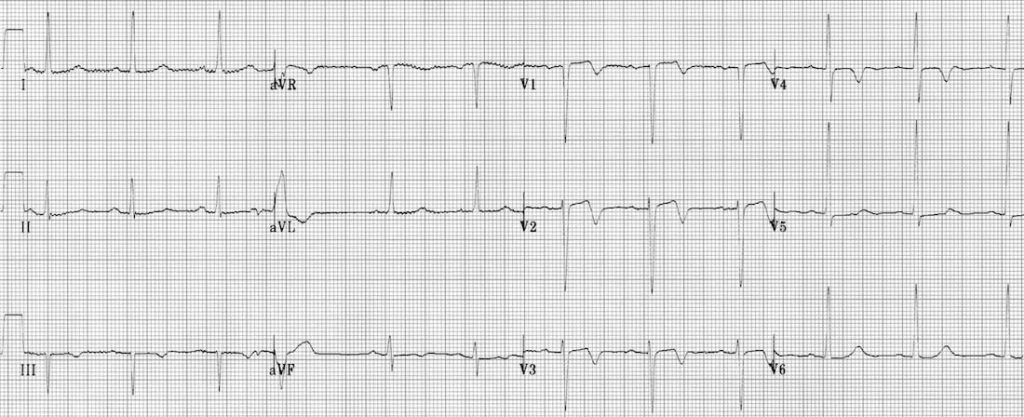
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
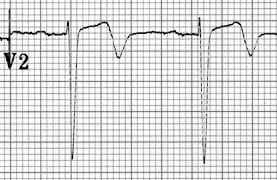
This is classic ECG of Wellens syndrome (Pattern A), demonstrating characteristic biphasic T waves in V1-3.
- This ECG pattern is highly predictive of a significant occlusive lesion of the LAD.
- The biphasic T waves are a marker of reperfusion and may occur after an aborted anterior STEMI.
- Despite often being pain free and having normal cardiac enzymes at presentation, these patients are at risk of sudden LAD re-occlusion leading to massive anterior STEMI and are best managed with early angiography and PCI / CABG.
CLINICAL PEARLS
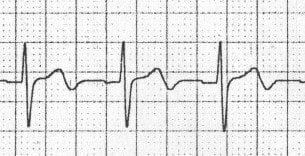
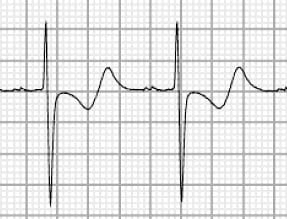
Biphasic T waves may be seen with both Wellens syndrome and hypokalaemia.
The main differentiating factor (apart from the clinical picture) is the direction of the T waves:
- Wellens’ biphasic T waves go UP then down.
- Hypokalaemic T waves go DOWN then up.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
